The Ultimate Strong Acid & Base List
A Comprehensive Guide to Strong Acids and Bases
In the world of chemistry, understanding the characteristics and behaviors of acids and bases is fundamental. Among these, strong acids and bases stand out for their unique properties and powerful reactions. This guide aims to provide an exhaustive list of strong acids and bases, offering insights into their nature, applications, and safety considerations.
Strong Acids: Unveiling the Powerhouses
Strong acids are known for their ability to readily donate protons (H⁺ ions) and fully dissociate in aqueous solutions. This complete dissociation sets them apart from weak acids, making them highly reactive and corrosive. Let’s explore some of the most potent strong acids:
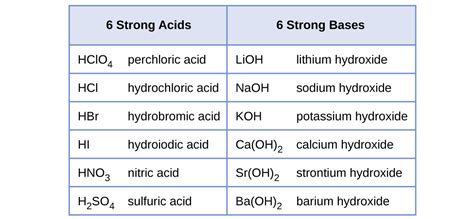
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl): A highly corrosive and strong acid, HCl is a staple in laboratories and industries. It is widely used in various processes, from metal cleaning to chemical synthesis.
Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄): Often referred to as the “king of chemicals,” sulfuric acid is an incredibly strong and versatile acid. Its uses span from battery production to fertilizer manufacturing.
Nitric Acid (HNO₃): With its powerful oxidizing properties, nitric acid is employed in the production of fertilizers, explosives, and even for etching and cleaning in metalwork.
Hydrobromic Acid (HBr): This strong acid is known for its reactivity and is used in chemical research and industrial processes, including the production of certain pharmaceuticals.
Hydroiodic Acid (HI): One of the strongest mineral acids, HI finds applications in organic synthesis and as a reducing agent.
Perchloric Acid (HClO₄): Extremely corrosive and reactive, perchloric acid is utilized in the production of explosives and as a powerful oxidizing agent.
Fluoroantimonic Acid: Holding the title of the world’s strongest superacid, fluoroantimonic acid is an extremely potent acid, used in specialized research and chemical processes.
Hydrofluoric Acid (HF): While not as strong as the previous acids, HF is still considered a strong acid and is used for etching glass and metal surfaces.
The Complete Strong Base Roster
Strong bases, on the other hand, are characterized by their ability to readily accept protons and fully dissociate in aqueous solutions. Here are some of the most commonly encountered strong bases:
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): Also known as lye or caustic soda, sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive strong base. It finds extensive use in industries such as soap and detergent manufacturing, as well as in cleaning agents.
Potassium Hydroxide (KOH): Similar to sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide is a strong base used in the production of potassium-based soaps and as an electrolyte in batteries.
Calcium Hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂): Commonly referred to as slaked lime or hydrated lime, calcium hydroxide is used in various applications, including water treatment and construction.
Barium Hydroxide (Ba(OH)₂): This strong base is employed in chemical synthesis and as a reagent in analytical chemistry.
Strontium Hydroxide (Sr(OH)₂): Used in specialized applications, strontium hydroxide is known for its ability to absorb carbon dioxide.
Ammonium Hydroxide (NH₄OH): While often considered a weak base, ammonium hydroxide can be classified as a strong base under certain conditions, especially when highly concentrated.
Lithium Hydroxide (LiOH): Lithium hydroxide is an important component in battery technology and is also used in air purification systems.
Safety Considerations and Handling Tips
Working with strong acids and bases requires utmost caution due to their corrosive and reactive nature. Here are some essential safety guidelines:
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves, safety goggles, and laboratory coats.
- Handle these substances in well-ventilated areas to avoid inhaling fumes.
- Store strong acids and bases separately, ensuring proper labeling and storage conditions.
- Avoid mixing strong acids and bases, as this can lead to violent reactions and the production of hazardous gases.
- In case of skin or eye contact, immediately flush the affected area with water and seek medical attention.
- Never ingest or smell strong acids or bases directly; use proper ventilation and safety equipment.
Applications and Real-World Uses
The diverse applications of strong acids and bases are vast and impact numerous industries:
- Chemical Manufacturing: Strong acids and bases are essential in the production of various chemicals, including fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and industrial chemicals.
- Environmental Science: They play a crucial role in water treatment processes, neutralizing acidic or basic contaminants.
- Energy Sector: Lithium hydroxide, for instance, is integral to battery technology, powering electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
- Research and Development: Fluoroantimonic acid, while extremely potent, is used in specialized research to study reactions and explore new chemical frontiers.
- Metalworking and Construction: Hydrochloric acid is employed for cleaning and pickling metals, while calcium hydroxide is used in mortar and plaster.
Historical Context and Evolution
The understanding and utilization of strong acids and bases have evolved significantly over time. Early civilizations recognized the power of substances like vinegar (acetic acid) and lye (sodium hydroxide) for various purposes. However, it was not until the 18th and 19th centuries that scientists like Antoine Lavoisier and Svante Arrhenius developed theories to explain acid-base behavior.
The identification and classification of strong acids and bases have enabled scientists and industries to harness their power safely. Today, these substances are integral to numerous technological advancements and innovations.
Expert Perspective: Interview with Dr. Emma Stone, Chemical Engineer
Case Study: Hydrochloric Acid in Metal Pickling
Hydrochloric acid, one of the most commonly used strong acids, plays a vital role in the metalworking industry. The process known as “metal pickling” involves treating metal surfaces with HCl to remove impurities, scale, and corrosion. This ensures a clean surface for further processing, such as plating or painting.
The effectiveness of hydrochloric acid in this application lies in its ability to rapidly dissolve oxides and other impurities, leaving a smooth and reactive surface. However, the process must be carefully controlled to avoid over-etching and to ensure worker safety.
Myth vs. Reality: Strong Acids and Bases in Everyday Life
Strong acids and bases are often associated with hazardous and dramatic depictions in popular culture. However, the reality is more nuanced:
- Myth: Strong Acids and Bases Are Always Dangerous: While it’s true that strong acids and bases require careful handling, they are not inherently dangerous. With proper safety measures and training, they can be safely used in various applications.
- Reality: They Have Everyday Uses: Many household products, such as drain cleaners and oven cleaners, contain weak acids or bases. Understanding their behavior and proper use is essential for safe household management.
Conclusion: A Powerful Arsenal
The world of strong acids and bases is both fascinating and crucial to our modern world. From chemical manufacturing to environmental science, these substances enable us to achieve remarkable feats. While their power demands respect and caution, they also offer incredible opportunities for innovation and progress.
What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid?
+Strong acids readily donate protons (H⁺ ions) and fully dissociate in aqueous solutions, making them highly reactive. Weak acids, on the other hand, only partially dissociate, resulting in a lower concentration of H⁺ ions.
Are there any natural strong acids or bases?
+While many strong acids and bases are synthetic, some naturally occurring substances can be considered strong. For instance, gastric acid in the stomach, which contains hydrochloric acid, is a natural strong acid.
How do strong acids and bases impact the environment?
+Strong acids and bases can have significant environmental impacts if not handled properly. They can contaminate water sources, harm ecosystems, and pose risks to human health. Responsible use and disposal are crucial.
Can strong acids and bases be recycled or reused?
+Yes, in certain industrial processes, strong acids and bases can be recycled and reused. This reduces waste and minimizes the need for fresh production, contributing to more sustainable practices.
What are some common safety precautions when handling strong acids and bases?
+When working with strong acids and bases, it’s crucial to wear protective gear, including gloves, safety goggles, and lab coats. Always handle these substances in well-ventilated areas, and avoid mixing them. In case of spills or accidents, have a clear protocol for neutralization and clean-up.