10 Things You Should Know About Room Temperature in Kelvin

Understanding room temperature in Kelvin might seem like a complex affair, but it’s an essential concept for anyone curious about the scientific intricacies of our surroundings. Here’s a breakdown of ten crucial insights to help you grasp this fundamental topic.
1. The Basics of Kelvin

The Kelvin scale is a temperature measurement system that starts at absolute zero, the coldest possible temperature where molecular motion ceases. Unlike the Celsius or Fahrenheit scales, Kelvin doesn’t have negative values; it’s an absolute scale that measures heat energy directly.
2. Room Temperature: A Precise Definition

When we talk about room temperature, we often mean a comfortable range for human beings. Scientifically, this is approximately 25 degrees Celsius, which translates to around 298 Kelvin. This temperature range is ideal for various biological processes and human comfort.
3. The Significance of Absolute Zero
Absolute zero, or 0 Kelvin, is a theoretical concept that represents a state where no heat energy exists. It’s an unattainable temperature in the real world, but scientists use it as a reference point to measure all other temperatures.
4. Comparing Kelvin to Other Scales
While Celsius and Fahrenheit scales are more familiar, the Kelvin scale has unique advantages. It simplifies calculations in scientific fields like physics and chemistry, as it directly relates to the average kinetic energy of particles.
5. The Role of Kelvin in Gas Laws
Kelvin is crucial in understanding gas laws, which describe the behavior of gases. For instance, the ideal gas law, PV = nRT, uses Kelvin temperature (represented by ’T’) to calculate the relationship between pressure, volume, and the number of moles of gas.
6. Everyday Applications of Kelvin
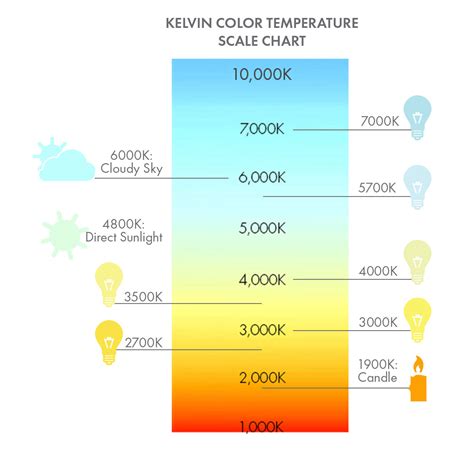
Although we don’t often think about it, Kelvin temperatures are used in various everyday situations. For example, the color temperature of light bulbs is often measured in Kelvin, with higher Kelvin values indicating a cooler, more blue-tinted light.
7. Historical Context
The Kelvin scale was developed by William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, in the 19th century. Thomson, a renowned physicist, named the scale after himself, reflecting his significant contributions to thermodynamics.
8. Converting Between Scales
Converting temperatures between Kelvin, Celsius, and Fahrenheit is straightforward. For example, to convert Celsius to Kelvin, simply add 273.15. This adjustment accounts for the difference between the freezing point of water (0 degrees Celsius) and absolute zero (0 Kelvin).
9. Extreme Temperatures in Kelvin
While room temperature is a comfortable 298 Kelvin, the universe encompasses an incredible range of temperatures. For instance, the surface of the Sun reaches temperatures over 5,000 Kelvin, while the cosmic microwave background radiation is approximately 2.7 Kelvin.
10. The Future of Temperature Measurement
As technology advances, new methods for temperature measurement are being developed. However, the Kelvin scale remains a cornerstone of scientific measurement, ensuring consistency and accuracy in various fields.
Key Takeaway
Grasping the concept of room temperature in Kelvin offers a deeper understanding of the world around us. It bridges the gap between everyday experiences and the scientific principles that govern our universe.
Further Exploration
- Explore the historical development of temperature scales and their impact on scientific discovery.
- Investigate the practical applications of the Kelvin scale in various industries, from meteorology to engineering.
- Delve into the mathematical relationships between temperature, energy, and molecular motion.
What is the average room temperature in Kelvin, and why is it significant?
+The average room temperature, approximately 25 degrees Celsius, translates to around 298 Kelvin. This temperature is significant as it aligns with the comfort zone for human beings and various biological processes. It serves as a reference point for understanding the thermal conditions in which we thrive.
How does the Kelvin scale compare to Celsius and Fahrenheit in practical use?
+The Kelvin scale simplifies scientific calculations and directly relates to particle energy, making it ideal for physics and chemistry. Celsius and Fahrenheit are more familiar for everyday use but require conversions for scientific applications.
What are some real-world examples of Kelvin temperature measurements?
+Kelvin temperatures are used in various fields. For instance, the color temperature of light bulbs is measured in Kelvin, with higher values indicating cooler light. In meteorology, temperatures in Kelvin provide a more precise understanding of atmospheric conditions.
How has the Kelvin scale influenced scientific research and discovery?
+The Kelvin scale has played a pivotal role in scientific research, particularly in thermodynamics and the study of gases. It provides a consistent and accurate measurement system, facilitating advancements in various fields and ensuring reproducibility in experiments.