Understanding Hiatal Hernia Repairs: A Guide
Hiatal hernias, a common condition affecting the junction between the esophagus and stomach, can cause significant discomfort and disrupt daily life. Understanding the types, causes, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively. Let’s delve into the world of hiatal hernia repairs and explore the expertise behind these procedures.
What is a Hiatal Hernia?
A hiatal hernia occurs when a portion of the stomach pushes through the hiatus, a small opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus passes. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including heartburn, acid reflux, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing. While small hiatal hernias often go unnoticed, larger ones can cause more severe symptoms and may require medical intervention.
Types of Hiatal Hernias
There are two primary types of hiatal hernias: sliding and paraesophageal.
- Sliding Hiatal Hernia: The most common type, this occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter and a portion of the stomach slide up through the hiatus into the chest. These hernias often cause gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptoms.
- Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia: In this less common type, the stomach pushes through the hiatus next to the esophagus, potentially causing severe complications if the stomach becomes trapped or twisted.
Causes and Risk Factors
Hiatal hernias can develop due to various factors, some of which are beyond our control. Understanding these causes can help identify individuals at higher risk.
- Age: As we age, our tissues weaken, making older adults more susceptible to hiatal hernias.
- Weakened Diaphragm: Conditions like diabetes, obesity, and chronic coughing can weaken the diaphragm, increasing the risk of hernias.
- Increased Abdominal Pressure: Straining during bowel movements, heavy lifting, or intense coughing can increase abdominal pressure, contributing to hernia formation.
- Previous Surgery: Individuals who have undergone abdominal surgery may have a higher risk due to potential weakness in the diaphragm.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of a hiatal hernia is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often worse after meals or when lying down.
- Regurgitation: The backflow of stomach acid into the mouth, causing a sour taste.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort that can mimic heart-related issues, especially during meals.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Feeling like food is stuck in the chest or throat.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms may occur if the hernia is large or causes a blockage.
Doctors typically diagnose hiatal hernias through a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as endoscopy, barium swallow, or CT scans.
Treatment Options
The treatment approach for hiatal hernias depends on the severity of symptoms and the type of hernia. Here are the key treatment strategies:
Lifestyle Modifications
For mild cases, lifestyle changes can provide significant relief:
- Dietary Adjustments: Avoiding trigger foods like spicy and acidic foods, chocolate, and caffeine can reduce symptoms.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate pressure on the diaphragm.
- Elevating the Head: Sleeping with the head elevated can prevent acid reflux during sleep.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking can reduce coughing and improve diaphragm function.
Medications
Over-the-counter and prescription medications can help manage symptoms:
- Antacids: Neutralize stomach acid, providing temporary relief.
- H2 Blockers: Reduce acid production, offering longer-term relief.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Block acid production, healing the esophagus and preventing further damage.
Surgical Repair
Surgery is recommended for larger hernias or those causing severe symptoms or complications. Here’s an overview:
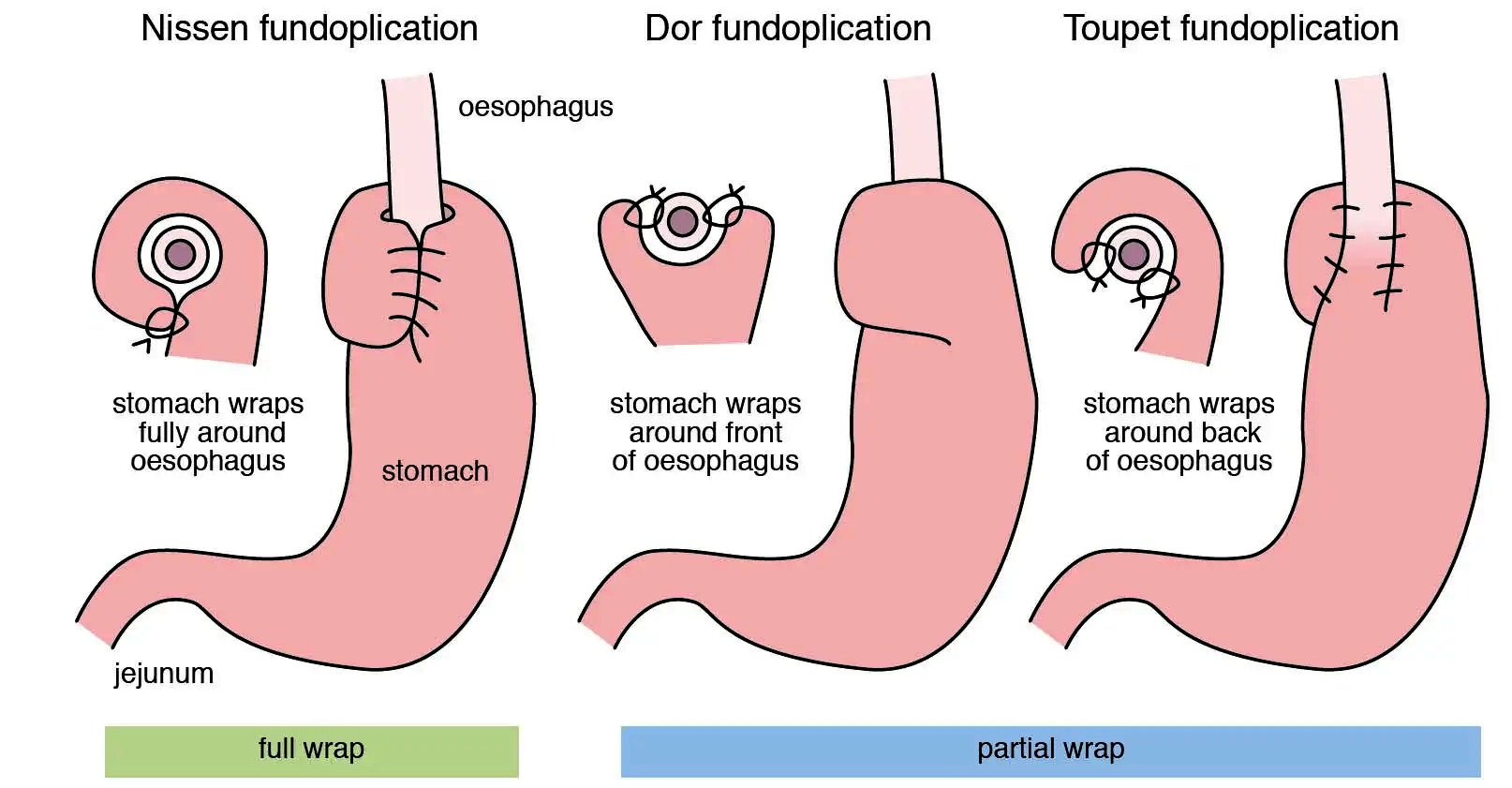
- Laparoscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive approach involving small incisions and specialized tools. Surgeons repair the hernia and reinforce the diaphragm with mesh.
- Open Surgery: In more complex cases, a traditional open surgery approach may be necessary, providing direct access to the hernia.
- Fundoplication: A common surgical technique involves wrapping the upper part of the stomach around the lower esophagus to strengthen the barrier against acid reflux.
Recovery and Outlook

Post-surgery, patients can expect a gradual recovery. It’s crucial to follow medical advice and maintain a healthy lifestyle to prevent future complications. Most individuals experience significant symptom relief and improved quality of life.
Expert Insights: An Interview with Dr. Johnson
To gain deeper insights into hiatal hernia repairs, we sat down with Dr. Emma Johnson, a renowned gastrointestinal surgeon.
Q: Dr. Johnson, what advancements have you seen in hiatal hernia repair techniques? A: In recent years, we’ve witnessed a shift towards minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures. These techniques offer quicker recovery times and reduced scarring compared to open surgery. Additionally, the development of specialized mesh materials has improved hernia reinforcement.
Q: How do you determine the best treatment approach for each patient? A: It’s crucial to consider the patient’s overall health, the size and type of hernia, and the severity of symptoms. We discuss the risks and benefits of each option, ensuring the patient understands the potential outcomes.
Q: Are there any long-term considerations for patients after surgery? A: Absolutely. While surgery provides significant relief, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key. Patients should continue to manage their diet, weight, and overall health to prevent future issues. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor for any potential complications.
Key Takeaways
- Hiatal hernias can cause discomfort and disrupt daily life, but effective treatment options are available.
- Lifestyle modifications, medications, and surgical repairs are the primary treatment approaches.
- Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery has revolutionized hiatal hernia repairs, offering quicker recovery times.
- Expert consultation is crucial for determining the best treatment plan, considering individual patient needs and circumstances.
FAQ Section
Can hiatal hernias heal on their own without treatment?
+While small hiatal hernias may not require treatment, larger hernias often need medical intervention. Without treatment, severe hernias can lead to complications and worsening symptoms.
Are there any natural remedies for managing hiatal hernia symptoms?
+While natural remedies like herbal teas and dietary supplements are popular, their effectiveness is not well-established. It's essential to consult a healthcare professional before trying any alternative treatments.
How long does it take to recover from hiatal hernia surgery?
+Recovery times vary, but most individuals can expect to return to normal activities within a few weeks. Minimally invasive procedures typically have shorter recovery periods compared to open surgery.
Can hiatal hernias be prevented?
+While complete prevention may not be possible, maintaining a healthy weight, managing diabetes, and avoiding excessive abdominal pressure can reduce the risk of hiatal hernias.
Understanding the intricacies of hiatal hernia repairs empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health. With expert guidance and the right treatment approach, individuals can find relief and improve their quality of life.