Master the Art: Excel Categorization Simplified
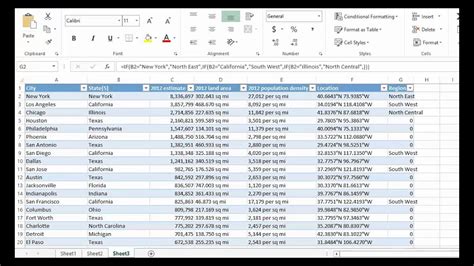
Welcome to the ultimate guide on mastering the art of Excel categorization. Effective data management is a cornerstone of efficient work, especially in today's data-driven world. For many professionals, Excel is a trusted companion, but harnessing its full potential for categorization can be a game-changer. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of Excel categorization, offering expert tips and tricks to simplify your data organization and enhance your productivity.
The Power of Excel Categorization
Excel, with its robust features and widespread use, is an invaluable tool for professionals across industries. However, the true potential of Excel lies in its ability to transform raw data into meaningful insights. Categorization plays a pivotal role in this process, enabling users to organize, analyze, and interpret data with precision.
Whether you're a seasoned Excel user or a novice looking to hone your skills, understanding the art of categorization is essential. It empowers you to make sense of complex datasets, identify patterns, and make informed decisions. In this article, we will explore a range of techniques and best practices to help you master Excel categorization, ensuring your data is not just organized but optimized for efficiency and analysis.
Understanding the Basics: Excel’s Categorization Fundamentals
Before we dive into advanced categorization techniques, let’s lay the groundwork by understanding the fundamental concepts and tools Excel provides for categorization.
Data Types and Formats
Excel recognizes various data types, each with its own unique characteristics and formatting options. Common data types include text, numbers, dates, and times. Understanding these data types is crucial, as it forms the basis for effective categorization. For instance, proper date formatting allows for easier sorting and filtering, while text formatting can help distinguish between different categories.
Let's take a look at a practical example. Imagine you have a dataset containing customer information, including their names, ages, and purchase histories. By recognizing that the "Age" column contains numerical data and formatting it accordingly, you can easily sort and filter the data to identify trends or analyze specific age groups.
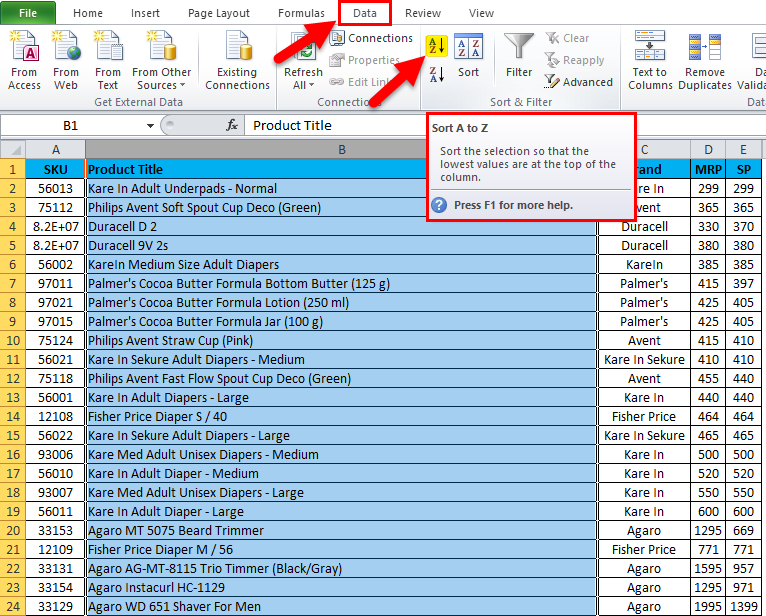
Sorting and Filtering: The Basics of Data Organization
Sorting and filtering are fundamental tools for organizing and analyzing data in Excel. Sorting allows you to arrange data in a specific order, whether it’s alphabetically, numerically, or by date. Filtering, on the other hand, enables you to selectively display only the data that meets certain criteria, making it easier to focus on specific categories or subsets of data.
For instance, if you have a large dataset with sales data for various products, you can use filtering to display only the records for a specific product category. This simplifies your analysis and allows you to quickly identify trends or performance metrics for that particular category.
Conditional Formatting: Visualizing Data Categories
Conditional formatting is a powerful Excel feature that allows you to apply specific formatting rules based on the values in your data. This tool is particularly useful for visually distinguishing between different categories or highlighting important data points. By applying conditional formatting, you can quickly identify trends, outliers, or patterns within your dataset.
Consider a scenario where you have a list of students' test scores. By applying conditional formatting, you can highlight the top performers in green, average scores in yellow, and lower scores in red. This visual categorization not only makes it easier to identify high-achievers but also helps you quickly assess the overall performance of the class.
Advanced Excel Categorization Techniques
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s explore some advanced techniques that will take your Excel categorization skills to the next level.
PivotTables: Dynamic Data Categorization
PivotTables are a powerful Excel feature that allows you to summarize, analyze, and present large datasets in a flexible and dynamic manner. They are particularly useful for categorizing and organizing data based on specific criteria. With PivotTables, you can quickly create customizable reports, analyze data from different angles, and gain valuable insights.
Imagine you have a dataset containing sales data for multiple products over several years. By using PivotTables, you can easily categorize and analyze this data by product, year, region, or any other relevant criteria. This dynamic categorization allows you to quickly assess sales trends, identify top-performing products, and make informed business decisions.
Data Validation: Ensuring Accurate Categorization
Data validation is an essential aspect of Excel categorization, as it helps ensure the accuracy and integrity of your data. By setting specific validation rules, you can control the type of data entered into a cell or range of cells, preventing errors and maintaining data consistency.
For example, if you have a spreadsheet for employee information, you can use data validation to ensure that the "Gender" column contains only valid entries such as "Male," "Female," or "Other." This prevents inaccurate or inconsistent data entry, making your categorization more reliable.
Formula-Based Categorization: Unlocking Advanced Analysis
Excel’s powerful formula capabilities allow you to perform advanced categorization and analysis. By leveraging functions and formulas, you can create dynamic and automated categorization systems that adapt to your data. This is particularly useful when dealing with complex datasets or when you need to apply specific rules for categorization.
Consider a scenario where you have a dataset with customer feedback, and you want to categorize the feedback based on sentiment. By using formulas and functions like IF, VLOOKUP, or even TEXTJOIN, you can analyze the feedback text and assign it to different sentiment categories, such as "Positive," "Negative," or "Neutral."
Excel Categorization for Data Visualization
Effective data visualization is an essential component of data analysis and presentation. Excel offers a range of chart and graph types that can help you visually represent your categorized data, making it easier to communicate insights and trends.
Choosing the Right Chart Type
Excel provides a wide array of chart types, each suited for different types of data and analysis. When categorizing data for visualization, it’s crucial to select the appropriate chart type that best represents your data and highlights the key insights you want to convey.
For instance, if you have categorized your data into different product categories and want to compare their sales performance, a bar chart or column chart would be an excellent choice. On the other hand, if you're analyzing trends over time, a line chart might be more suitable.
Customizing Charts for Impactful Visuals
Excel’s chart customization options allow you to fine-tune the appearance and layout of your charts to create visually appealing and impactful visualizations. By adjusting chart elements such as titles, labels, legends, and colors, you can enhance the clarity and impact of your categorized data.
For example, if you're presenting a comparison of sales figures for different product categories, you can use contrasting colors to differentiate the categories and make the chart more visually engaging. Additionally, adding data labels or trendlines can provide valuable context and help your audience quickly grasp the key insights.
Real-World Excel Categorization Examples

To illustrate the power and versatility of Excel categorization, let’s explore some real-world examples across different industries and use cases.
Financial Analysis: Categorizing Transaction Data
In the financial industry, Excel is widely used for analyzing transaction data. By categorizing transactions based on expense types, departments, or time periods, financial analysts can gain valuable insights into spending patterns, identify areas for cost-cutting, and make informed financial decisions.
For instance, a financial analyst might use Excel to categorize a company's monthly expenses by department. This categorization allows them to quickly assess the budget allocations for each department, identify any unusual expenses, and make recommendations for budget optimization.
Healthcare: Patient Data Categorization
In the healthcare sector, Excel plays a crucial role in managing and analyzing patient data. By categorizing patient information based on demographics, medical conditions, or treatment outcomes, healthcare professionals can identify trends, assess the effectiveness of treatments, and improve patient care.
Consider a scenario where a hospital uses Excel to categorize patient data by age groups and medical conditions. This categorization enables the hospital administration to identify high-risk patient populations, optimize resource allocation, and develop targeted prevention strategies.
Retail: Product Sales Categorization
For retail businesses, Excel is an essential tool for analyzing product sales data. By categorizing sales data based on product categories, sales channels, or customer segments, retailers can gain insights into product performance, identify best-selling items, and make informed decisions about inventory management and marketing strategies.
A retail analyst might use Excel to categorize sales data by product category and analyze the sales trends for each category. This categorization helps them identify top-performing products, assess the performance of new product launches, and make strategic decisions to optimize sales and profit margins.
Tips and Best Practices for Effective Excel Categorization
To ensure your Excel categorization efforts are efficient and effective, here are some tips and best practices to keep in mind:
- Plan Your Categorization Structure: Before you start categorizing your data, take the time to plan and define your categorization structure. Consider the goals and objectives of your analysis, and ensure your categories align with these goals. A well-planned categorization structure will make your analysis more focused and meaningful.
- Use Consistent Naming Conventions: Consistency is key when it comes to categorization. Establish and adhere to clear naming conventions for your categories. This ensures that your data is easily understood and searchable, making it simpler to analyze and collaborate with others.
- Leverage Excel's Built-in Functions: Excel offers a vast array of built-in functions and tools specifically designed for categorization and analysis. Familiarize yourself with functions like VLOOKUP, SUMIF, and COUNTIF, as these can greatly simplify your categorization tasks and enhance your analysis capabilities.
- Automate with Macros: If you find yourself performing repetitive categorization tasks, consider creating macros in Excel. Macros allow you to automate complex tasks, saving you time and effort. With macros, you can quickly apply categorization rules to your data with just a few clicks.
- Regularly Review and Update Your Categories: As your data evolves and your analysis needs change, it's essential to regularly review and update your categorization structure. Outdated or irrelevant categories can lead to inaccurate insights. Stay agile and adapt your categorization to ensure it remains relevant and meaningful.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Excel Categorization
Excel categorization is a powerful skill that can revolutionize the way you manage and analyze data. By understanding the fundamentals, exploring advanced techniques, and applying best practices, you can transform your data into actionable insights. Whether you’re a financial analyst, healthcare professional, or retail expert, mastering Excel categorization will empower you to make informed decisions, drive business growth, and deliver exceptional results.
Remember, effective data categorization is not just about organizing data; it's about telling a story with your data. With the right techniques and tools, Excel becomes your narrative companion, helping you craft compelling data-driven narratives that resonate with your audience and drive positive outcomes.
So, embrace the art of Excel categorization, and let your data speak volumes.
How can I effectively categorize large datasets in Excel?
+When dealing with large datasets, it’s crucial to establish a clear categorization structure and utilize Excel’s powerful tools. Start by defining your categories and ensuring they align with your analysis goals. Utilize PivotTables to dynamically categorize and analyze your data, and leverage functions like VLOOKUP and TEXTJOIN for advanced categorization. Additionally, consider using Excel’s filtering and sorting features to focus on specific subsets of data.
What are some best practices for visually representing categorized data in Excel charts?
+When creating charts to represent categorized data, choose the appropriate chart type based on the nature of your data and the insights you want to convey. Customize your charts by adjusting titles, labels, legends, and colors to enhance clarity and visual appeal. Consider adding data labels or trendlines to provide additional context and make your charts more informative.
How can I ensure data consistency and accuracy in my Excel categorization?
+To maintain data consistency and accuracy, establish clear naming conventions for your categories and ensure they are consistently applied throughout your dataset. Utilize data validation rules to control the type of data entered into specific cells or ranges, preventing errors and ensuring data integrity. Regularly review and update your categories to adapt to changing analysis needs.



