Master Excel: Calculate Hours Between Times
Excel is a powerful tool that professionals and individuals alike rely on for data analysis and management. One common task when working with time-related data is calculating the duration between two time values. Whether you're tracking employee work hours, monitoring project timelines, or analyzing any time-based data, understanding how to calculate hours between times is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of this task, exploring various methods and providing real-world examples to ensure you master this crucial Excel skill.
Understanding the Challenge: Calculating Hours Between Times
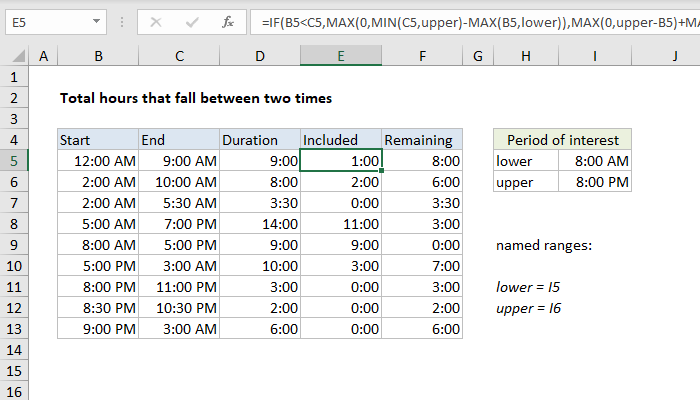
When dealing with time-based data in Excel, you might encounter situations where you need to determine the elapsed time between two specific time values. This could be as simple as calculating the duration between a start and end time for a task or as complex as considering various time formats and time zones. Excel offers a range of functions and techniques to tackle these challenges, and we will explore them in detail.
Method 1: Using the TIME Function for Basic Calculations

The TIME function is a fundamental tool for working with time values in Excel. It allows you to construct a time value by specifying hours, minutes, and seconds. This function is particularly useful when you want to perform basic calculations involving time durations.
Syntax and Usage
The syntax for the TIME function is as follows:
TIME(hour, minute, second)
Here's an example of how you can use the TIME function to calculate the duration between two time values:
Suppose you have a start time of 9:00 AM and an end time of 11:30 AM. To calculate the duration, you can use the following formula:
TIME(11, 30, 0) - TIME(9, 0, 0)
This formula will return a result of 2:30:00, indicating a duration of 2 hours and 30 minutes.
Handling Wrap-Around Times
One important aspect to consider when working with time durations is the concept of “wrap-around” times. Excel’s time format has a 24-hour cycle, which means that a time value of 25:00 is equivalent to 1:00 on the following day. To handle such cases, you can use the MOD function in combination with the TIME function.
Method 2: Utilizing the MOD Function for Wrap-Around Handling
The MOD function is an essential tool for managing wrap-around times in Excel. It calculates the remainder of a division operation, which can be useful for handling time durations that span multiple days.
Syntax and Usage
The syntax for the MOD function is as follows:
MOD(number, divisor)
To illustrate the usage of the MOD function, let's consider a scenario where you have a start time of 18:00 and an end time of 2:00 on the following day. The duration calculation using the TIME function alone would result in 10:00:00, which is incorrect.
To correctly calculate the duration, you can use the following formula:
TIME(MOD(B2-A2, 1), 0, 0)
In this formula, B2 represents the end time, and A2 represents the start time. The MOD function ensures that the duration is correctly calculated, even when the time values span multiple days.
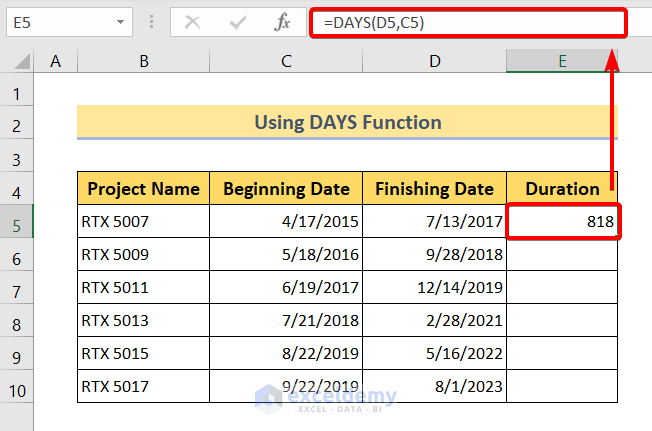
Method 3: Advanced Time Calculations with the DATEDIF Function
For more complex time calculations, especially when dealing with dates and times, the DATEDIF function comes into play. This function allows you to calculate the difference between two dates, providing various output formats, including “h” for hours.
Syntax and Usage
The syntax for the DATEDIF function is as follows:
DATEDIF(start_date, end_date, unit)
To calculate the duration in hours between two dates and times, you can use the following formula:
DATEDIF(B2, A2, “h”)
In this formula, B2 represents the end date and time, and A2 represents the start date and time. The DATEDIF function will return the duration in hours, considering both the date and time components.
Handling Time Zones and Daylight Saving Time
When working with time-based data across different time zones or during daylight saving time transitions, it’s crucial to consider the impact on your calculations. Excel’s time functions may not automatically adjust for these changes. To ensure accurate results, you may need to apply additional adjustments or consider using specialized tools or formulas.
Real-World Applications and Examples

Let’s explore some practical scenarios where calculating hours between times is essential:
Employee Work Hours
In a workforce management context, calculating the hours worked by employees is vital for payroll and productivity analysis. By utilizing the techniques discussed, you can accurately determine the duration between an employee’s clock-in and clock-out times, considering breaks and overtime.
Project Timeline Analysis
When managing projects, tracking the duration between task start and end times is crucial for monitoring progress and identifying potential delays. Excel’s time calculation functions can help you visualize and analyze project timelines effectively.
Transportation and Logistics
In industries like transportation and logistics, calculating the duration between shipment or delivery times is essential for optimizing routes and ensuring timely deliveries. Excel’s time calculation capabilities can provide valuable insights for supply chain management.
Conclusion: Mastering Time Calculations in Excel
Calculating hours between times in Excel is a fundamental skill for professionals across various industries. By understanding the different methods and functions available, you can tackle a wide range of time-based data analysis tasks. Whether you’re managing employee work hours, analyzing project timelines, or optimizing transportation routes, Excel’s powerful time calculation tools will empower you to make data-driven decisions.
FAQs
How can I handle time values that exceed 24 hours in Excel?
+
To handle time values that exceed 24 hours, you can use the TIME function in combination with the MOD function. This allows you to correctly calculate durations that span multiple days.
Can I calculate the duration between two dates without considering time in Excel?
+
Yes, you can calculate the duration between two dates without time values using the DATEDIF function. Specify the “d” unit to get the number of days between the dates.
How do I format time values in Excel to ensure accuracy in calculations?
+
To format time values correctly, ensure that the cells containing time data are formatted as Time in the Excel format menu. This ensures that Excel interprets the values as time and performs calculations accurately.



