Nurse vs Pharmacist: Who Earns More?
In the healthcare industry, nurses and pharmacists play vital roles in patient care and medication management. When it comes to earning potential, both professions offer lucrative opportunities, but the question remains: who takes home a higher paycheck? Let's delve into the factors that influence the earnings of nurses and pharmacists and explore the data to determine which profession emerges as the higher-earning career path.
The Role of Nurses and Pharmacists in Healthcare

Nurses and pharmacists are essential members of the healthcare team, each contributing unique skills and expertise to ensure optimal patient outcomes. Nurses provide direct patient care, offering compassionate support and implementing medical treatments. They are often the primary point of contact for patients, offering holistic care and education. On the other hand, pharmacists specialize in medication management, ensuring patients receive the right drugs at the right doses. They play a crucial role in reviewing prescriptions, providing drug information, and educating patients about their medications.
While both professions are indispensable, there are distinct differences in their education, training, and daily responsibilities. These differences also extend to their earning potential, which we will explore in detail.
Education and Training Requirements

The path to becoming a nurse or a pharmacist begins with education and training. Let’s break down the academic journey for each profession:
Nursing Education
Nurses typically pursue one of three educational routes: an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN), a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN), or a direct-entry Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) for individuals with non-nursing bachelor’s degrees. ADN programs, often offered by community colleges, take around two years to complete and provide a solid foundation in nursing practice. BSN programs, available at universities, typically take four years and offer a more comprehensive education, including leadership and research skills. MSN programs, aimed at experienced nurses, can take one to two years and focus on advanced nursing practice and specialization.
After completing their nursing education, graduates must pass the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN) to obtain their nursing license and begin practicing.
Pharmacy Education
Pharmacists, on the other hand, follow a more specialized educational path. They must complete a Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) degree, which is a professional doctoral program typically lasting four years. Pharmacy schools require a strong background in science and mathematics, and students must complete rigorous coursework and clinical rotations to graduate.
Following graduation, pharmacists must pass the North American Pharmacist Licensure Examination (NAPLEX) to obtain their license and practice as registered pharmacists.
Salary Comparison: Nurses vs. Pharmacists
Now, let’s delve into the earnings of nurses and pharmacists, comparing their average salaries and exploring the factors that influence their income.
Nurse Salaries
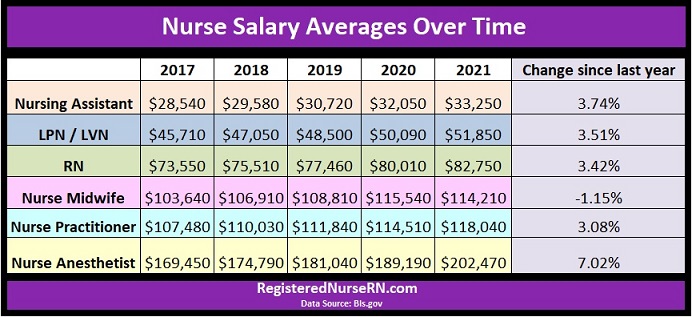
According to recent data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for registered nurses (RNs) was $77,600 as of May 2020. However, earnings can vary significantly based on factors such as education, specialization, and work setting.
For instance, nurses with a BSN or higher degree often earn more than their ADN-educated counterparts. Additionally, certain nursing specialties, such as critical care or oncology, may command higher salaries due to the specialized skills and knowledge required.
The work setting also plays a crucial role in nurse salaries. Nurses working in hospitals, especially in specialized units, often earn more than those in outpatient clinics or long-term care facilities. Furthermore, nurses in high-demand regions or those with experience and advanced certifications may negotiate higher salaries.
Pharmacist Salaries
Pharmacists, with their advanced education and specialized skills, generally earn higher salaries than nurses. The BLS reports that the median annual wage for pharmacists was $128,710 as of May 2020. This figure reflects the demand for pharmacists’ expertise in medication management and the critical role they play in patient safety.
Similar to nurses, pharmacist salaries can vary based on factors such as work setting and specialization. Pharmacists working in hospitals or retail pharmacies may earn different salaries, with hospital pharmacists often commanding higher wages due to the complexity of their work. Additionally, pharmacists with specialized certifications, such as those in oncology or nuclear pharmacy, may earn premium salaries for their unique skills.
Factors Influencing Salary
Beyond education and work setting, several other factors can influence the earning potential of nurses and pharmacists:
- Experience: As with most professions, experience plays a significant role in salary growth. Both nurses and pharmacists can expect their earnings to increase as they gain more years of practice.
- Specialization: Choosing a specialized field within nursing or pharmacy can lead to higher salaries. For example, nurse anesthetists and clinical pharmacists often earn above-average wages due to their advanced skills and responsibilities.
- Location: The cost of living and demand for healthcare professionals vary across different regions. Nurses and pharmacists working in high-demand areas or in cities with a higher cost of living may earn higher salaries to compensate for the increased expenses.
- Employer: The type of employer can also impact earnings. Nurses and pharmacists working for large healthcare systems or government agencies may have different salary structures compared to those employed by smaller clinics or independent pharmacies.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Both nursing and pharmacy offer excellent career growth prospects and advancement opportunities. Let’s explore the pathways for professional development in each field.
Nursing Career Advancement
Nurses have a wide range of advancement options, which often involve continuing education and specialization. Here are some common career advancement paths for nurses:
- Advanced Practice Registered Nurses (APRNs): APRNs, such as nurse practitioners, nurse anesthetists, and nurse midwives, hold advanced degrees and provide specialized care. They often have prescription privileges and can work independently or in collaboration with physicians.
- Nurse Educators: Experienced nurses with advanced degrees can transition into academic roles, teaching and mentoring future nurses. Nurse educators play a crucial role in shaping the next generation of healthcare professionals.
- Nurse Managers and Administrators: Nurses with strong leadership skills can advance into management roles, overseeing nursing units or entire healthcare facilities. These positions involve strategic planning, budgeting, and staff supervision.
- Specialized Nurses: Nurses can specialize in various fields, such as oncology, critical care, or pediatrics. Specialization often requires additional training and certification but can lead to higher salaries and greater job satisfaction.
Pharmacy Career Advancement
Pharmacists also have opportunities for career growth and specialization. Here are some common advancement paths for pharmacists:
- Pharmacy Management: Pharmacists with leadership skills can advance into management positions, overseeing pharmacy operations, staffing, and budgeting. They may work in retail pharmacies, hospitals, or long-term care facilities.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Pharmacists can transition into the pharmaceutical industry, working in research and development, clinical trials, or marketing. This path often requires additional training and a strong understanding of drug development and regulations.
- Specialized Pharmacists: Similar to nurses, pharmacists can specialize in fields such as oncology, nuclear pharmacy, or toxicology. Specialization often involves additional education and certification and can lead to higher-paying positions.
- Independent Pharmacy Ownership: Some pharmacists choose to open their own independent pharmacies, providing personalized care and services to their communities. This path requires business acumen and a strong understanding of pharmacy operations.
Work-Life Balance and Job Satisfaction

When considering a career path, it’s essential to evaluate not only the earning potential but also the work-life balance and job satisfaction it offers. Let’s compare the work-life balance and job satisfaction aspects of nursing and pharmacy.
Nursing Work-Life Balance and Job Satisfaction
Nursing can be a rewarding career, offering a strong sense of purpose and the opportunity to make a positive impact on patients’ lives. However, the nature of nursing work can also be demanding, with long hours, irregular shifts, and high-stress situations. Nurses often work weekends, holidays, and nights, which can impact their work-life balance.
Despite the challenges, many nurses find great satisfaction in their work, especially when they see the positive outcomes of their care. The close patient interactions and the opportunity to develop long-term relationships with patients can be extremely rewarding.
Pharmacy Work-Life Balance and Job Satisfaction
Pharmacists, on the other hand, often have more regular working hours and may enjoy a better work-life balance. While retail pharmacists may work weekends and evenings, their schedules are typically more predictable than those of nurses. Hospital pharmacists may also have shift work, but their hours are often more consistent.
Job satisfaction for pharmacists can be high, as they play a critical role in patient care and medication management. Pharmacists have the opportunity to build relationships with patients and provide valuable drug information and counseling. Additionally, pharmacists in specialized fields, such as nuclear pharmacy or toxicology, may find their work particularly rewarding due to the unique challenges and responsibilities involved.
Conclusion: Weighing the Factors
When comparing nurses and pharmacists in terms of earning potential, it’s clear that pharmacists generally earn higher salaries due to their advanced education and specialized skills. However, it’s important to note that salary is just one aspect to consider when choosing a career path. Work-life balance, job satisfaction, and personal interests should also play a significant role in your decision.
Nursing offers a rewarding career with the opportunity to provide direct patient care and build meaningful relationships. Pharmacists, on the other hand, contribute to patient safety and medication management, playing a critical role in the healthcare system. Both professions have their unique advantages and challenges, and the choice ultimately depends on your individual goals, interests, and values.
Whether you choose to pursue a career in nursing or pharmacy, rest assured that both professions offer excellent opportunities for growth, advancement, and making a positive impact on patients' lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can nurses earn as much as pharmacists with additional education and specialization?
+
Yes, nurses can significantly increase their earning potential by pursuing advanced degrees and specializing in high-demand fields. Advanced Practice Registered Nurses (APRNs), such as nurse practitioners, often earn competitive salaries comparable to those of pharmacists.
Are there opportunities for nurses and pharmacists to work in research or academia?
+
Absolutely! Both nurses and pharmacists can transition into research or academic roles. Nurses can become nurse educators or researchers, while pharmacists can work in pharmaceutical research or teach at pharmacy schools.
How do the career advancement paths of nurses and pharmacists compare in terms of leadership roles?
+
Both professions offer opportunities for leadership roles. Nurses can advance into management positions, overseeing nursing units or entire healthcare facilities. Pharmacists can become pharmacy managers or even open their own independent pharmacies.
Are there any salary differences between nurses and pharmacists based on gender or ethnicity?
+
Yes, there may be some salary disparities based on gender and ethnicity in both professions. However, it’s important to note that these disparities are not unique to nursing and pharmacy and are being actively addressed through advocacy and policy changes.


