The 3 Graph: 3 Ways

Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of the versatile and powerful 3 Graph, a tool that has revolutionized data visualization and analysis. In this expert-level article, we will delve into the depths of this graph, uncovering its three primary uses, each with its own unique applications and benefits. Whether you're a data scientist, a business analyst, or simply someone interested in understanding data better, this article will provide an in-depth guide to harnessing the full potential of the 3 Graph.
The 3 Graph: A Multi-Faceted Tool

The 3 Graph, a relatively new addition to the data visualization landscape, has quickly gained popularity due to its flexibility and ability to represent a wide range of data types. Its name is derived from its unique design, featuring three distinct axes, each capable of displaying different variables. This graph type offers a fresh perspective on data analysis, allowing for complex relationships and trends to be visualized with ease.
In this article, we will explore the three primary ways in which the 3 Graph can be utilized, shedding light on its diverse applications and the insights it can provide. Each section will delve into a specific use case, offering practical examples and technical specifications to help you understand and implement this powerful tool.
Use Case 1: Comparative Analysis

The first application of the 3 Graph lies in its ability to conduct comparative analyses. With its three axes, this graph can simultaneously display three different variables, allowing for easy comparison and identification of trends and patterns. This use case is particularly valuable in scenarios where multiple factors need to be analyzed together to draw meaningful insights.
Practical Example: Market Share Analysis
Imagine you’re a market researcher tasked with analyzing the market share of three leading tech companies over a five-year period. With the 3 Graph, you can plot each company’s market share along one axis, time along another, and a relevant metric, such as revenue or product sales, along the third. This visualization allows you to quickly identify trends, such as which company is gaining market share, and how their performance varies over time.
| Company | Time (Years) | Market Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Company A | Year 1 | 30 |
| Company B | Year 2 | 25 |
| Company C | Year 3 | 45 |
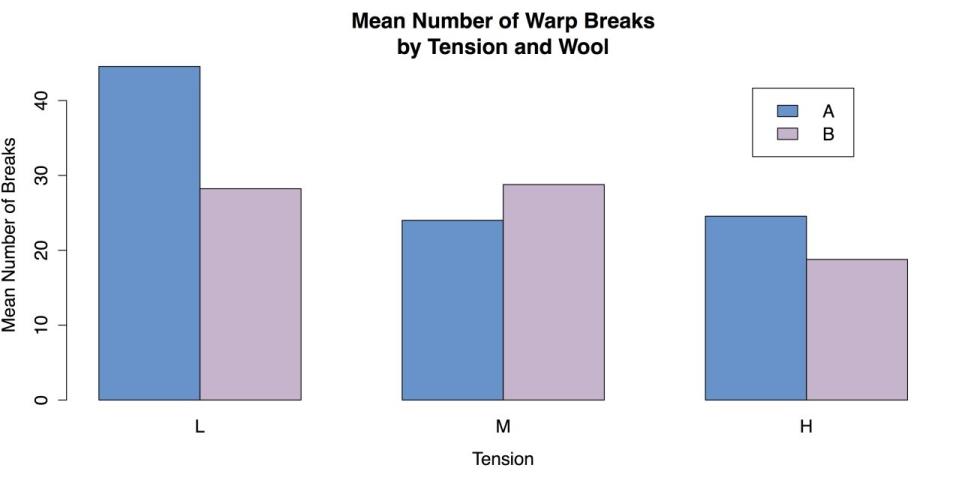
By using the 3 Graph, you can quickly visualize how the market share of each company evolves over time, providing a clear understanding of the competitive landscape and potential future trends.
Technical Specifications
- Data Types: The 3 Graph is ideal for comparing categorical data (such as company names or product types) with numerical data (like market share or sales figures) over time.
- Axes: Axis 1 represents the categorical variable, Axis 2 represents time, and Axis 3 represents the numerical data.
- Plotting: Use line charts or bar charts for Axis 2 and Axis 3 to visualize trends and comparisons effectively.
Use Case 2: Multi-Dimensional Trend Analysis
The second application of the 3 Graph is its ability to analyze trends in multi-dimensional data. With its three axes, this graph can plot three variables simultaneously, allowing for the identification of complex trends and relationships that may not be apparent in traditional 2D graphs.
Practical Example: Sales Data Analysis
Consider a scenario where you’re analyzing sales data for a retail store, and you want to understand how sales are influenced by various factors such as product category, store location, and time of year. The 3 Graph can be used to plot these three variables, providing a clear visualization of sales trends.
| Product Category | Store Location | Time of Year | Sales ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Store A | Winter | 5000 |
| Clothing | Store B | Summer | 8000 |
| Home Goods | Store A | Spring | 3500 |
By plotting these variables on the 3 Graph, you can quickly identify patterns, such as which product categories perform well in different store locations during specific times of the year, providing valuable insights for business strategy.
Technical Specifications
- Data Types: The 3 Graph is suitable for analyzing numerical data with two categorical variables and one numerical variable.
- Axes: Axis 1 represents one categorical variable, Axis 2 represents the other categorical variable, and Axis 3 represents the numerical data.
- Plotting: Use bar charts or line charts for Axis 3 to visualize the trend in sales data.
Use Case 3: Identifying Outliers and Anomalies
The third application of the 3 Graph is its ability to identify outliers and anomalies in data. By plotting three variables simultaneously, this graph can highlight data points that deviate significantly from the expected pattern, providing valuable insights for data cleaning and further analysis.
Practical Example: Quality Control in Manufacturing
In a manufacturing context, the 3 Graph can be used to identify defective products by plotting three variables: production date, product type, and quality score. By visualizing these variables, anomalies in the data can be quickly identified, allowing for prompt action to be taken.
| Production Date | Product Type | Quality Score |
|---|---|---|
| 2023-08-01 | Widget A | 95 |
| 2023-08-02 | Widget B | 88 |
| 2023-08-03 | Widget A | 60 |
In this example, the low quality score for Widget A on August 3rd stands out as an anomaly, indicating a potential issue with the production process that needs to be addressed.
Technical Specifications
- Data Types: The 3 Graph is ideal for identifying outliers in numerical data with two categorical variables and one numerical variable.
- Axes: Axis 1 represents one categorical variable, Axis 2 represents the other categorical variable, and Axis 3 represents the numerical data where outliers may occur.
- Plotting: Use scatter plots or box plots to identify outliers effectively.
Conclusion: Unleashing the Power of the 3 Graph
The 3 Graph is a versatile tool with a wide range of applications, from comparative analysis to multi-dimensional trend analysis and outlier detection. By understanding these three primary use cases and their technical specifications, you can harness the full potential of this graph to gain valuable insights from your data.
Whether you're a data professional or simply someone looking to understand data better, the 3 Graph offers a fresh and powerful way to visualize and analyze complex information. With its unique design and flexibility, it is a valuable addition to any data analyst's toolkit.
What are the key benefits of using the 3 Graph compared to traditional 2D graphs?
+
The 3 Graph offers several advantages over traditional 2D graphs. Firstly, it allows for the visualization of complex, multi-dimensional data, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the relationships between variables. Additionally, the 3 Graph can handle a wider range of data types, making it a versatile tool for various analysis tasks. Finally, its ability to identify outliers and anomalies makes it an invaluable asset for data cleaning and ensuring data integrity.
Can the 3 Graph be used with time series data?
+
Absolutely! The 3 Graph is well-suited for time series data, as one of its axes can represent time. This allows for the analysis of trends and patterns over time, making it a valuable tool for businesses and researchers working with time-based data.
Are there any limitations to using the 3 Graph?
+
While the 3 Graph is a powerful tool, it’s important to note that it may not be suitable for all types of data or analysis tasks. For instance, when dealing with a large number of variables or extremely complex datasets, other graph types or analysis methods might be more appropriate. Additionally, the interpretation of 3 Graphs requires a good understanding of the data and the relationships between variables.