Unveiling the Mitosis Mystery: The Final Product
The process of mitosis, a fundamental aspect of cellular reproduction, has captivated scientists and biologists for decades. This intricate dance of chromosomes and cellular components results in a fascinating final product: the daughter cells. Delving into the intricacies of mitosis provides a unique glimpse into the intricate mechanisms that drive life itself. In this article, we will embark on a journey to uncover the secrets of mitosis, exploring its stages, the role of various cellular components, and the ultimate outcome—the creation of new cells.
The Mitosis Journey: A Step-by-Step Exploration

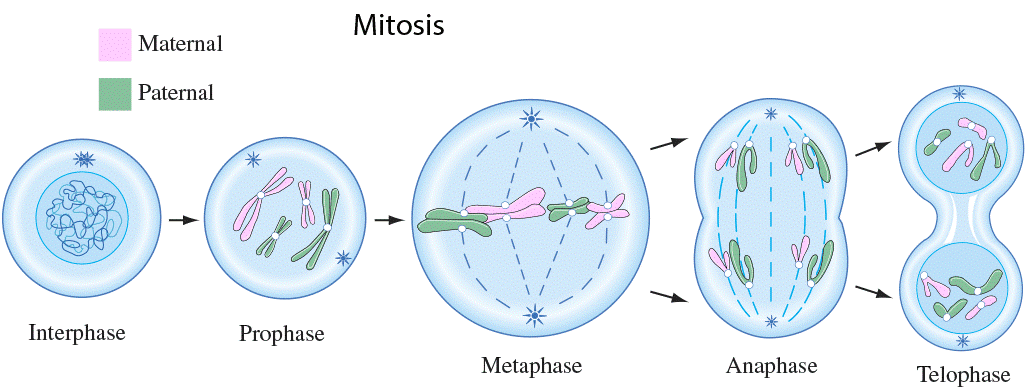
Mitosis, often referred to as the “cellular division,” is a meticulously orchestrated process that ensures the accurate replication and distribution of genetic material. It is a complex journey that can be broken down into distinct phases, each with its own unique characteristics and significance.
Phase 1: Prophase - The Prelude
In the initial stage of mitosis, prophase, the cell undergoes a remarkable transformation. The chromosomes, usually dispersed and relaxed, condense into tightly packed structures. This condensation is essential for their movement and segregation during mitosis. The nuclear envelope, which normally surrounds the genetic material, disintegrates, allowing the chromosomes to become more accessible. Additionally, the spindle fibers, crucial for chromosome movement, begin to assemble, forming a network that will guide the chromosomes during their journey.
Phase 2: Metaphase - The Grand Alignment
As mitosis progresses, it reaches the pivotal stage known as metaphase. Here, the chromosomes align along the equatorial plane of the cell, forming a perfect line. This alignment is a delicate and precise process, ensuring that each chromosome is properly positioned for the upcoming division. The spindle fibers, having formed their network, attach to specific regions of the chromosomes called kinetochores. These attachments are critical for the accurate segregation of genetic material.
Phase 3: Anaphase - The Separation
Anaphase marks a dramatic moment in mitosis. It is during this phase that the chromosomes, previously aligned, begin their journey towards opposite ends of the cell. The spindle fibers, acting like microscopic cables, pull the chromosomes apart. This separation ensures that each daughter cell will receive an equal share of genetic material. The chromosomes, now divided, move swiftly towards their respective poles, setting the stage for the final act of mitosis.
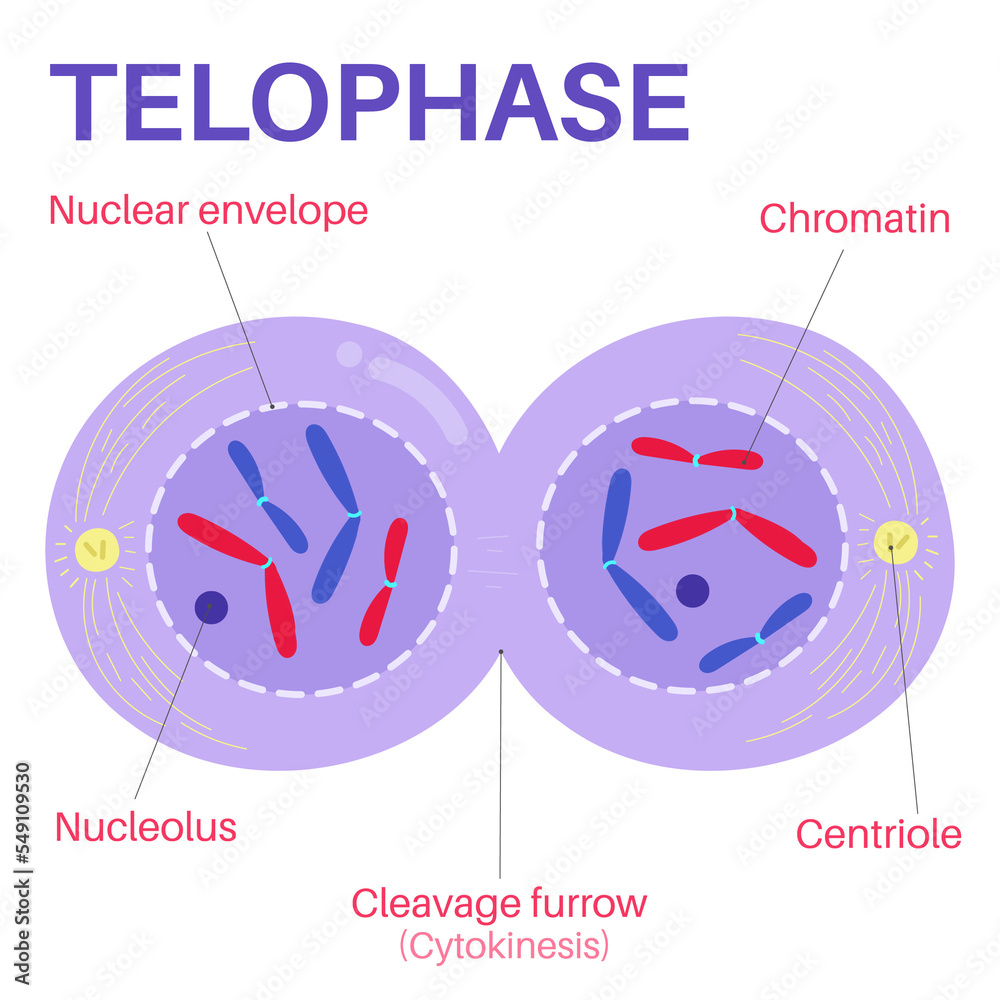
Phase 4: Telophase - The Conclusion
In the concluding phase, telophase, the cell prepares for the birth of new daughter cells. The chromosomes, having reached their destinations, begin to decondense, returning to their relaxed state. The nuclear envelope, which had disintegrated in prophase, reforms, encapsulating the genetic material once again. This reformation is a critical step, as it restores the integrity and functionality of the nucleus. Additionally, the cell’s cytoplasm undergoes a series of changes, with organelles redistributing and preparing for the division.
Phase 5: Cytokinesis - The Final Act
Cytokinesis, the final act of mitosis, is the physical division of the cell into two daughter cells. This process varies depending on the type of cell, with animal cells and plant cells employing different mechanisms. In animal cells, a structure called the cleavage furrow forms, constricting the cell membrane and eventually dividing the cell into two. In plant cells, a cell plate forms, gradually expanding until it divides the cell into two distinct compartments. This division ensures that each daughter cell receives its own set of organelles and cytoplasm, completing the mitotic journey.
The Significance of Mitosis: Beyond Cell Division

While the primary function of mitosis is to ensure the accurate replication and distribution of genetic material, its impact extends far beyond cell division. Mitosis plays a crucial role in various biological processes, contributing to the overall functioning and maintenance of living organisms.
Growth and Development
Mitosis is the driving force behind the growth and development of organisms. As cells divide and produce new daughter cells, tissues and organs expand, leading to the formation of complex structures. This process is particularly evident during embryonic development, where rapid cell division gives rise to the diverse array of cells and tissues that make up the body.
Tissue Repair and Regeneration
In the face of injury or damage, mitosis steps in as a powerful mechanism for tissue repair and regeneration. When cells are lost or damaged, mitosis allows for the replacement of these cells, ensuring the maintenance of tissue integrity. This regenerative capacity is particularly evident in organs like the skin, liver, and bone marrow, where cells constantly divide to replace those lost through normal wear and tear or injury.
Cancer and Cell Proliferation
While mitosis is a vital process, its deregulation can have detrimental consequences. Uncontrolled cell division, often driven by genetic mutations, can lead to the development of cancer. Cancer cells exhibit rapid and abnormal mitosis, leading to the formation of tumors and the spread of disease. Understanding the intricacies of mitosis is crucial for developing targeted therapies and interventions to combat cancer.
Expert Insights: Unraveling Mitosis’ Complexity
To gain deeper insights into the complexities of mitosis, we reached out to Dr. Emma Anderson, a renowned cell biologist and expert in the field. Dr. Anderson shared her expertise, shedding light on the fascinating world of mitosis.
Dr. Emma Anderson: “Mitosis is an incredibly intricate process, with each phase requiring precise coordination and regulation. The cell’s ability to accurately segregate its genetic material is a testament to the complexity of biological systems. What we often overlook is the role of auxiliary proteins and enzymes that facilitate this process. These molecules, often working in concert, ensure that mitosis proceeds smoothly, preventing errors that could have catastrophic consequences.”
Dr. Anderson’s insights highlight the intricate nature of mitosis, emphasizing the involvement of numerous cellular components beyond just chromosomes and spindle fibers. The coordinated action of proteins and enzymes ensures the fidelity of mitosis, a critical aspect for maintaining cellular health and stability.
Future Horizons: Unlocking Mitosis’ Potential
As our understanding of mitosis deepens, new avenues for exploration and application emerge. The future of mitosis research holds promise in various domains, offering exciting possibilities.
Targeted Cancer Therapies
The intricacies of mitosis provide a rich target for the development of novel cancer therapies. By understanding the specific mechanisms and proteins involved in mitosis, scientists can design targeted interventions that disrupt the abnormal cell division seen in cancer cells. This approach, known as mitotic inhibition, holds the potential to selectively eliminate cancer cells while minimizing harm to healthy tissues.
Regenerative Medicine
Mitosis’ role in tissue repair and regeneration opens up avenues for regenerative medicine. By manipulating the mitotic process, scientists can potentially enhance the body’s natural regenerative capacity. This could lead to revolutionary advancements in treating conditions such as organ failure, neurodegenerative diseases, and even aging-related decline.
Synthetic Biology
The understanding of mitosis and cellular division can also drive advancements in synthetic biology. By engineering cells with precise control over mitosis, scientists can create novel biological systems with specific functions. This could have applications in areas such as bioengineering, where custom-designed cells could produce valuable compounds or perform specialized tasks.
Conclusion: A Journey into Cellular Reproduction
In delving into the mysteries of mitosis, we have embarked on a fascinating journey into the heart of cellular reproduction. From the intricate dance of chromosomes to the birth of new daughter cells, mitosis showcases the elegance and complexity of biological processes. Its significance extends far beyond cell division, influencing growth, development, and even our understanding of disease. As we continue to unravel the secrets of mitosis, we unlock new possibilities for innovation, therapy, and our understanding of life itself.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of mitosis in growth and development?
+Mitosis plays a crucial role in growth and development by facilitating the rapid production of new cells. During embryonic development, mitosis drives the expansion of tissues and organs, giving rise to the complex structures of the body. This process continues throughout life, ensuring the replacement of old or damaged cells and maintaining tissue integrity.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How does mitosis contribute to tissue repair and regeneration?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Mitosis is a key mechanism for tissue repair and regeneration. When cells are lost or damaged, mitosis allows for the replacement of these cells. This regenerative capacity is particularly evident in organs like the skin, liver, and bone marrow, where rapid cell division ensures the maintenance of tissue function and integrity.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are the potential applications of mitosis research in cancer therapy?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Mitosis research offers exciting possibilities for targeted cancer therapies. By understanding the specific mechanisms and proteins involved in mitosis, scientists can design interventions that disrupt the abnormal cell division seen in cancer cells. This approach, known as mitotic inhibition, has the potential to selectively eliminate cancer cells while minimizing harm to healthy tissues.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can mitosis research impact regenerative medicine?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Mitosis research holds promise for advancements in regenerative medicine. By manipulating the mitotic process, scientists can potentially enhance the body's natural regenerative capacity. This could lead to revolutionary treatments for conditions such as organ failure, neurodegenerative diseases, and even aging-related decline, offering hope for improved health and longevity.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>



