Unraveling the Cell Theory's 3 Fundamentals.

The cell is the fundamental unit of life, a concept that forms the bedrock of modern biology. Unveiled over centuries of scientific exploration, the cell theory has three foundational principles that underpin our understanding of the living world. Let’s delve into these principles, exploring their historical evolution, practical implications, and future potential.
The Historical Evolution of the Cell Theory

The journey towards understanding the cell began with early observations made by scientists who, with the aid of rudimentary microscopes, witnessed tiny compartments within living organisms. However, it was not until the 19th century that the concept of cells gained scientific recognition.
Early Observations and Microscopy
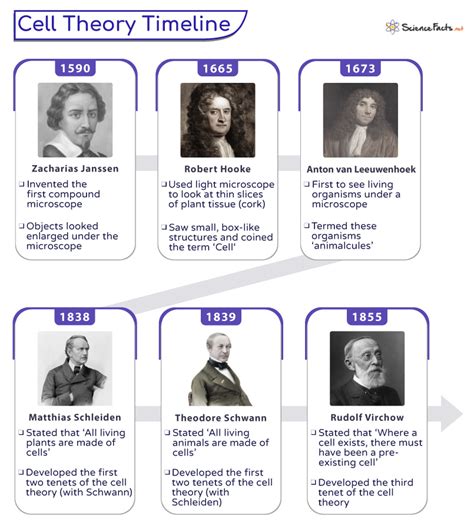
In the 1600s, scientists like Robert Hooke and Anton van Leeuwenhoek were among the first to observe cells, although they lacked the context to fully grasp their significance. Hooke, an English scientist, is credited with coining the term ‘cell’ after observing the structured compartments within cork, likening them to the small rooms occupied by monks. Meanwhile, van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch scientist, was renowned for his ability to grind lenses and build powerful microscopes. He observed microscopic life forms, including bacteria, and described them as ‘animalcules’.
The Rise of Cell Theory
It was during the 1800s that the concept of cells gained momentum, thanks to the work of scientists like Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow. Schleiden, a German botanist, observed that all plants are composed of cells, while Schwann, a German zoologist, made a similar observation about animals. These independent discoveries led to the formulation of the first two principles of cell theory: all living organisms are made of cells, and cells are the basic units of life.
Virchow, another German scientist, contributed the third principle when he proposed that ‘omnis cellula e cellula’—all cells come from pre-existing cells. This principle, which contradicted the then-popular theory of spontaneous generation, revolutionized our understanding of life’s origins and paved the way for modern biology.
The Practical Implications of Cell Theory
The cell theory has profound implications across various fields of science and medicine.
Biology and Medicine
In biology, the cell theory provides a foundational framework for understanding life processes. It guides research in areas such as cell biology, genetics, and developmental biology. In medicine, the cell theory is crucial for diagnosing and treating diseases. For instance, understanding the normal structure and function of cells allows doctors to identify abnormal cells, such as those in cancer, and develop targeted treatments.
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering
The cell theory has also fueled advancements in biotechnology and genetic engineering. Scientists can now manipulate cells and their components to create new products, improve agricultural yields, and even develop novel therapies for diseases. Techniques like gene editing, which target specific sequences within cells, would be impossible without a deep understanding of cell theory.
Environmental Science and Ecology
Cell theory is essential for understanding the structure and function of ecosystems. It helps scientists comprehend the role of different organisms and how they interact with each other and their environment. For instance, understanding the cellular processes of plants can inform strategies for carbon sequestration and sustainable agriculture.
Future Potential and Emerging Trends
As our understanding of cells deepens, so does the potential for groundbreaking discoveries and applications.
Single-Cell Analysis
Advances in technology have enabled the study of individual cells, providing unprecedented insights into cellular diversity and function. Single-cell analysis allows researchers to identify rare cell types, track cellular changes over time, and even uncover the cellular origins of diseases. This technology is poised to revolutionize personalized medicine, allowing for precise diagnoses and treatments tailored to individual patients.
Synthetic Biology
Synthetic biology, an emerging field at the intersection of biology and engineering, aims to design and construct new biological systems and living organisms. By manipulating cells and their components, scientists can create novel organisms with specific functions, such as producing biofuels or detecting environmental pollutants. The potential of synthetic biology is vast, offering solutions to some of humanity’s most pressing challenges.
Cellular Agriculture
Cellular agriculture is another exciting application of cell theory. This field involves the production of agricultural products, such as meat and dairy, from cell cultures rather than traditional farming methods. By growing cells in laboratories, scientists can create sustainable and ethical alternatives to traditional agriculture, addressing issues like animal welfare and environmental degradation.
Conclusion
The cell theory, with its three fundamental principles, continues to shape our understanding of life and guide scientific research. From its early beginnings to its modern applications, the cell theory has proven to be a robust framework for exploring the complexities of the living world. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of cells, we open new doors to innovation and discovery, offering hope for a better future.