Understanding Conduction: An Everyday Example
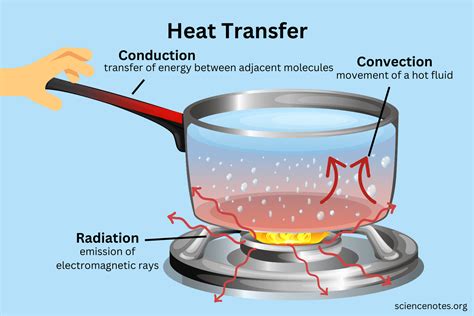
We often take for granted the simple yet fascinating phenomenon of heat transfer through conduction, which plays a vital role in our daily lives. From cooking meals to keeping our homes warm, this process is an essential part of many practical applications. To illustrate its principles, let’s delve into a relatable scenario involving a common kitchen appliance: the electric stove.
Imagine preparing a delicious breakfast on a cool morning. You turn on the stove, setting the temperature to medium-high, and place a pan on the heated surface. Almost immediately, you notice the pan’s handle becoming warm, and within a minute, it’s too hot to touch without an oven mitt. This is a clear demonstration of heat conduction in action.
What is Heat Conduction?

Heat conduction is the process by which thermal energy is transferred between particles of a substance or from one substance to another due to a temperature gradient. In simpler terms, it's the way heat moves from a hotter area to a cooler one until both reach thermal equilibrium. This process occurs in solids, liquids, and gases but is most effective in solids due to their tightly packed molecular structure.
In our stove example, the electric heating element, when turned on, generates thermal energy. This energy is then transferred to the pan through direct contact, as the pan is in physical proximity to the heat source. The pan’s material, typically metal, has a high thermal conductivity, meaning it allows heat to pass through it easily. As a result, the heat energy quickly spreads throughout the pan, from the base to the handle, warming up the entire surface.
Key Takeaway
Conduction is a fundamental heat transfer mechanism that relies on direct contact between substances. It's particularly efficient in materials with high thermal conductivity, like metals, and plays a crucial role in various everyday applications, from cooking to home heating systems.
Now, let’s explore some other real-world scenarios where conduction is at play:
-
Home Heating
In colder months, central heating systems use conduction to warm up our homes. Radiators, for instance, are heated with hot water or steam, which then conducts its thermal energy to the surrounding air. This warm air circulates, heating up the entire room.
-
Cooking Techniques
Apart from stoves, conduction is vital in various cooking methods. For example, when frying an egg, the heat from the pan is conducted to the egg, cooking it evenly. Similarly, when baking a cake, the heat from the oven is conducted through the cake batter, ensuring a delicious, fluffy texture.
-
Thermal Insulation
Understanding conduction also helps us grasp the importance of insulation. Insulating materials, like fiberglass or foam, have low thermal conductivity. They are designed to slow down heat transfer, keeping warm air inside a building during winter and cool air inside during summer.
In conclusion, heat conduction is an everyday phenomenon that impacts our lives in numerous ways. By recognizing its role in simple activities like cooking or maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures, we can appreciate the underlying physics that govern our world.
What are some materials with high thermal conductivity?
+Metals like copper, aluminum, and silver have extremely high thermal conductivity. This is why they’re often used in cooking utensils and electrical wiring. Other materials with good thermal conductivity include graphite and diamond.
How does conduction differ from convection and radiation in heat transfer?
+Conduction involves heat transfer through direct contact between substances, while convection relies on the movement of fluids (liquids or gases) to transfer heat. Radiation, on the other hand, is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves, without the need for a medium.
Can you provide examples of materials with low thermal conductivity?
+Materials like wood, plastic, and air have relatively low thermal conductivity. This is why they’re commonly used as insulators to prevent heat transfer.
What factors influence the rate of heat conduction?
+The rate of heat conduction is influenced by several factors, including the temperature gradient (difference in temperature), the cross-sectional area of the material, and the distance over which the heat is being conducted. Additionally, the material’s thermal conductivity plays a crucial role.