10 Factors Influencing Ambient Temperature

Ambient Temperature Dynamics: Understanding the Complex Web of Influences
The ambient temperature, a seemingly simple concept, is a result of numerous intricate factors working together. These elements create a complex network that determines the heat or coolness of our surroundings. Let’s delve into the top 10 factors that significantly impact ambient temperature, unraveling the science behind our daily experiences.
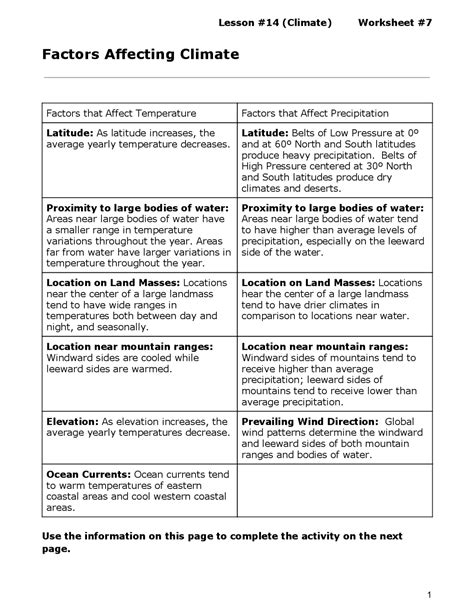
- Solar Radiation: The sun’s rays are the primary driver of temperature changes on Earth. The intensity of solar radiation, influenced by factors like season, latitude, and time of day, directly affects the heat absorbed by the Earth’s surface. During summer, with longer daylight hours, more solar energy reaches the surface, leading to higher temperatures.
Solar radiation is the ultimate source of energy that drives Earth's climate systems. Its variability across different regions and times of the year plays a pivotal role in shaping ambient temperature patterns.
- Dr. Elena Martínez, Climate Scientist
Atmospheric Composition: The gases present in our atmosphere, particularly greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane, trap heat and contribute to the greenhouse effect. This effect regulates Earth’s temperature, preventing rapid cooling at night and maintaining a habitable climate. However, human activities have altered atmospheric composition, leading to concerns about global warming.
Altitude and Topography: Altitude significantly impacts temperature due to changes in air pressure and density. As elevation increases, the air becomes thinner, resulting in lower temperatures. Additionally, mountainous regions experience complex temperature variations due to the influence of topography on wind patterns and solar radiation distribution.
Ocean Currents: The vast oceans act as massive heat reservoirs, influencing global climate patterns. Warm ocean currents, such as the Gulf Stream, carry heat from the tropics towards higher latitudes, moderating temperatures and creating unique microclimates along their paths. In contrast, cold currents like the California Current can lead to cooler coastal temperatures.
Wind Patterns: Wind plays a crucial role in redistributing heat across the globe. Prevailing winds, like the trade winds and westerlies, transport warm or cool air masses, affecting regional climates. Local wind patterns, such as sea breezes and mountain winds, also impact ambient temperatures by influencing the movement of air near the surface.
Land Use and Urbanization: Human activities and land use significantly affect local temperatures. Urban areas, with their abundance of concrete and asphalt, create heat islands due to the absorption and retention of solar radiation. This phenomenon leads to higher temperatures in cities compared to surrounding rural areas.
Vegetation Cover: The presence of vegetation, particularly forests, influences ambient temperature through transpiration and shading. Trees release water vapor during transpiration, cooling the surrounding air. Additionally, forests provide shade, reducing the impact of direct sunlight and moderating temperatures.
Soil Moisture: Soil moisture levels impact the transfer of heat between the Earth’s surface and the atmosphere. Wet soils absorb more heat during the day, releasing it at night, thus regulating temperature fluctuations. In contrast, dry soils can lead to increased daytime temperatures and cooler nights.
Cloud Cover: Clouds act as both insulators and reflectors of solar radiation. Thick cloud cover can trap heat, leading to warmer nights, while also blocking sunlight during the day, resulting in cooler temperatures. The type and altitude of clouds play a significant role in determining their impact on ambient temperature.
Human Activities: Beyond land use, direct human activities like industrial processes, transportation, and energy production contribute to local temperature changes. The release of heat and pollutants into the atmosphere can alter microclimates, affecting ambient temperatures and air quality.
Understanding the intricate web of factors influencing ambient temperature is crucial for climate science, urban planning, and environmental management. By recognizing these influences, we can make informed decisions to mitigate the impacts of climate change and create sustainable environments.
Further Exploration:
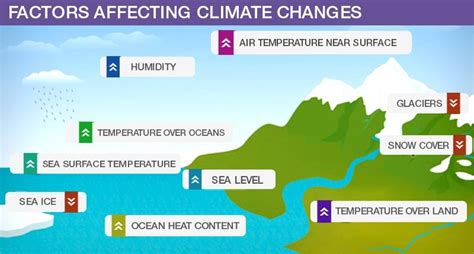
- How do El Niño and La Niña events impact global temperature patterns?
- What role does deforestation play in altering local temperature dynamics?
- Can we harness the power of ocean currents for renewable energy while maintaining ecological balance?
- How do different cloud types affect temperature and precipitation patterns?
- What strategies can cities employ to mitigate the urban heat island effect?
What is the primary driver of seasonal temperature variations on Earth?
+Seasonal temperature variations are primarily driven by the tilt of Earth's axis, causing different latitudes to receive varying amounts of solar radiation throughout the year. This tilt results in distinct seasons, with summer bringing more intense solar radiation and higher temperatures, while winter experiences reduced radiation and cooler temperatures.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How do greenhouse gases impact ambient temperature?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, act as heat-trapping agents in the atmosphere. They absorb and re-emit long-wave radiation, preventing heat from escaping into space. This process, known as the greenhouse effect, regulates Earth's temperature, keeping it habitable. However, excess greenhouse gases lead to global warming, causing a rise in average temperatures.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can urban heat islands be mitigated through green infrastructure?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes, urban heat islands can be effectively mitigated through the implementation of green infrastructure. Strategies such as increasing green spaces, planting trees, and incorporating green roofs and walls help to reduce heat absorption, provide shade, and enhance evaporation, leading to cooler urban temperatures and improved air quality.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What is the role of ocean currents in moderating coastal temperatures?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Ocean currents play a vital role in moderating coastal temperatures by transporting heat from the equator towards higher latitudes. Warm ocean currents, like the Gulf Stream, bring warmer waters to coastal regions, preventing extreme cold temperatures. Conversely, cold currents, such as the California Current, can lead to cooler coastal temperatures.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>


