The 200°C to Fahrenheit Guide
Understanding Temperature Scales
When it comes to measuring temperature, different parts of the world use various scales, each with its unique characteristics and historical origins. One such scale is the Fahrenheit scale, widely recognized and utilized in the United States and a few other countries. Conversely, the Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is the standard metric system unit for temperature measurement and is extensively used globally.
In this guide, we will focus on the Fahrenheit scale and provide an in-depth understanding of how to convert a specific temperature, 200°C, to its equivalent on the Fahrenheit scale. We will delve into the mathematical formula, offer practical examples, and explore the historical context that led to the development of these temperature scales. Additionally, we will discuss the implications of using different temperature scales and how they impact various scientific, industrial, and everyday applications.
The Fahrenheit Scale: A Historical Perspective
The Fahrenheit scale was devised by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, a German-Dutch physicist and engineer, in the early 18th century. Fahrenheit based his scale on three reference points: the temperature of a water and ice mixture, which he designated as 32°F, the temperature of the human body, approximately 96°F, and the boiling point of water, which he set at 212°F. This scale has since undergone minor adjustments, with the human body temperature reference point being revised to the more commonly used 98.6°F.
The Fahrenheit scale’s initial development was influenced by the need for a temperature scale that could accurately measure both freezing and boiling points of water, as well as the temperature of the human body. Fahrenheit’s scale gained popularity and was widely adopted, particularly in the United States, where it remains the predominant temperature scale used today.
Converting 200°C to Fahrenheit: The Formula and Example
To convert a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit, we use the following formula:
Temperature in Fahrenheit = (Temperature in Celsius × 9/5) + 32
Using this formula, let’s convert 200°C to Fahrenheit:
Step-by-Step Conversion Process
-
Multiply 200°C by 9/5: 200 × 9/5 = 360.
-
Add 32 to the result: 360 + 32 = 392.
Therefore, 200°C is equal to 392°F.
Implications and Practical Applications
The conversion of temperature scales is crucial in various fields, from scientific research to everyday life. Here are some practical applications and implications of using different temperature scales:
Scientific Research: In scientific experiments and studies, temperature is a critical parameter. Researchers often need to convert temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit, especially when collaborating with colleagues or publishing in international journals that use different scales.
Meteorology and Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists and weather forecasters work with temperature data in both Celsius and Fahrenheit. Accurate conversions are essential for providing weather reports and predictions that are easily understandable to the public, especially in regions where both scales are used.
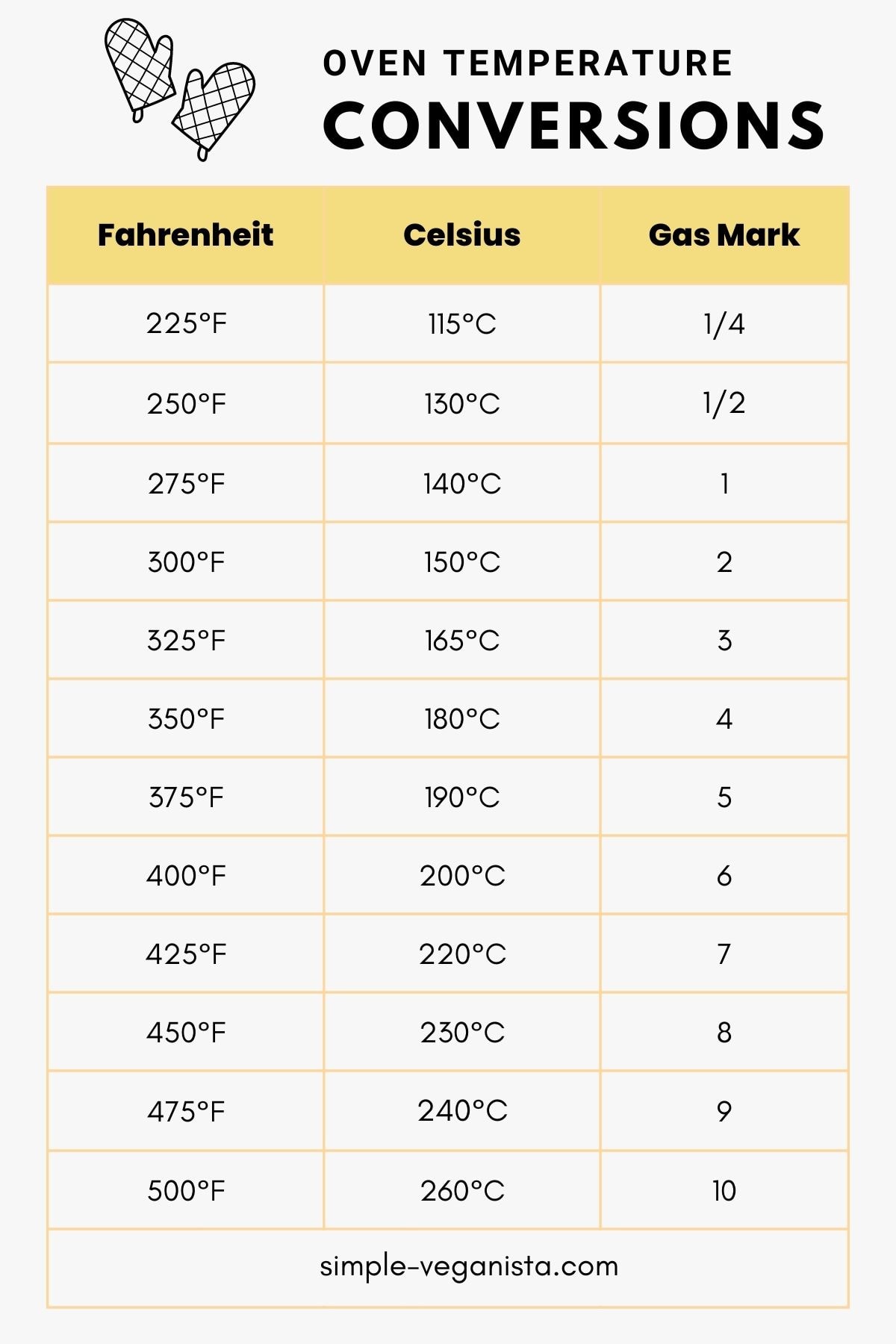
Cooking and Baking: Culinary professionals and home cooks frequently encounter recipes that use different temperature scales. Converting temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit is vital to ensure precise cooking and baking results, as oven settings are often calibrated differently in various countries.
International Travel and Cultural Exchange: When traveling to different countries, understanding temperature scales becomes essential. Knowing how to convert temperatures allows individuals to interpret weather forecasts, understand cooking instructions, and communicate effectively about temperature-related matters.
Industrial Processes: Many industries, such as manufacturing, chemical processing, and energy production, rely on precise temperature measurements. Converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit is necessary for ensuring process control, quality assurance, and safety protocols.
Historical Context: The Development of Temperature Scales
The evolution of temperature scales is a fascinating journey that reflects the advancements in scientific understanding and the need for standardized measurement systems. Here’s a brief overview:
Ancient Times: Early civilizations, such as the Greeks and Romans, used various methods to measure temperature, including the use of water and air thermoscopes. However, these methods lacked precision and were more qualitative than quantitative.
17th Century: The invention of the mercury thermometer by Evangelista Torricelli in the 17th century marked a significant advancement in temperature measurement. This device allowed for more accurate and reproducible temperature readings.
Celsius Scale: Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, introduced the Celsius scale in the mid-18th century. Initially, the scale was inverted, with 0° representing the boiling point of water and 100° representing the freezing point. Later, the scale was reversed, leading to the modern Celsius scale we use today.
Fahrenheit Scale: As mentioned earlier, Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit developed his scale based on the freezing and boiling points of water and the temperature of the human body. The Fahrenheit scale gained prominence and became widely adopted, particularly in English-speaking countries.
Kelvin and Absolute Zero: In the 19th century, William Thomson, later known as Lord Kelvin, introduced the Kelvin scale, which is based on absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature. The Kelvin scale is widely used in scientific and engineering contexts, as it provides a more intuitive and practical representation of temperature.
Myth vs. Reality: Common Misconceptions about Temperature Scales
When it comes to temperature scales, several misconceptions and myths often circulate. Let’s address some of these:
Myth: Celsius and Fahrenheit scales are incompatible and cannot be converted accurately.
Reality
Celsius and Fahrenheit scales can be easily converted using a simple mathematical formula. The conversion is precise and allows for accurate temperature representation across both scales.
Myth: The Fahrenheit scale is outdated and should be replaced by the Celsius scale.
Reality
While the Celsius scale is the standard metric system unit for temperature, the Fahrenheit scale continues to be widely used, particularly in the United States. Both scales have their advantages and are suitable for different contexts and audiences.
Myth: The Kelvin scale is the most accurate temperature scale.
Reality
The Kelvin scale is indeed an important scale used in scientific and engineering contexts, as it represents temperature in relation to absolute zero. However, it is not necessarily more accurate than the Celsius or Fahrenheit scales for everyday temperature measurements.
Practical Guide: Converting Temperatures for Everyday Use
For those who frequently need to convert temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit, here’s a simple guide to make the process easier:
Mental Estimation: For quick estimations, remember that a difference of approximately 30°F is roughly equivalent to a difference of 16°C. This rule of thumb can provide a rough conversion for everyday situations.
Online Converters: Numerous online temperature conversion tools are available. These converters allow you to input a temperature in Celsius and instantly get the equivalent Fahrenheit value. They are convenient for quick conversions and can be bookmarked for easy access.
Mobile Apps: Various mobile apps are designed specifically for temperature conversion. These apps often provide additional features, such as weather forecasts, unit conversions for other measurements, and customizable temperature units.
Calculator: If you prefer a more traditional approach, a scientific calculator with temperature conversion functions can be a useful tool. These calculators often have built-in formulas for converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit.
Conclusion: Embracing the Diversity of Temperature Scales
In our globalized world, where collaboration and communication transcend borders, understanding and respecting different temperature scales is essential. Whether it’s scientific research, culinary adventures, or simply staying informed about the weather, the ability to convert temperatures accurately is a valuable skill.
By exploring the historical context, practical applications, and conversion formulas, we can appreciate the rich diversity of temperature scales and their significance in various fields. Remember, whether it’s 200°C or 392°F, the temperature remains the same, and the choice of scale is a matter of context and preference.
Temperature scales may differ, but the essence of measurement remains universal. Embrace the diversity, and let’s continue exploring the fascinating world of temperature and its impact on our lives.