5 Essential Concurrent Powers Tips
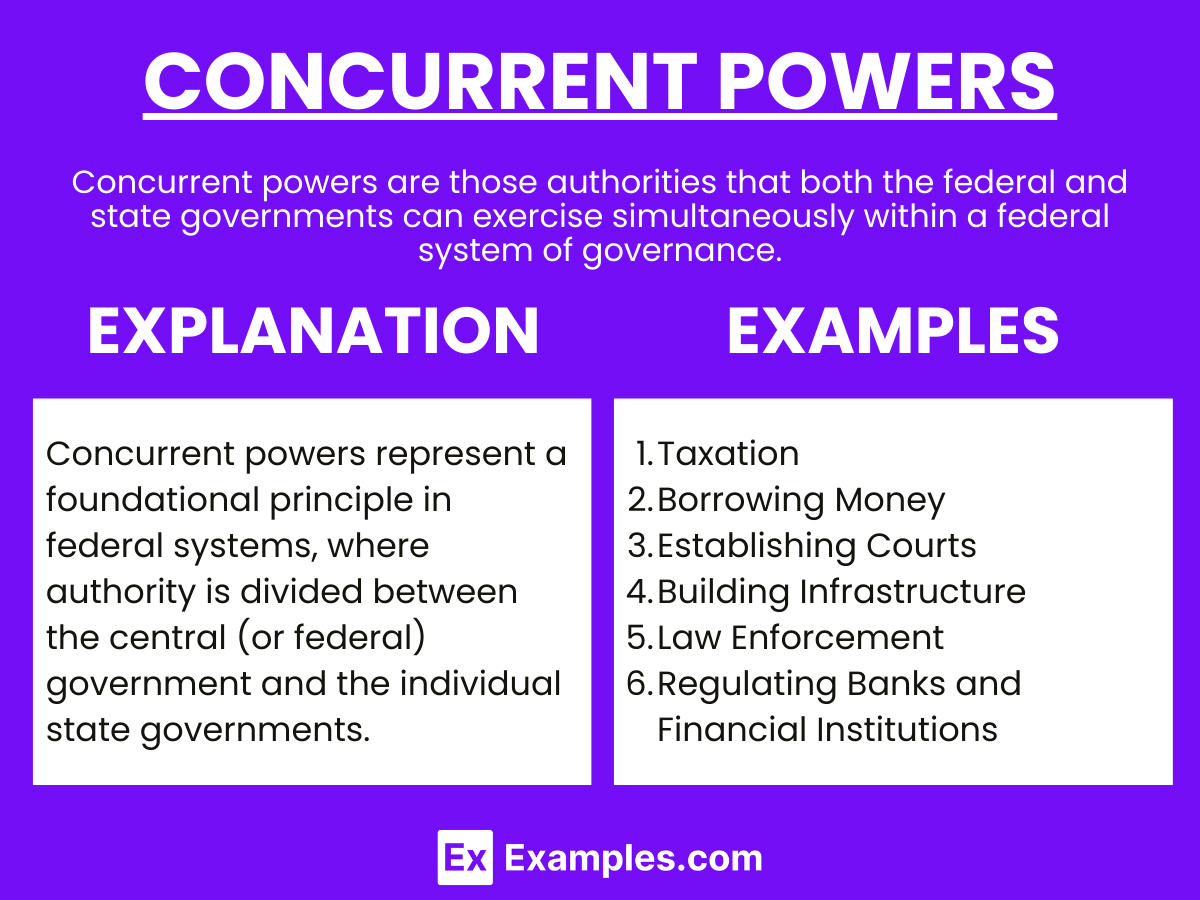
When it comes to understanding the intricate web of governance, one crucial aspect that often goes unnoticed is the concept of concurrent powers. These powers, shared by different levels of government, play a pivotal role in shaping policies and influencing our daily lives. Here are five essential tips to grasp the nuances of concurrent powers and their implications.
1. Understanding the Shared Sovereignty

Concurrent powers are a testament to the shared sovereignty within a federal system. Unlike unitary governments where power is centralized, federalism divides authority between national and regional governments. This division creates a delicate balance, ensuring that no single entity holds absolute power.
Consider the analogy of a jigsaw puzzle. Each piece, representing a level of government, fits together to form a complete picture of governance. Concurrent powers are like the interlocking edges of these puzzle pieces, ensuring a harmonious whole while preserving individual identities.
"In a federal system, concurrent powers are the threads that weave the fabric of governance, creating a tapestry of shared responsibility and cooperation."
2. Identifying the Key Areas of Concurrent Powers

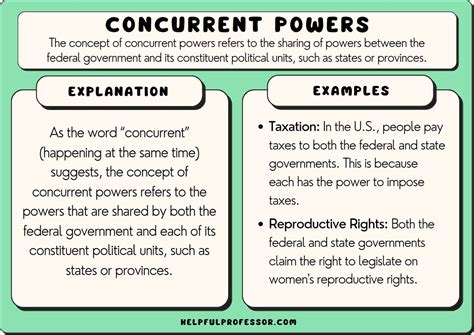
While concurrent powers can vary across jurisdictions, certain areas consistently fall under shared authority. These include taxation, commerce, environmental regulation, and social welfare programs. Understanding these key domains is essential to navigating the complexities of policy-making.
| Area | Impact |
|---|---|
| Taxation | Influences economic growth, investment, and public services. |
| Commerce | Regulates trade, promotes competition, and ensures market stability. |
| Environmental Regulation | Protects natural resources, addresses climate change, and ensures sustainable development. |
| Social Welfare | Provides safety nets, addresses inequality, and promotes social cohesion. |
By recognizing these areas, citizens and policymakers can better understand the interplay of powers and advocate for balanced decision-making.
3. Navigating the Power Dynamics
Concurrent powers introduce a complex web of relationships and power dynamics. National and regional governments often collaborate, negotiate, and compete for influence. This dynamic nature requires a delicate dance of cooperation and assertiveness.
Imagine a symphony orchestra, where each musician contributes to the overall harmony. Similarly, in the realm of concurrent powers, each level of government must strike the right balance between cooperation and asserting their unique role.
4. Addressing Potential Conflicts
Pros of Concurrent Powers
- Encourages innovation and diverse approaches to governance.
- Promotes a checks and balances system, preventing abuse of power.
- Allows for tailored solutions to regional needs and priorities.
Cons of Concurrent Powers
- Can lead to policy fragmentation and inconsistent implementation.
- May result in conflicts and disputes over jurisdiction and authority.
- Requires complex coordination and negotiation processes.
To mitigate conflicts, clear constitutional provisions and well-defined boundaries are crucial. Additionally, mechanisms for dispute resolution, such as judicial review or intergovernmental forums, can help navigate disagreements.
5. The Impact on Citizens and Businesses

Concurrent powers have a direct impact on the lives of citizens and the operations of businesses. They shape the regulatory environment, influence economic opportunities, and determine access to public services.
For citizens, concurrent powers can mean varied experiences across regions, from healthcare access to educational opportunities. Businesses, on the other hand, must navigate a complex landscape of regulations and policies, adapting their strategies to thrive in a diverse governance environment.
What is an example of a concurrent power in the United States?
+An example of a concurrent power in the U.S. is the regulation of interstate commerce. Both the federal government and individual states have the authority to regulate commerce within their respective jurisdictions, ensuring a balanced approach to trade and economic activity.
How do concurrent powers affect policy implementation?
+Concurrent powers can lead to varying interpretations and implementations of policies across different regions. This can result in inconsistencies and challenges for policymakers and citizens alike.
Are there any limitations to concurrent powers?
+Yes, concurrent powers are typically subject to constitutional limits and provisions. These limits ensure that power is not abused and that a balance is maintained between different levels of government.
How do concurrent powers impact regional disparities?
+Concurrent powers can both exacerbate and mitigate regional disparities. On one hand, they allow regions to tailor policies to their unique needs, but they can also lead to uneven access to resources and services if not carefully managed.
What is the role of the judiciary in concurrent powers disputes?
+The judiciary plays a crucial role in resolving disputes arising from concurrent powers. Courts interpret constitutional provisions and ensure that power is exercised within the boundaries set by the law, providing a crucial check on governmental authority.
In conclusion, understanding concurrent powers is essential for navigating the complex landscape of governance. By recognizing the shared sovereignty, identifying key areas, and navigating power dynamics, we can better appreciate the delicate balance that shapes our policies and lives.



