5 Expert Tips: Excel VLOOKUP
Excel VLOOKUP is an incredibly powerful function that has become an indispensable tool for data analysts, researchers, and professionals across various industries. With its ability to swiftly retrieve specific data from vast tables, VLOOKUP streamlines complex data retrieval processes, enhances productivity, and ensures accuracy in data management. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of Excel VLOOKUP, exploring its features, applications, and best practices through real-world examples and expert insights.
The Power of Excel VLOOKUP: Unlocking Data’s Potential
VLOOKUP, an acronym for Vertical Lookup, is an Excel function that searches for a specific value in the leftmost column of a table array and returns a value from the same row in a specified column. This powerful tool revolutionizes data retrieval, enabling users to extract information from large datasets efficiently and accurately. Imagine a scenario where you have a spreadsheet with customer details, and you need to find a specific customer’s email address based on their ID. VLOOKUP can retrieve this information effortlessly, saving you time and reducing the risk of errors.
Understanding VLOOKUP’s Syntax and Parameters
To utilize VLOOKUP effectively, understanding its syntax and parameters is crucial. The syntax for VLOOKUP is as follows: =VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup]). Let’s break down these parameters:
- lookup_value: This is the value you want to find in the leftmost column of the table array.
- table_array: The range of cells that VLOOKUP will search through. It should be a contiguous range with the first column containing the lookup values.
- col_index_num: The column number within the table array from which the matching value should be returned.
- [range_lookup]: An optional parameter that can be either TRUE or FALSE. TRUE enables approximate matching, while FALSE ensures an exact match.
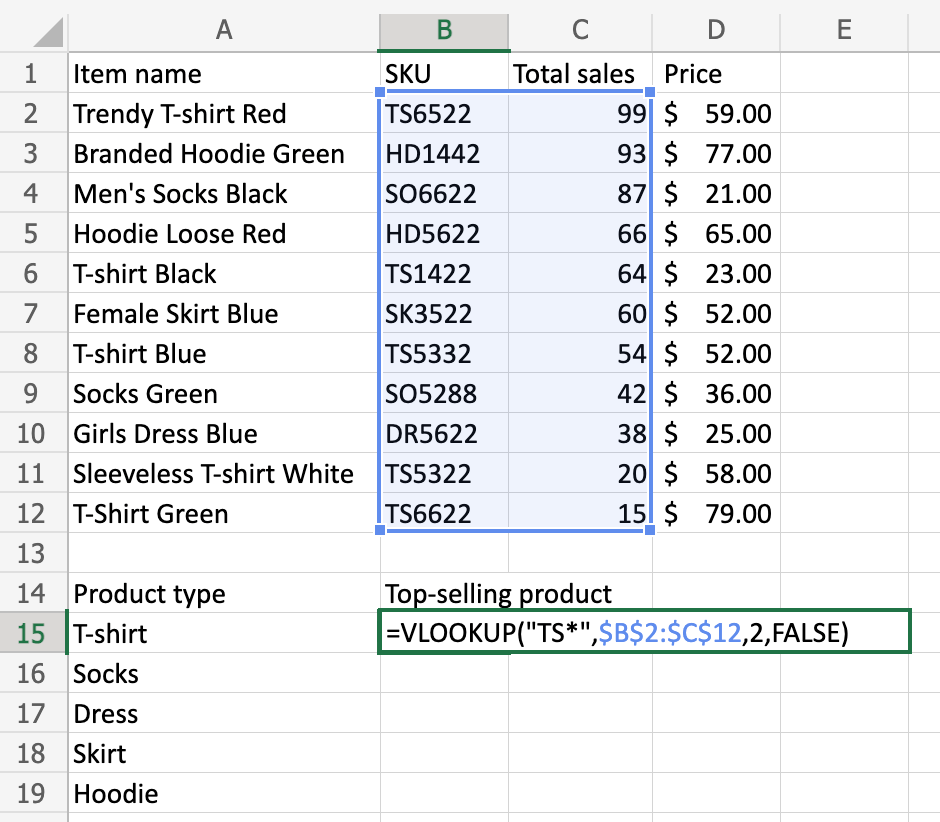
For example, if you want to find the price of a product with the ID "PROD001" in a table where the ID is in column A and the price is in column B, your VLOOKUP formula would be: =VLOOKUP("PROD001", A:B, 2, FALSE). Here, "PROD001" is the lookup value, A:B is the table array, 2 indicates the second column (price), and FALSE ensures an exact match.
Real-World Application: Excel VLOOKUP in Action
Consider a scenario where a sales team manages a large client database with thousands of entries. Each client record contains information such as name, contact details, and sales history. When a salesperson wants to find a client’s email address based on their name, VLOOKUP comes to the rescue. By creating a table array with client names in the first column and email addresses in the second, the salesperson can use VLOOKUP to quickly retrieve the email address, facilitating efficient communication and sales outreach.
| Client Name | Email Address |
|---|---|
| John Smith | john@example.com |
| Jane Doe | jane@example.com |
| Robert Johnson | robert@example.com |
In this table, a VLOOKUP formula searching for "Jane Doe" in the "Client Name" column and returning the value from the "Email Address" column would yield "jane@example.com".
Maximizing Efficiency: Best Practices for Excel VLOOKUP

To harness the full potential of VLOOKUP, it’s essential to follow some best practices. Here are some expert tips to ensure you’re using VLOOKUP effectively and efficiently:
1. Organize Your Data Correctly
VLOOKUP relies on a structured table array with the lookup values in the leftmost column. Ensure that your data is organized consistently and logically. Avoid blank cells or irregular formatting that could confuse the function. For instance, if your lookup values are customer IDs, make sure they are unique and consistently formatted across your dataset.
2. Utilize Exact Match for Accuracy
By default, VLOOKUP performs an approximate match, which means it may return a value from a similar but not exact match. This can lead to inaccurate results. To ensure precision, always set the range_lookup parameter to FALSE for an exact match. This is especially crucial when dealing with sensitive data or financial records.
3. Handle Errors Gracefully
VLOOKUP can return errors if it cannot find a match or if the table array is incorrectly formatted. To handle these errors gracefully, you can use the IFERROR function along with VLOOKUP. This ensures that your formula returns a custom message or value instead of an error, making your spreadsheets more user-friendly and error-free.
4. Combine VLOOKUP with Other Functions
VLOOKUP is versatile and can be combined with other Excel functions to create powerful data retrieval tools. For instance, you can use VLOOKUP with the INDEX and MATCH functions to retrieve data from non-adjacent columns or rows. This combination is particularly useful when dealing with complex datasets or when you need to retrieve data based on multiple criteria.
5. Consider Alternatives for Large Datasets
While VLOOKUP is efficient for small to medium-sized datasets, it may slow down when dealing with extensive tables. In such cases, consider using alternative functions like INDEX and MATCH, which offer similar functionality but are faster and more flexible. Additionally, Excel’s Power Query feature can handle large datasets efficiently, providing advanced data retrieval capabilities.
Advanced VLOOKUP Techniques: Taking Your Skills to the Next Level
Once you’ve mastered the basics of VLOOKUP, it’s time to explore more advanced techniques. Here are some expert tips to elevate your VLOOKUP skills:
Nested VLOOKUP: Retrieving Data from Multiple Tables
Nested VLOOKUP allows you to retrieve data from multiple tables or datasets. By combining multiple VLOOKUP functions, you can create a powerful data retrieval system. For example, imagine you have two tables: one with customer information and another with product details. You can use nested VLOOKUP to find a customer’s product preferences based on their ID, even if the product details are stored in a separate table.
Using VLOOKUP with Dynamic Ranges
Dynamic ranges, such as those created with Excel’s OFFSET function, can enhance the flexibility of VLOOKUP. By using dynamic ranges, you can ensure that VLOOKUP always references the correct table array, even if the data is added, removed, or rearranged. This technique is especially useful for maintaining accurate data retrieval in constantly changing datasets.
Error Handling with VLOOKUP and IFERROR
As mentioned earlier, VLOOKUP can return errors if a match is not found. To handle these errors gracefully, use the IFERROR function. For example, you can set up your VLOOKUP formula to return a custom message like “Data Not Found” if a match is not found, ensuring your spreadsheets are user-friendly and error-free.
Combining VLOOKUP with Other Lookup Functions
Excel offers a range of lookup functions, each with its own strengths. By combining VLOOKUP with functions like HLOOKUP (Horizontal Lookup), INDEX, and MATCH, you can create powerful data retrieval systems. For instance, you can use HLOOKUP to retrieve data from a table with headers across the top row, making it ideal for financial analysis or report generation.
Excel VLOOKUP: Future Implications and Innovations
As Excel continues to evolve, so do its functions and capabilities. While VLOOKUP remains a fundamental tool for data retrieval, Excel’s newer functions and features offer enhanced flexibility and performance. Here’s a glimpse into the future of data retrieval in Excel:
Excel’s XLOOKUP Function: A Modern Alternative
Excel’s XLOOKUP function, introduced in Excel 365, offers a more versatile and user-friendly alternative to VLOOKUP. XLOOKUP can perform both vertical and horizontal lookups, making it a powerful tool for data retrieval. It also offers additional features like lookup values on either side of the table and better error handling. As Excel continues to update its features, XLOOKUP is likely to become the go-to function for data retrieval.
Power Query: Revolutionizing Data Retrieval
Excel’s Power Query feature, available in Excel 2016 and later versions, provides a powerful platform for data retrieval and transformation. With Power Query, you can connect to various data sources, perform complex data transformations, and create dynamic data models. This feature is particularly useful for large datasets and complex data retrieval tasks, offering a more efficient and flexible alternative to traditional Excel functions.
Data Analytics and Automation: The Future of Excel
Excel’s future lies in its ability to support data analytics and automation. With features like Power Pivot, Power BI, and macros, Excel is becoming a powerful tool for data analysis and visualization. As data becomes more integral to decision-making, Excel’s capabilities in this domain will continue to expand, offering users advanced tools for data retrieval, analysis, and presentation.
Cloud Integration and Collaboration: Excel’s New Frontier
With the increasing importance of cloud computing and collaboration, Excel is evolving to support these trends. Excel’s integration with Microsoft’s cloud-based services, like OneDrive and SharePoint, enables seamless collaboration and data sharing. This integration opens up new possibilities for data retrieval and analysis, especially in team-based projects or when working with remote data sources.
Can VLOOKUP be used for horizontal lookups?
+No, VLOOKUP is specifically designed for vertical lookups. For horizontal lookups, you can use the HLOOKUP function, which searches for a value in the top row of a table and returns a value from the same column in a specified row.
What happens if VLOOKUP cannot find a match?
+If VLOOKUP cannot find a match, it will return an error. To handle this gracefully, you can use the IFERROR function to specify a custom message or value to be returned instead of the error.
Is VLOOKUP faster than other lookup functions?
+VLOOKUP is generally faster than functions like INDEX and MATCH when dealing with small to medium-sized datasets. However, for large datasets, INDEX and MATCH are often more efficient and flexible.