How to Connect HDD to Router

In today's digital world, storage and data management have become increasingly important. Many individuals and businesses rely on hard disk drives (HDDs) for their data storage needs, but what happens when you want to access that data remotely or share it across a network? Connecting an HDD to your router can be a convenient solution, allowing seamless access to your files from anywhere within the network's reach. This guide will walk you through the process of setting up an HDD with your router, covering everything from the required components to the actual setup and configuration.
Understanding the Components and Requirements

Before diving into the setup process, it’s crucial to understand the components and requirements for connecting an HDD to your router. Here’s a breakdown of what you’ll need:
Network Attached Storage (NAS)
A NAS device is essentially a specialized storage system designed to connect to a network. It acts as a central storage hub, allowing multiple devices to access the stored data simultaneously. NAS devices typically consist of one or more HDDs enclosed in a network-ready enclosure. They offer various features, including RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations for data redundancy and improved performance.
When choosing a NAS, consider factors such as storage capacity, number of drive bays, compatibility with your existing network, and additional features like media streaming or backup capabilities.
HDDs for NAS
While you can use standard HDDs for NAS, it’s recommended to opt for NAS-specific HDDs. These drives are designed to handle the rigorous demands of continuous operation in a NAS environment. They often offer features like enhanced reliability, improved data transfer rates, and longer lifespans. NAS HDDs are available in various capacities, typically ranging from 2TB to 16TB, and can be purchased individually or as part of a NAS kit.
Router and Network Infrastructure
Your router plays a crucial role in facilitating the connection between your NAS and other devices on your network. Ensure that your router has sufficient ports and supports the necessary protocols for NAS connectivity. Additionally, consider the overall network infrastructure, including the number of devices connected and the desired data transfer speeds.
Other Considerations
Apart from the hardware components, there are a few other considerations to keep in mind. Firstly, ensure that your NAS and router are compatible with each other in terms of connection protocols and data transfer rates. Secondly, consider the physical setup; ensure that your NAS is easily accessible and has adequate ventilation to prevent overheating. Lastly, remember to have the necessary cables and adapters to connect your NAS to the router.
Step-by-Step Setup Process
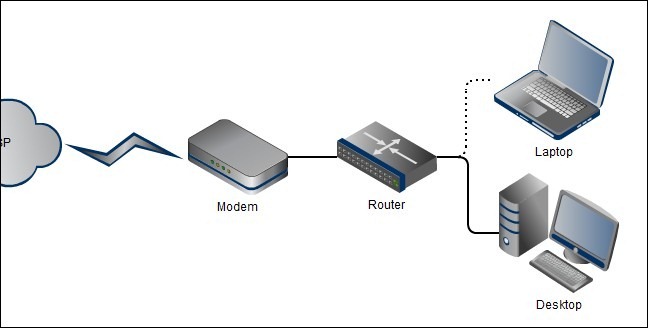
Now that we’ve covered the components and requirements, let’s dive into the step-by-step process of connecting your HDD to your router using a NAS setup.
Step 1: Prepare the NAS Device
Start by assembling your NAS device according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If you’re using a pre-built NAS kit, this step may be as simple as plugging in the HDDs and connecting the power supply. However, if you’re building your own NAS, you’ll need to install the HDDs into the NAS enclosure, connect the necessary cables, and ensure proper cooling.
Step 2: Connect the NAS to the Router
Use an Ethernet cable to connect your NAS to your router. Typically, you’ll connect the NAS to one of the LAN ports on your router. Ensure that the connection is secure and that the NAS is powered on.
Step 3: Configure the NAS
Access the NAS’s configuration interface through a web browser or dedicated software provided by the manufacturer. Here, you’ll need to set up the NAS’s basic settings, including the network configuration, user accounts, and file sharing permissions. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for a step-by-step guide on configuring your specific NAS model.
Step 4: Configure the Router
Access your router’s configuration interface, usually through a web browser. Navigate to the port forwarding or NAT (Network Address Translation) settings. Here, you’ll need to forward specific ports associated with the NAS to the IP address of the NAS device. This step ensures that incoming network traffic reaches the NAS correctly.
Step 5: Test the Connection
Once the NAS and router configurations are complete, test the connection. Access the NAS through a network-connected device, such as a computer or smartphone. Ensure that you can browse the files on the NAS and that data transfer speeds meet your expectations. If any issues arise, check the NAS and router configurations and troubleshoot as needed.
Advanced NAS Features and Considerations
While the basic setup process covered above will get your NAS up and running, there are several advanced features and considerations to explore to maximize the potential of your NAS.
RAID Configurations
RAID, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is a technology that allows you to combine multiple HDDs into a single logical unit, offering benefits such as increased storage capacity, improved performance, and data redundancy. There are various RAID levels, each with its own advantages and trade-offs. For example, RAID 0 provides enhanced performance by striping data across multiple drives, while RAID 1 mirrors data for redundancy.
Media Streaming and Transcoding
Many NAS devices offer media streaming capabilities, allowing you to stream music, videos, and photos to various devices on your network. Some NAS models even support transcoding, which enables the device to convert media files on the fly to formats compatible with your playback devices, ensuring seamless streaming experiences.
Backup and Disaster Recovery
NAS devices can play a crucial role in backup and disaster recovery strategies. Many NAS models offer backup software or support popular backup solutions, allowing you to automatically back up data from your computers or servers to the NAS. Additionally, some NAS devices provide remote backup and replication features, ensuring that your data is safe even in the event of a disaster.
Performance Optimization
To ensure optimal performance from your NAS, consider factors such as network congestion, data transfer speeds, and HDD performance. Monitor your network traffic and adjust your NAS settings as needed to optimize performance. Additionally, consider using SSDs (Solid-State Drives) as cache drives in your NAS to further enhance data transfer speeds.
Security and Access Control
When connecting an HDD to your router via a NAS, security and access control become crucial considerations. Here are some key aspects to keep in mind:
- User Accounts and Permissions: Set up user accounts on your NAS and assign appropriate permissions to control access to different folders and files. This ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive data.
- Encryption and Security Protocols: Enable encryption protocols such as SSL/TLS to secure data transmission between devices and the NAS. Additionally, consider using secure authentication methods like 2-factor authentication to enhance security.
- Firewall and Port Forwarding: Configure your router's firewall to allow incoming traffic to the NAS. Ensure that only necessary ports are forwarded to minimize potential security risks.
- Regular Updates and Patching: Keep your NAS firmware and software up to date to address any security vulnerabilities. Regularly apply patches and updates provided by the manufacturer to maintain a secure environment.
Future Implications and Recommendations

Connecting an HDD to your router via a NAS opens up a world of possibilities for data management and accessibility. As you explore the capabilities of your NAS, consider the following future implications and recommendations to enhance your setup:
Scalability and Expansion
As your data storage needs grow, consider the scalability of your NAS. Many NAS devices support expansion through additional drive bays or expansion units. Plan for future expansion by choosing a NAS with ample drive bays and the ability to support larger storage capacities.
Data Redundancy and Disaster Recovery
Implementing data redundancy measures, such as RAID configurations, can help protect your data in the event of HDD failures. Additionally, consider off-site backups or cloud storage solutions to ensure that your data is recoverable even in the event of a disaster at your primary location.
Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
Regularly monitor the performance and health of your NAS and HDDs. Implement a maintenance schedule to check for errors, bad sectors, and other potential issues. Keep an eye on HDD temperatures and ensure proper cooling to prevent overheating, which can lead to data loss or HDD failures.
Network and Data Security
As your NAS becomes a central hub for your data, network and data security become increasingly important. Stay informed about the latest security threats and best practices. Implement strong passwords, enable encryption, and regularly update your NAS firmware and software to minimize potential vulnerabilities.
Backup Strategies
Develop robust backup strategies to protect your data. Consider implementing a 3-2-1 backup rule: maintain three copies of your data, store it on two different types of media, and keep one copy off-site or in the cloud. This ensures that even if one copy is lost or corrupted, you still have multiple recovery options.
Conclusion
Connecting an HDD to your router via a NAS provides a powerful and flexible solution for data storage and management. By following the step-by-step setup process and exploring the advanced features and considerations outlined in this guide, you can create a robust and secure network storage environment. Remember to prioritize security, scalability, and data redundancy to ensure the longevity and accessibility of your data.
Can I use any HDD with my router for network storage?
+While you can technically use any HDD with a router for network storage, it’s highly recommended to use NAS-specific HDDs. These drives are designed to handle the continuous operation and rigorous demands of a NAS environment, offering enhanced reliability and improved performance.
How do I choose the right NAS for my needs?
+When selecting a NAS, consider factors such as storage capacity, number of drive bays, compatibility with your existing network, and additional features like media streaming or backup capabilities. Research different NAS models and choose one that aligns with your specific requirements and budget.
What are some common security measures I should implement for my NAS?
+To enhance the security of your NAS, implement measures such as user accounts and permissions, encryption protocols (like SSL/TLS), secure authentication methods (like 2-factor authentication), and regular updates and patches for the NAS firmware and software. Additionally, configure your router’s firewall to allow only necessary ports to minimize potential security risks.
Can I access my NAS remotely when I’m away from my home network?
+Yes, many NAS devices support remote access, allowing you to access your NAS files and data when you’re away from your home network. This is achieved through various methods, including remote desktop connections, VPN (Virtual Private Network) setups, or cloud-based access solutions provided by the NAS manufacturer.