Excel's Trial Balance: A Simple Format Guide
In the world of accounting and financial management, the Trial Balance is a fundamental concept and a crucial step in the accounting process. It serves as a tool to ensure the accuracy and integrity of a company's financial records and is an essential prerequisite for preparing financial statements. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of creating a Trial Balance in Excel, a widely used software that simplifies this process for accountants and financial professionals.
Understanding the Trial Balance

A Trial Balance is a summary of all ledger accounts in a general ledger, with debit balances listed in one column and credit balances in another. Its primary purpose is to verify the equality of debits and credits, a fundamental principle in double-entry bookkeeping. By listing all account balances, the Trial Balance helps identify any errors or discrepancies in the accounting records before the preparation of financial statements.
In Excel, creating a Trial Balance is a straightforward process, but it requires careful attention to detail to ensure accuracy. Let's explore the steps and best practices to craft an effective Trial Balance format in Excel.
Preparing the Excel Sheet
Before diving into the specifics of creating a Trial Balance, it’s essential to set up your Excel sheet correctly. Here are the initial steps to get started:
- Open a new Excel workbook and save it with a relevant filename, such as "Trial Balance."
- Set up your sheet with the necessary columns: Account Name, Account Number, Debit Balance, and Credit Balance. You may also include additional columns for account descriptions or any other relevant information.
- Format your columns appropriately. For instance, you might want to use accounting number format for the Debit and Credit Balance columns to display dollar amounts with two decimal places and a comma separator.
- Insert row and column headers to make your sheet more readable and professional.
- Consider adding filters to your sheet to make it easier to search and sort data.
By setting up your Excel sheet with these initial steps, you create a structured and organized environment for your Trial Balance, making the process more efficient and accurate.
Entering Account Balances
Now, it’s time to enter the account balances into your Excel sheet. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure a smooth and error-free process:
- Input the account names and numbers in the respective columns. Ensure that the account names and numbers correspond accurately to your general ledger.
- Enter the debit and credit balances for each account. Double-check these figures to avoid errors. You can use Excel's SUM function to calculate the total debit and credit balances and compare them with your general ledger totals.
- As you enter the balances, consider using Excel's conditional formatting to highlight any discrepancies or negative balances. This feature can help you quickly identify potential errors or oversights.
- Sort your data by account name or number to ensure a logical and consistent order. This makes it easier to review and verify the balances.
- Use Excel's filtering feature to narrow down your data and focus on specific accounts or types of accounts. This is particularly useful when dealing with large datasets.
By following these steps and leveraging Excel's features, you can efficiently enter and organize your account balances, setting the foundation for an accurate Trial Balance.
Calculating the Trial Balance
Once you have entered all the account balances, it’s time to calculate the Trial Balance. This is a critical step to ensure the accuracy of your financial records and identify any potential errors.
- In a new row below your account data, create a summary row. Label this row as "Total" or "Grand Total."
- Use Excel's SUM function to calculate the total debit and credit balances. Place these totals in the respective columns of your summary row.
- Compare the total debits and credits. If they match, your Trial Balance is in equilibrium, indicating that your financial records are balanced and accurate. However, if the totals do not match, you have an imbalance, which requires further investigation to identify and rectify any errors.
- In the case of an imbalance, review your account balances carefully. Check for any missing or incorrect entries, and ensure that all transactions have been posted correctly to the appropriate accounts.
- Consider using Excel's error-checking features, such as the Error Checking tool or the Error Checking Options dialog box, to identify and resolve potential issues.
By meticulously calculating and reviewing your Trial Balance, you ensure the accuracy and integrity of your financial records, a crucial aspect of effective financial management.
Advanced Excel Techniques for Trial Balance
Excel offers a plethora of advanced features that can enhance your Trial Balance process and make it even more efficient and accurate. Here are some techniques to consider:
Using Formulas and Functions
Excel’s extensive range of formulas and functions can streamline your Trial Balance process. Here are some key functions to utilize:
- SUM: As mentioned earlier, the SUM function is crucial for calculating total debit and credit balances.
- VLOOKUP: This function can be used to retrieve account information from other worksheets or workbooks, making it easier to maintain consistency and accuracy across multiple sheets.
- IFERROR: This function is invaluable for handling errors and ensuring your Trial Balance remains accurate. It allows you to specify an alternative value or action to take when an error occurs, preventing errors from propagating throughout your sheet.
- COUNTIF: Use this function to count the number of accounts with specific characteristics, such as accounts with a positive balance or those exceeding a certain threshold. This can help you identify patterns and anomalies in your data.
Conditional Formatting
Conditional formatting is a powerful tool in Excel that allows you to highlight cells based on specific conditions. This can be particularly useful for identifying discrepancies and negative balances in your Trial Balance.
- Set up conditional formatting rules to highlight cells with negative balances or imbalances. This visual cue makes it easier to spot potential errors and take corrective action.
- Use conditional formatting to color-code accounts based on their type or category. This can help you quickly identify and analyze specific types of accounts, such as asset accounts, liability accounts, or revenue accounts.
PivotTables
PivotTables are a versatile tool in Excel that allow you to summarize, analyze, explore, and present your data. They can be particularly useful for analyzing your Trial Balance data and gaining insights.
- Use PivotTables to summarize your Trial Balance data by account type or category. This can help you quickly identify the total balances for different types of accounts, such as assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses.
- Create PivotTables to analyze your Trial Balance data over time. This can help you track the growth or decline of specific accounts or identify seasonal trends in your financial records.
By leveraging these advanced Excel techniques, you can transform your Trial Balance process, making it more efficient, accurate, and insightful.
Real-World Examples
Let’s explore a real-world scenario to illustrate the application of the Trial Balance in Excel.
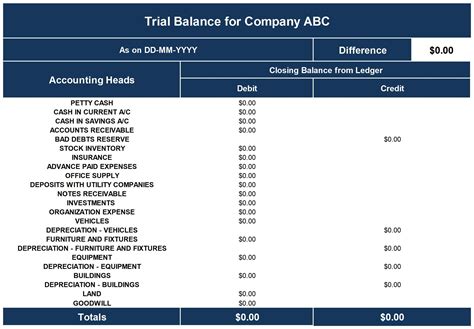
Scenario: ABC Company’s Trial Balance
ABC Company, a mid-sized retail business, wants to create a Trial Balance in Excel to verify the accuracy of its financial records before preparing its quarterly financial statements.
The company's accounting team has already compiled a list of all the company's accounts and their respective balances. Now, they need to create a Trial Balance in Excel to ensure the accuracy of these records.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how ABC Company can create their Trial Balance in Excel:
- Open a new Excel workbook and save it as "ABC Company Trial Balance."
- Set up the sheet with the necessary columns: Account Name, Account Number, Debit Balance, and Credit Balance. Include additional columns for account descriptions and any other relevant information.
- Format the columns appropriately. Use accounting number format for the Debit and Credit Balance columns, and apply filters to the sheet for easy data sorting and searching.
- Enter the account names, numbers, and balances into the respective columns. Double-check these figures to ensure accuracy.
- Use Excel's SUM function to calculate the total debit and credit balances. Place these totals in a summary row labeled "Total."
- Compare the total debits and credits. If they match, the Trial Balance is in equilibrium. If not, investigate the discrepancies to identify and rectify any errors.
- In this scenario, ABC Company discovers that the total debits do not match the total credits. Upon further investigation, they find that a transaction was incorrectly posted to the wrong account, causing the imbalance.
- ABC Company rectifies the error and recalculates the Trial Balance. This time, the totals match, indicating a balanced and accurate Trial Balance.
By following these steps and leveraging Excel's features, ABC Company can efficiently create a Trial Balance, ensuring the accuracy of their financial records and paving the way for the preparation of their quarterly financial statements.
Future Implications
The Trial Balance, as a fundamental concept in accounting, will continue to be a vital tool for financial professionals. As technology advances, tools like Excel will play an increasingly important role in simplifying and enhancing the Trial Balance process.
In the future, we can expect to see even more advanced features and functionalities in Excel, making it even easier to create, analyze, and interpret Trial Balances. Additionally, the integration of Excel with other accounting software and cloud-based solutions will further streamline the financial management process.
As financial professionals, staying abreast of these advancements and leveraging the power of tools like Excel will be crucial to maintaining accurate financial records and making informed business decisions.
What is the purpose of a Trial Balance in accounting?
+A Trial Balance serves as a tool to verify the accuracy and integrity of a company’s financial records. It ensures that the total debits equal the total credits, a fundamental principle in double-entry bookkeeping.
Why is it important to create a Trial Balance in Excel?
+Creating a Trial Balance in Excel simplifies the process of verifying financial records. Excel’s features, such as formulas, functions, and conditional formatting, make it easier to calculate, analyze, and identify errors in the Trial Balance.
What are some common errors to look for in a Trial Balance?
+Common errors in a Trial Balance include missing or incorrect account balances, posting transactions to the wrong accounts, and mathematical errors in calculating totals. It’s crucial to review the Trial Balance carefully to identify and rectify these errors.


