5 Key PERT Review Techniques

The Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) is a valuable methodology widely employed in project management. PERT analysis provides a systematic approach to planning, scheduling, and estimating the duration of tasks within a project. By incorporating various techniques, PERT enables project managers to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and enhance project efficiency.
In this article, we will delve into five essential PERT review techniques, exploring their applications and benefits. By understanding and implementing these techniques, project managers can effectively manage project timelines, mitigate risks, and improve overall project success.
1. Critical Path Analysis

Critical Path Analysis is a fundamental PERT technique that identifies the longest sequence of dependent tasks within a project. This critical path determines the minimum time required to complete the entire project. By analyzing the critical path, project managers can prioritize tasks, allocate resources effectively, and identify potential bottlenecks or delays.
For instance, consider a software development project. The critical path analysis reveals that the testing and deployment phases are crucial, as they are interdependent and cannot be accelerated without impacting the overall project timeline. By focusing on these critical tasks and ensuring efficient resource allocation, project managers can maintain a smooth project flow and meet deadlines.
| Project Phase | Duration |
|---|---|
| Design | 3 weeks |
| Development | 4 weeks |
| Testing | 2 weeks |
| Deployment | 1 week |
| Total Critical Path Duration | 10 weeks |

By utilizing critical path analysis, project managers can optimize the project schedule, allocate additional resources to critical tasks if needed, and ensure a timely project completion.
Benefits of Critical Path Analysis
- Improved project timeline management: Critical path analysis helps project managers visualize the sequence of tasks and their dependencies, enabling better planning and scheduling.
- Resource allocation optimization: By identifying critical tasks, project managers can allocate resources more efficiently, ensuring that the project stays on track.
- Risk mitigation: Understanding the critical path allows for proactive risk management. Project managers can anticipate potential delays and take preventive measures.
2. Activity Duration Estimation

Activity duration estimation is a crucial aspect of PERT analysis, as it involves predicting the time required to complete each task within a project. This estimation process considers various factors, such as historical data, expert opinions, and uncertainty.
Let's consider an example of constructing a new office building. The activity duration estimation for each construction phase, such as foundation work, structural framing, and interior finishing, is critical for accurate project planning. By estimating these durations accurately, project managers can create a realistic project timeline and allocate resources accordingly.
| Construction Phase | Estimated Duration (weeks) |
|---|---|
| Foundation Work | 4-6 |
| Structural Framing | 8-10 |
| Exterior Finishing | 6-8 |
| Interior Finishing | 10-12 |
By employing activity duration estimation techniques, project managers can make informed decisions, adjust project plans if needed, and communicate realistic expectations to stakeholders.
Advantages of Activity Duration Estimation
- Realistic project planning: Accurate duration estimation ensures that project timelines are based on reliable data, leading to more realistic planning.
- Resource optimization: With precise duration estimates, project managers can allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that the right people are available at the right time.
- Risk assessment: By considering uncertainty in duration estimation, project managers can identify potential risks and develop contingency plans.
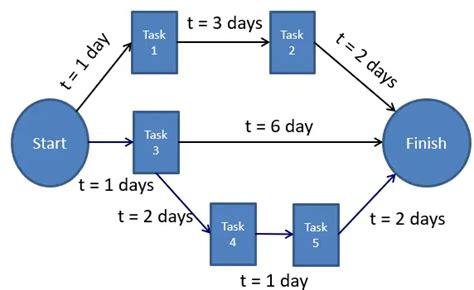
3. PERT Network Diagrams
PERT Network Diagrams provide a visual representation of project tasks, their dependencies, and the project’s overall structure. These diagrams are valuable tools for project managers to communicate project plans, identify critical paths, and analyze task relationships.
For example, in a marketing campaign project, a PERT Network Diagram can illustrate the sequence of tasks, such as market research, strategy development, creative execution, and campaign launch. By visualizing these tasks and their dependencies, project managers can easily identify potential delays and optimize the project workflow.
Sample PERT Network Diagram
(Insert a simple diagram representing the marketing campaign project with nodes and arrows indicating task dependencies)
Key Benefits of PERT Network Diagrams
- Clear project visualization: Network diagrams provide a concise and visual representation of the project, making it easier for project managers and stakeholders to understand the project’s structure.
- Improved communication: Visualizing the project plan enhances communication among team members and stakeholders, ensuring a shared understanding of the project.
- Risk analysis: By identifying task dependencies, project managers can assess potential risks and develop contingency plans to mitigate them.
4. Float or Slack Analysis
Float or Slack Analysis is a technique used to determine the amount of flexibility or buffer time available in a project schedule. It helps project managers understand how much time a task or the entire project can be delayed without impacting the overall project completion date.
Imagine a project to develop a new mobile application. Float analysis reveals that the development phase has a float of 2 weeks, indicating that the development team has a buffer of 2 weeks before the project is delayed. This information allows project managers to allocate resources efficiently and prioritize tasks accordingly.
| Project Phase | Duration | Float (weeks) |
|---|---|---|
| Design | 3 weeks | 1 |
| Development | 6 weeks | 2 |
| Testing | 2 weeks | 0 |
| Deployment | 1 week | 0 |
Advantages of Float Analysis
- Resource optimization: Understanding float allows project managers to allocate resources strategically, ensuring that critical tasks receive the necessary attention.
- Risk management: By identifying tasks with limited or no float, project managers can focus on mitigating risks associated with those tasks.
- Schedule flexibility: Float analysis provides project managers with the flexibility to accommodate unexpected delays or changes without impacting the overall project timeline.
5. Variance Analysis
Variance Analysis is a PERT technique that compares the actual project progress with the planned schedule. It helps project managers identify deviations from the original plan, assess the impact of changes, and make necessary adjustments.
In a construction project, variance analysis can be used to compare the actual progress with the planned timeline. If a particular phase takes longer than expected, variance analysis reveals the extent of the delay and its impact on the overall project schedule. This information enables project managers to take corrective actions and ensure the project stays on track.
| Construction Phase | Planned Duration (weeks) | Actual Duration (weeks) | Variance (weeks) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation Work | 4 | 5 | +1 |
| Structural Framing | 8 | 9 | +1 |
| Exterior Finishing | 6 | 7 | +1 |
| Interior Finishing | 10 | 12 | +2 |
Benefits of Variance Analysis
- Real-time project monitoring: Variance analysis provides project managers with up-to-date information on project progress, enabling them to make timely decisions.
- Identifying deviations: By comparing actual progress with the plan, project managers can quickly identify deviations and take corrective actions.
- Adjusting project plans: Variance analysis allows project managers to adjust project schedules, resource allocation, and task dependencies to ensure project success.
Conclusion
The five PERT review techniques discussed in this article provide project managers with powerful tools to manage project timelines, optimize resources, and enhance project efficiency. By employing critical path analysis, activity duration estimation, PERT network diagrams, float analysis, and variance analysis, project managers can make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and deliver successful projects.
Understanding and implementing these techniques allows project managers to stay ahead of potential challenges, communicate effectively with stakeholders, and ultimately deliver projects that meet or exceed expectations.
FAQ
What is the purpose of PERT analysis in project management?
+PERT analysis is used to plan, schedule, and estimate the duration of tasks within a project. It helps project managers optimize resource allocation, identify critical paths, and manage project timelines effectively.
How does critical path analysis contribute to project management?
+Critical path analysis identifies the longest sequence of dependent tasks, which determines the minimum time required to complete the project. It helps project managers prioritize tasks, allocate resources efficiently, and identify potential delays.
Why is activity duration estimation important in PERT analysis?
+Activity duration estimation predicts the time needed for each task, leading to realistic project planning. It allows project managers to allocate resources effectively, consider uncertainty, and make informed decisions.



