Right Lung Mass: Understanding the ICD-10 Code

A mass in the right lung can be a concerning finding, and it’s essential to understand the implications and the associated ICD-10 code for accurate medical documentation and diagnosis. The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision (ICD-10), is a standardized system used globally to classify and code various medical conditions, including lung masses. Let’s delve into the specifics of this condition and its ICD-10 code.
The right lung, one of the two primary organs of respiration, can sometimes develop masses or lesions, which may be benign or malignant. These masses can be detected through imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, and their presence often prompts further investigation and diagnostic procedures. Accurate coding of these masses is crucial for healthcare providers, insurance companies, and researchers to ensure proper treatment, reimbursement, and tracking of disease trends.
Understanding the ICD-10 Code for Right Lung Mass

The ICD-10 code for a right lung mass is C34.1, specifically for a malignant neoplasm of the right upper lobe of the lung. This code is part of the broader category of ‘Malignant Neoplasms of the Bronchus and Lung’ under the ICD-10 classification. Here’s a breakdown of the code:
C34.1: This code indicates a malignant tumor in the right upper lobe of the lung. The ‘C’ category covers ‘Neoplasms,’ and the subsequent digits provide more specific details about the location and nature of the tumor.
Malignant Neoplasm: The term ‘malignant neoplasm’ refers to cancer, indicating that the mass is a potentially life-threatening growth. Malignant tumors can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body, making them a serious health concern.
Right Upper Lobe: The right lung is divided into three lobes—the upper, middle, and lower lobes. The ‘1’ in the code (C34.1) specifies the upper lobe, which is the highest section of the right lung.
Diagnosing and Treating Right Lung Masses

When a mass is detected in the right lung, healthcare professionals follow a systematic approach to determine the nature of the lesion:
Imaging Studies: Initial imaging tests, such as chest X-rays or CT scans, often reveal the presence of a mass. These images provide valuable information about the size, location, and characteristics of the lesion.
Biopsy: To confirm the diagnosis, a biopsy is often necessary. This involves obtaining a tissue sample from the mass, which can be done through a bronchoscopy or a needle biopsy guided by imaging. The sample is then examined under a microscope by a pathologist to determine if it is benign or malignant.
Staging: If the biopsy confirms cancer, further tests may be conducted to determine the stage of the disease. Staging helps assess the extent of the cancer and whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs.
Treatment Planning: The treatment approach for a right lung mass depends on various factors, including the type of cancer, its stage, the patient’s overall health, and their preferences. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these modalities.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for individuals with a right lung mass depends on several factors, including the type of cancer, its stage at diagnosis, and the individual’s overall health. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. Survival rates for lung cancer vary widely based on these factors, and it’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals for an accurate prognosis.
Prevention and Risk Factors
While not all lung masses can be prevented, certain lifestyle choices and environmental factors can reduce the risk of developing lung cancer:
Smoking Cessation: Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer. Quitting smoking or avoiding tobacco products altogether is the most effective way to reduce the risk.
Exposure to Toxins: Avoiding exposure to harmful substances like asbestos, radon gas, and certain industrial chemicals can lower the risk of lung cancer.
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and a balanced lifestyle can contribute to overall well-being and potentially reduce the risk of various cancers.
Conclusion
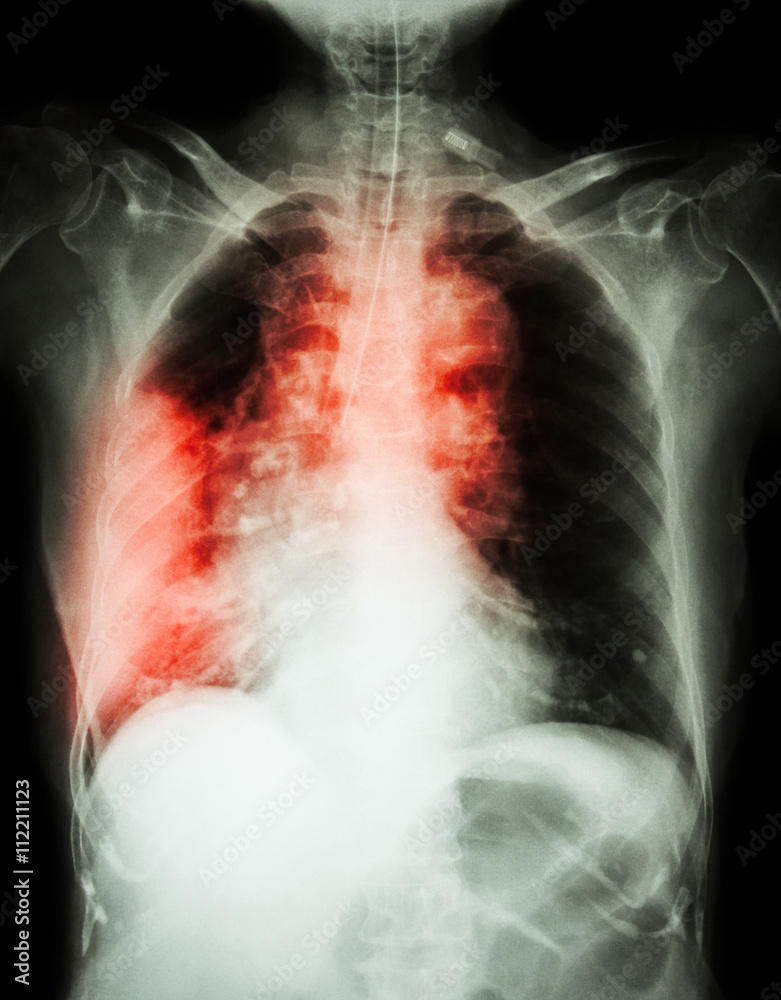
Understanding the ICD-10 code C34.1 for a right lung mass is crucial for accurate medical documentation and diagnosis. This code, specifically for a malignant neoplasm in the right upper lobe, highlights the serious nature of the condition. Early detection, proper diagnosis, and timely treatment are key to improving outcomes for individuals with a right lung mass. By raising awareness and promoting healthy lifestyle choices, we can work towards reducing the incidence of lung cancer and improving survival rates.
What are the symptoms of a right lung mass?
+Symptoms of a right lung mass can vary depending on the size and location of the lesion. Common symptoms include persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and repeated respiratory infections. However, some individuals with lung masses may not experience any noticeable symptoms, especially in the early stages.
How is a right lung mass diagnosed?
+Diagnosis typically involves a combination of imaging tests, such as X-rays and CT scans, to detect the presence of a mass. Biopsy, either through bronchoscopy or needle biopsy, is then performed to confirm the nature of the lesion. Pathological examination of the tissue sample determines whether the mass is benign or malignant.
Can a right lung mass be treated successfully?
+The treatment success of a right lung mass depends on various factors, including the type of cancer, its stage, and the patient’s overall health. Early-stage lung cancers have higher cure rates, and treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these. The multidisciplinary approach to lung cancer treatment has improved survival rates significantly.
Are there any screening tests for lung masses?
+Screening tests for lung masses are primarily recommended for high-risk individuals, such as heavy smokers or those with a family history of lung cancer. Low-dose CT scans are often used for lung cancer screening, as they can detect small masses at an early stage. However, screening is not routinely recommended for the general population due to the potential risks and costs associated with further diagnostic procedures.
What is the role of surgery in treating right lung masses?
+Surgery plays a crucial role in the treatment of right lung masses, especially in early-stage cancers. Surgical options include lobectomy (removal of the affected lobe), wedge resection (removal of a small portion of the lung), or pneumonectomy (removal of the entire lung). The choice of surgical approach depends on the size, location, and extent of the mass, as well as the patient’s overall health.



