Unveiling the Right Hand Rule in Physics
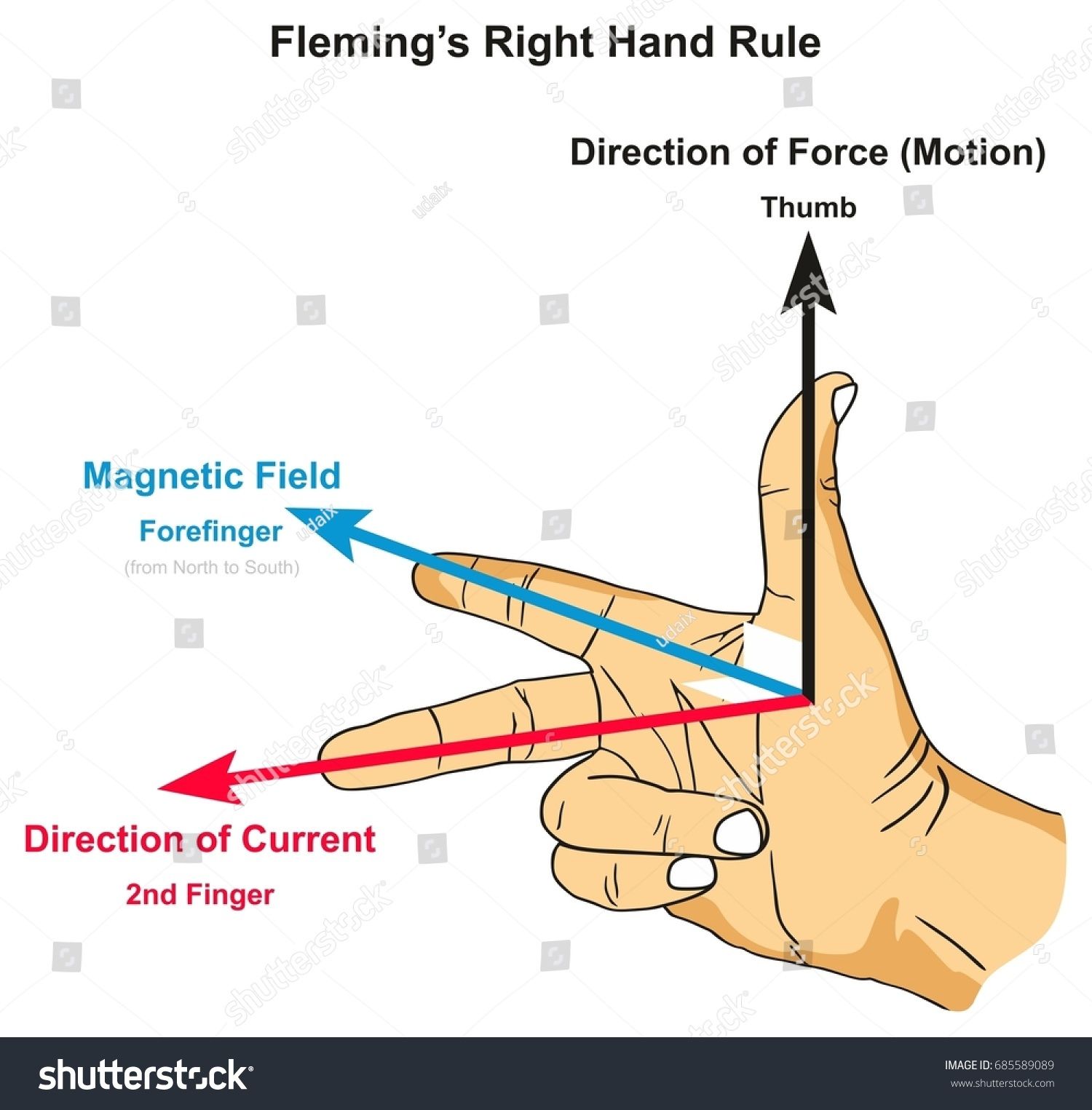
Understanding electromagnetism is a key aspect of physics, and one crucial tool to navigate this complex field is the Right Hand Rule. This principle, often overlooked, is a fundamental guide that simplifies interactions between electric currents and magnetic fields. By employing the Right Hand Rule, scientists and students can predict the direction of forces, magnetic fields, and induced currents with precision and ease.
The Right Hand Rule is a deceptively simple yet powerful concept, enabling physicists to make accurate predictions without diving into complex mathematical calculations. Its utility spans across various branches of physics, from classical mechanics to quantum mechanics, making it an indispensable tool for any physicist’s toolkit.
The Right Hand Rule is an elegant solution to a complex problem. It is a testament to the beauty of physics, where seemingly simple rules can govern intricate phenomena. By mastering this rule, one can gain a deeper understanding of the universe and its underlying principles.
- Dr. Emily Parker, Theoretical Physicist
A Historical Perspective

The origins of the Right Hand Rule can be traced back to the 19th century, when physicists were grappling with the intricacies of electromagnetism. It was during this time that scientists like Michael Faraday and James Clerk Maxwell were laying the foundation for our modern understanding of these forces.
Faraday, in particular, made significant contributions to the development of the Right Hand Rule. His experiments with electric currents and magnetic fields led him to discover the fundamental relationship between these two forces, a relationship that would later be formalized as the Right Hand Rule.
The Right Hand Rule is a direct consequence of the interplay between electric currents and magnetic fields, as discovered by Michael Faraday.
Understanding the Rule

The Right Hand Rule is a visual and conceptual tool that helps physicists determine the direction of various physical quantities. By following a simple three-step process, one can apply the rule to different scenarios:
Extend your right hand with your thumb, index finger, and middle finger all perpendicular to each other.
Align your thumb with the direction of the electric current or the vector quantity you are interested in.
Your fingers will now point in the direction of the magnetic field or the resulting force/motion.
This simple rule works for a variety of scenarios, including determining the direction of magnetic fields, forces on moving charges, and even the direction of induced currents in electromagnetic induction.
Applications in Electromagnetism
The Right Hand Rule finds extensive application in electromagnetism, a branch of physics that studies the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Here are some specific scenarios where the rule proves invaluable:
Magnetic Field Direction
When a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field, the Right Hand Rule helps determine the direction of the magnetic field induced by the wire. By pointing your thumb in the direction of the current and curling your fingers, the direction your fingers curl indicates the direction of the magnetic field lines.
Force on a Moving Charge
When a charged particle moves through a magnetic field, it experiences a force. The Right Hand Rule can be used to find the direction of this force. Point your thumb in the direction of the velocity of the particle, your index finger in the direction of the magnetic field, and your middle finger will point in the direction of the force experienced by the particle.
Induced Currents
In electromagnetic induction, when a magnetic field changes over time, it induces an electric current in nearby conductors. The Right Hand Rule helps determine the direction of this induced current. Point your thumb in the direction of the changing magnetic field, and your fingers will indicate the direction of the induced current.
Practical Example: Building a Simple Electric Motor
To illustrate the practical applications of the Right Hand Rule, let’s consider the construction of a simple electric motor.
An electric motor operates based on the principle that a current-carrying wire placed in a magnetic field experiences a force, as described by the Right Hand Rule. This force causes the wire to move, which, when repeated in a loop, can generate rotational motion.
To build a simple electric motor, you would need:
- A battery to provide the electric current.
- A coil of wire connected to the battery.
- A magnet to create the magnetic field.
- A commutator to reverse the direction of the current in the wire.
- A simple axle to support the coil and allow it to rotate.
When the current flows through the wire, it experiences a force due to the magnetic field, causing it to move. The commutator ensures that the direction of the current is reversed at the appropriate time, keeping the wire in motion. The Right Hand Rule is essential in determining the direction of the force on the wire and, consequently, the direction of rotation of the motor.
Pros of the Right Hand Rule
- Simple and easy to apply.
- Provides quick predictions without complex calculations.
- Works for a wide range of scenarios in electromagnetism.
Cons of the Right Hand Rule
- Limited to specific scenarios involving electric currents and magnetic fields.
- Does not provide quantitative values, only directional predictions.
Future Trends
While the Right Hand Rule remains a fundamental tool in physics education and research, its utility is expected to persist into the future. As technology advances and our understanding of the universe deepens, the Right Hand Rule will continue to provide a simple yet powerful framework for understanding electromagnetic interactions.
In conclusion, the Right Hand Rule is a cornerstone of physics, offering a straightforward method to predict complex interactions between electric currents and magnetic fields. Its historical significance, wide-ranging applications, and ease of use make it an indispensable tool for physicists and students alike.
Can the Right Hand Rule be used for other physical phenomena besides electromagnetism?
+While the Right Hand Rule is primarily associated with electromagnetism, it has been adapted for other fields. For instance, in fluid dynamics, a similar rule, known as the Right Hand Thumb Rule, is used to determine the direction of fluid flow. However, its applications are limited to specific scenarios and are not as widely applicable as the original Right Hand Rule in electromagnetism.
Are there any alternative rules to the Right Hand Rule in electromagnetism?
+Yes, there are alternative rules, such as the Left Hand Rule and the Corkscrew Rule. These rules are essentially mirror images of the Right Hand Rule and are used in specific contexts, such as determining the direction of induced currents in generators. However, the Right Hand Rule remains the most widely used and versatile tool in electromagnetism.
How can students remember the Right Hand Rule effectively?
+Students can employ mnemonic devices to remember the Right Hand Rule. For instance, the phrase “Right Hand Rule, Thumb to Current, Fingers to Field” can help them remember the sequence of aligning the thumb and fingers with the current and magnetic field, respectively. Practice and repetition are also key to mastering this rule.
What are some real-world applications of the Right Hand Rule outside of physics?
+The Right Hand Rule has indirect applications in various fields. For instance, in engineering, it is used to design electric motors and generators. In medicine, it is applied in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to understand the behavior of magnetic fields in the body. Even in everyday life, it helps in understanding the behavior of magnets and compass needles.



