Unraveling Pseudohyponatremia: A Concise ICD-10 Guide

Understanding Pseudohyponatremia: When Serum Sodium Levels Mislead
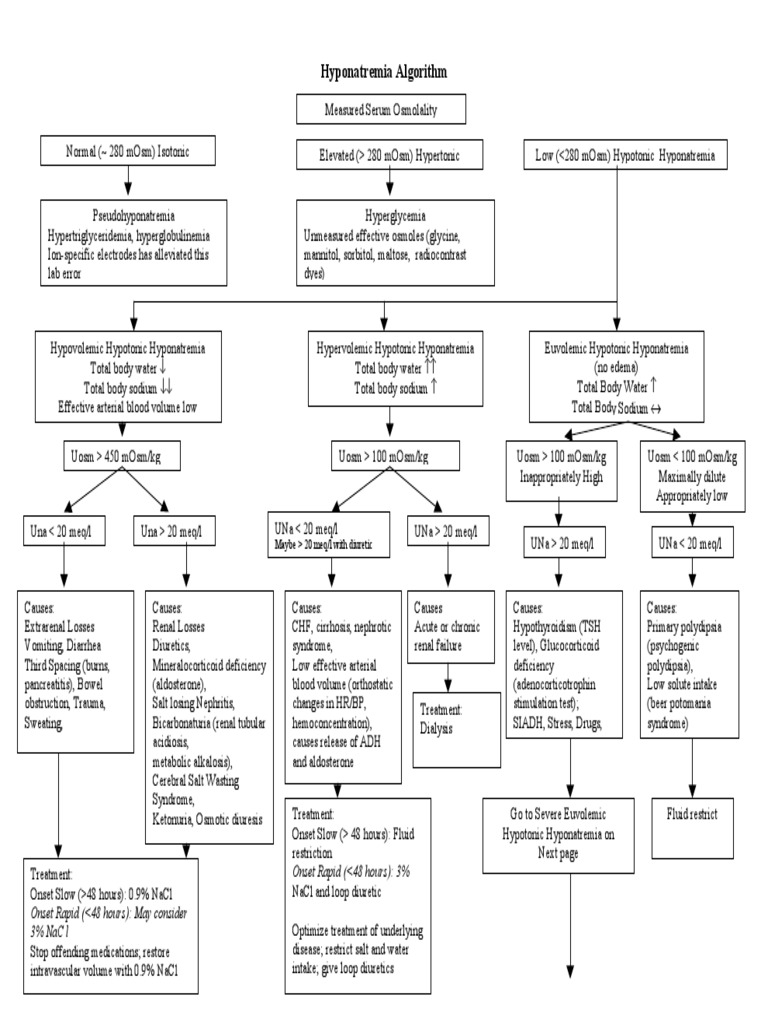
Pseudohyponatremia, a phenomenon that can confound medical professionals, occurs when serum sodium levels appear lower than they actually are, leading to a false diagnosis of hyponatremia. This condition is not as straightforward as it seems and requires a nuanced understanding of the factors at play. In this concise guide, we will delve into the intricacies of pseudohyponatremia, its causes, and how it is classified and diagnosed according to the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision (ICD-10).
The Complexity of Serum Sodium Measurement
Serum sodium, a crucial electrolyte, plays a vital role in maintaining fluid balance and cellular function. Its concentration is typically measured to assess hydration status and identify electrolyte imbalances. However, the measurement of serum sodium is not without its complexities. Pseudohyponatremia arises due to certain physiological or analytical factors that affect the accuracy of this measurement.
Causes of Pseudohyponatremia
This condition can be triggered by a variety of factors, each with its own unique mechanism:
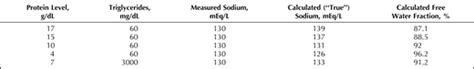
Hyperlipidemia: Elevated levels of lipids, particularly triglycerides, can lead to a decrease in serum sodium concentration. This is because lipids interfere with the measurement process, causing an apparent reduction in sodium levels.
Hyperproteinemia: High protein concentrations, often seen in conditions like multiple myeloma or during intense physical exercise, can result in pseudohyponatremia. Proteins can affect the activity of the sodium-selective electrode used in serum sodium measurement, leading to inaccurate readings.
Cold Diuresis: In individuals exposed to cold temperatures, the body may experience increased urine output, known as cold diuresis. This can lead to a dilution of serum sodium, resulting in a falsely low measurement.
Analytical Interference: Certain analytical techniques used to measure serum sodium may be susceptible to interference from other substances. For instance, the presence of bilirubin or certain medications can affect the accuracy of the test, leading to pseudohyponatremia.
ICD-10 Classification and Diagnosis
The ICD-10 provides a standardized framework for classifying and coding medical conditions, including pseudohyponatremia. Here’s how this condition is categorized:
Code: The specific ICD-10 code for pseudohyponatremia is E87.3. This code is assigned to conditions where there is a discrepancy between measured and actual serum sodium levels.
Clinical Presentation: Individuals with pseudohyponatremia may exhibit signs and symptoms similar to those of true hyponatremia, such as nausea, vomiting, headache, and, in severe cases, seizures or coma. However, these symptoms are not directly caused by a sodium imbalance but rather by the underlying condition leading to pseudohyponatremia.
Diagnosis: Diagnosing pseudohyponatremia requires a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. It is crucial to consider the possibility of pseudohyponatremia, especially in patients with conditions known to cause this phenomenon.
Treatment: The management of pseudohyponatremia primarily involves addressing the underlying condition. For example, in cases of hyperlipidemia, lipid-lowering medications may be prescribed. Treatment aims to correct the physiological factors contributing to the inaccurate sodium measurement.
Implications and Considerations
Pseudohyponatremia can have significant clinical implications, as it may lead to misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment. Here are some key points to consider:
Differential Diagnosis: It is essential to differentiate pseudohyponatremia from true hyponatremia, as the treatment approaches for these conditions differ. A thorough understanding of the patient’s medical history and the use of additional laboratory tests can aid in making an accurate diagnosis.
Repetitive Testing: In cases where pseudohyponatremia is suspected, repetitive testing using different methods or techniques may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. This ensures that the measured serum sodium levels are not influenced by the factors causing the apparent decrease.
Patient Education: Educating patients about pseudohyponatremia and its potential causes can be beneficial. Understanding that their sodium levels may be affected by certain conditions or medications can help individuals interpret their test results accurately.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities
Pseudohyponatremia serves as a reminder of the intricate nature of medical diagnostics. It highlights the importance of a holistic approach to patient care, where clinical judgment, laboratory expertise, and a thorough understanding of physiological processes come together. By unraveling the complexities of this condition, healthcare professionals can ensure accurate diagnoses and provide appropriate care to their patients.
FAQ Section
What is the primary cause of pseudohyponatremia?
+Pseudohyponatremia can be triggered by various factors, including hyperlipidemia, hyperproteinemia, cold diuresis, and analytical interference. Each of these factors affects the measurement of serum sodium levels, leading to an apparent decrease.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can pseudohyponatremia be distinguished from true hyponatremia?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Distinguishing pseudohyponatremia from true hyponatremia requires a comprehensive evaluation. Medical professionals consider the patient's medical history, physical examination, and additional laboratory tests. By identifying the underlying cause of the apparent sodium decrease, healthcare providers can differentiate between the two conditions.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are the potential consequences of misdiagnosing pseudohyponatremia as true hyponatremia?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment, potentially causing harm to the patient. For example, administering sodium supplements to a patient with pseudohyponatremia due to hyperlipidemia may not address the underlying condition and could even be detrimental. Accurate diagnosis is crucial to ensure effective management.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Are there any specific laboratory tests to confirm pseudohyponatremia?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes, repetitive testing using different methods or techniques can help confirm pseudohyponatremia. For instance, a comparison of serum sodium levels measured by direct and indirect methods can provide valuable insights. Additionally, measuring other electrolytes and assessing urine osmolality can aid in the diagnosis.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>



