The Amazing Science of Water

Introduction

Water, a simple molecule, H2O, has captivated scientists and researchers for centuries with its extraordinary properties and unique behavior. From its ability to sustain life to its role in shaping our planet’s geology and climate, water’s science is nothing short of astounding. In this article, we delve into the depths of this essential substance, exploring its chemistry, physics, and the myriad ways it influences our world.
The story of water is a tale of complexity within simplicity, revealing a world of fascinating phenomena that underpin our very existence. Prepare to embark on a journey that will challenge your perceptions and deepen your appreciation for this most familiar yet enigmatic substance.
The Chemistry of Water: A Molecular Marvel

At its core, water is a deceptively simple molecule, consisting of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom. Yet, this humble combination gives rise to a chemical powerhouse. The unique arrangement of electrons within the water molecule creates a polar bond, with the oxygen atom attracting electrons more strongly than the hydrogens. This polarity endows water with a host of remarkable properties.
Water’s polarity makes it an exceptional solvent, capable of dissolving a vast array of substances, from salts to acids and bases. This solubility plays a pivotal role in the transport of nutrients and waste within living organisms and is essential for the chemical reactions that sustain life.
Additionally, the hydrogen bonds between water molecules contribute to its high surface tension and unique viscosity. These properties enable water to form droplets, defy gravity in capillary action, and provide a supportive medium for aquatic life. The strength of hydrogen bonds also accounts for water’s high boiling point, which is vital for its role in the water cycle and the regulation of Earth’s climate.
The Physics of Water: Fluid Dynamics and Beyond
The physics of water is a rich and complex field, offering insights into the behavior of fluids and the forces that govern them. One of the most striking phenomena is water’s ability to defy gravity and rise through narrow tubes—a process known as capillary action. This occurs due to the interplay between the adhesive forces between water and the tube’s material and the cohesive forces between water molecules.
Water’s fluid dynamics are equally fascinating. From the graceful flow of rivers to the powerful turbulence of ocean currents, water’s behavior is shaped by a multitude of factors, including viscosity, density, and the forces exerted by its container. These dynamics have profound implications for the movement of nutrients, pollutants, and energy throughout our ecosystems.
Moreover, water’s phase transitions—from solid ice to liquid water and gaseous vapor—are governed by intricate physical principles. Understanding these transitions is key to unraveling the mysteries of Earth’s climate, weather patterns, and the very processes that shape our planet’s geology.
Water’s Role in Shaping Our Planet
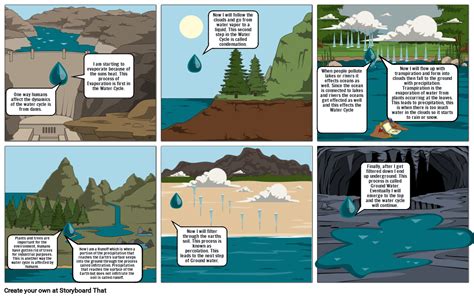
Water is not merely a passive observer in the grand theater of Earth’s history; it is a key player in the dramatic processes that have shaped our planet over billions of years. The water cycle, driven by the sun’s energy, is a relentless engine that circulates water through the atmosphere, oceans, and land, shaping landscapes and influencing climate patterns.
The erosive power of water has carved majestic canyons, sculpted intricate coastlines, and deposited vast sedimentary formations. From the Grand Canyon to the Great Barrier Reef, water’s handiwork is evident in some of Earth’s most awe-inspiring natural wonders.
Water’s influence extends beyond the surface. Deep within the Earth, water plays a critical role in geological processes, contributing to the movement of tectonic plates and the formation of volcanoes and mountain ranges. The presence of water is also believed to be a key factor in the emergence of life on our planet, highlighting its role as a catalyst for biological evolution.
The Biological Significance of Water
Water is the lifeblood of our planet, essential for the existence and functioning of all known life forms. Its unique properties make it an ideal medium for biological processes. Water’s ability to dissolve a wide range of substances facilitates the transport of nutrients and the removal of waste, while its polarity enables it to act as a solvent for vital biochemical reactions.
The human body, composed of over 60% water, relies on this precious resource for numerous physiological functions. From the hydration of cells to the regulation of body temperature, water is integral to our very being. Dehydration, even in small amounts, can have significant impacts on our health and well-being, underscoring the critical importance of adequate water intake.
Beyond its role in individual organisms, water is a key factor in the evolution and diversity of life on Earth. From the vast oceans that harbor an abundance of marine life to the delicate ecosystems of freshwater lakes and rivers, water provides the habitat and resources necessary for the proliferation of countless species.
Water Conservation and Sustainability
As we delve into the science of water, it becomes increasingly clear that this resource is not only precious but also finite. With growing global populations and changing climatic conditions, the sustainable management of water resources has become a critical issue.
Conservation efforts must address a range of challenges, from reducing water waste and pollution to implementing efficient irrigation practices in agriculture. The development of water-efficient technologies and the promotion of responsible water usage are essential steps toward ensuring a sustainable future.
Furthermore, the protection of natural water sources, such as wetlands and aquifers, is vital for maintaining the health of ecosystems and ensuring a reliable water supply for future generations. By understanding the science of water and its intricate connections to our planet’s systems, we can make informed decisions to preserve this essential resource.
A Global Perspective: Water’s Impact on Society
Water’s influence extends far beyond the realms of science and nature. It is intricately woven into the fabric of human society, shaping cultures, economies, and political landscapes. Access to clean, safe water is a fundamental human right, yet it remains a privilege for many.
Water scarcity and pollution pose significant challenges to communities around the globe. From the drought-stricken regions of Africa to the water-stressed cities of Asia, the impacts of water-related issues are profound. They affect not only health and well-being but also economic development, social stability, and environmental sustainability.
Conversely, the availability of abundant water resources has been a driving force behind the rise of civilizations. From the mighty rivers of ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia to the modern-day water infrastructure of developed nations, water has been a catalyst for progress and a symbol of prosperity.
Future Prospects: Navigating the Water Crisis
As we look to the future, the specter of a global water crisis looms large. Population growth, climate change, and increasing water demands from various sectors are placing unprecedented pressure on our water resources. To address these challenges, we must harness the power of science and innovation.
Advanced water treatment technologies, such as desalination and wastewater recycling, offer promising solutions for augmenting water supplies. Additionally, the development of water-efficient practices in agriculture, industry, and domestic settings is crucial for reducing water consumption and minimizing waste.
Moreover, the integration of water management strategies with broader climate change mitigation and adaptation efforts is essential. By adopting a holistic approach that considers the interconnectedness of water, energy, and environmental systems, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient future.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The science of water reveals a world of wonder and complexity, a testament to the beauty and brilliance of our natural world. Yet, as we have seen, water’s importance extends far beyond its scientific marvels. It is a resource upon which our very survival depends, and its conservation and sustainable management are critical responsibilities.
As global citizens, we must recognize the value of water and embrace our role in its stewardship. From making conscious choices in our daily water usage to advocating for policies that prioritize water conservation, each of us can contribute to a more sustainable future.
Let the science of water inspire us to action, to protect and preserve this precious resource for generations to come. Together, we can ensure that water’s story continues to be one of life, resilience, and the enduring power of nature.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the significance of water’s polarity in its chemical behavior?
+Water’s polarity, resulting from the unequal distribution of electrons in the oxygen-hydrogen bond, gives it exceptional chemical properties. It makes water an excellent solvent, able to dissolve a wide range of substances, and facilitates vital biochemical reactions. This polarity also contributes to water’s high surface tension and viscosity, influencing its behavior in various contexts.
How does water’s role in the water cycle influence Earth’s climate and weather patterns?
+The water cycle, driven by solar energy, is a critical regulator of Earth’s climate. As water evaporates, it carries heat energy from the surface, cooling the planet. Condensation releases this energy back into the atmosphere, warming it. These processes influence weather patterns, affecting temperature, humidity, and precipitation.
What are some examples of water’s impact on geological processes?
+Water plays a vital role in geological processes such as plate tectonics and mountain building. It acts as a lubricant, facilitating the movement of tectonic plates. Additionally, water’s presence in the Earth’s mantle contributes to the formation of volcanoes and the uplift of mountain ranges.
How does water conservation benefit the environment and society?
+Water conservation reduces the strain on natural water sources, preserving aquatic ecosystems and ensuring a sustainable water supply for future generations. It also helps mitigate the impacts of water scarcity and pollution, benefiting public health, economic development, and social stability.
What are some innovative solutions for addressing the global water crisis?
+Advanced water treatment technologies like desalination and wastewater recycling offer promising solutions. Additionally, promoting water-efficient practices in agriculture, industry, and domestic settings, along with integrating water management with climate change mitigation and adaptation efforts, can help address the global water crisis.



