The Secret Life of Prickly Poppies

Unveiling the Intriguing World of Prickly Poppies
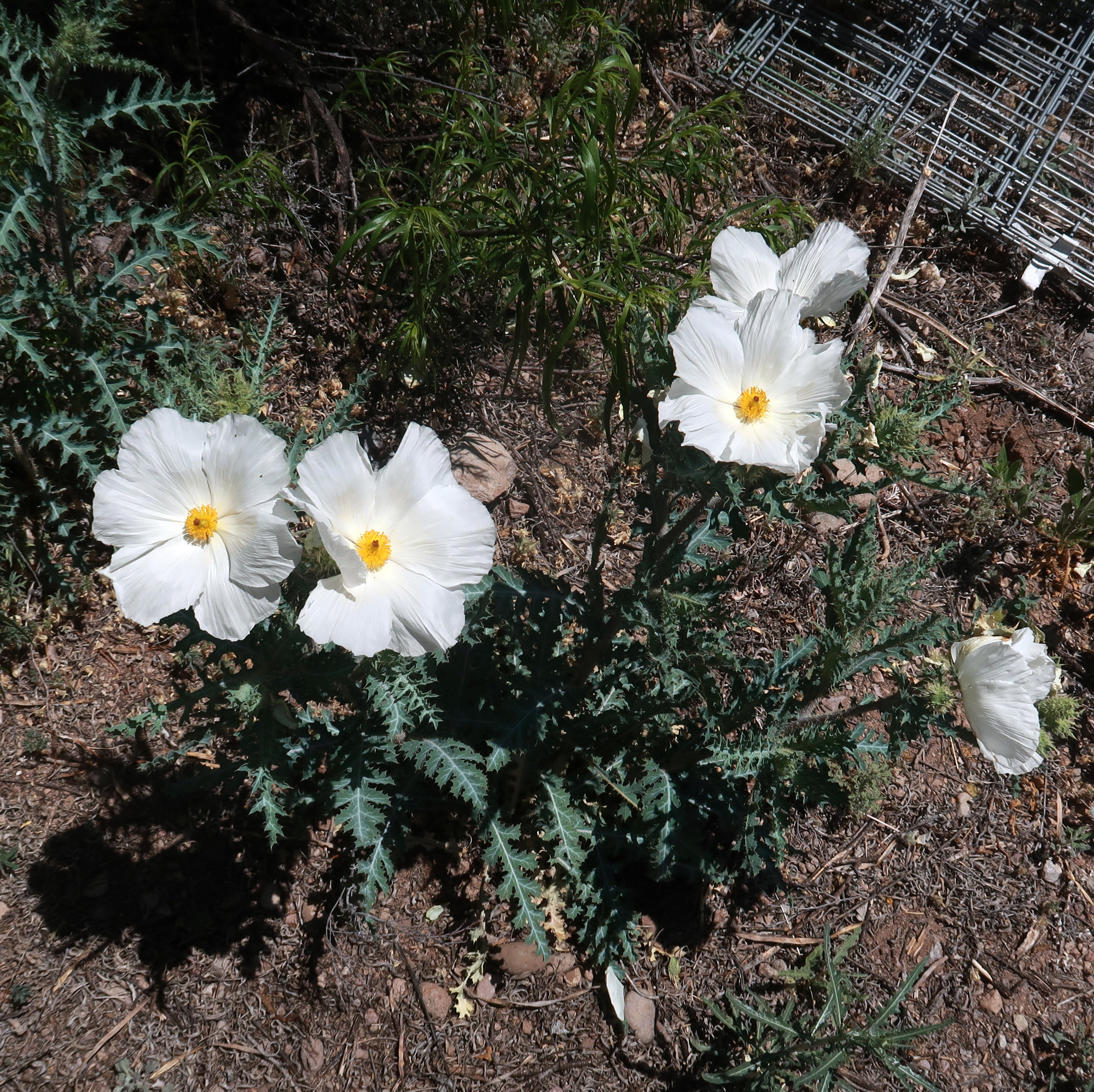

The botanical realm has countless secrets waiting to be discovered, and among them, the prickly poppy stands out as a captivating enigma. Despite its unassuming appearance, this plant species has a unique and complex life cycle that has intrigued botanists and nature enthusiasts alike. From its spiky exterior to its remarkable adaptations, the prickly poppy offers a fascinating glimpse into the diverse strategies of plant survival.
The prickly poppy, with its seemingly defensive mechanisms, has evolved a fascinating array of strategies to thrive in its specific ecological niche. It's a testament to the incredible diversity and adaptability of the plant kingdom.Dr. Emily Stone, Botanist
Botanical Basics
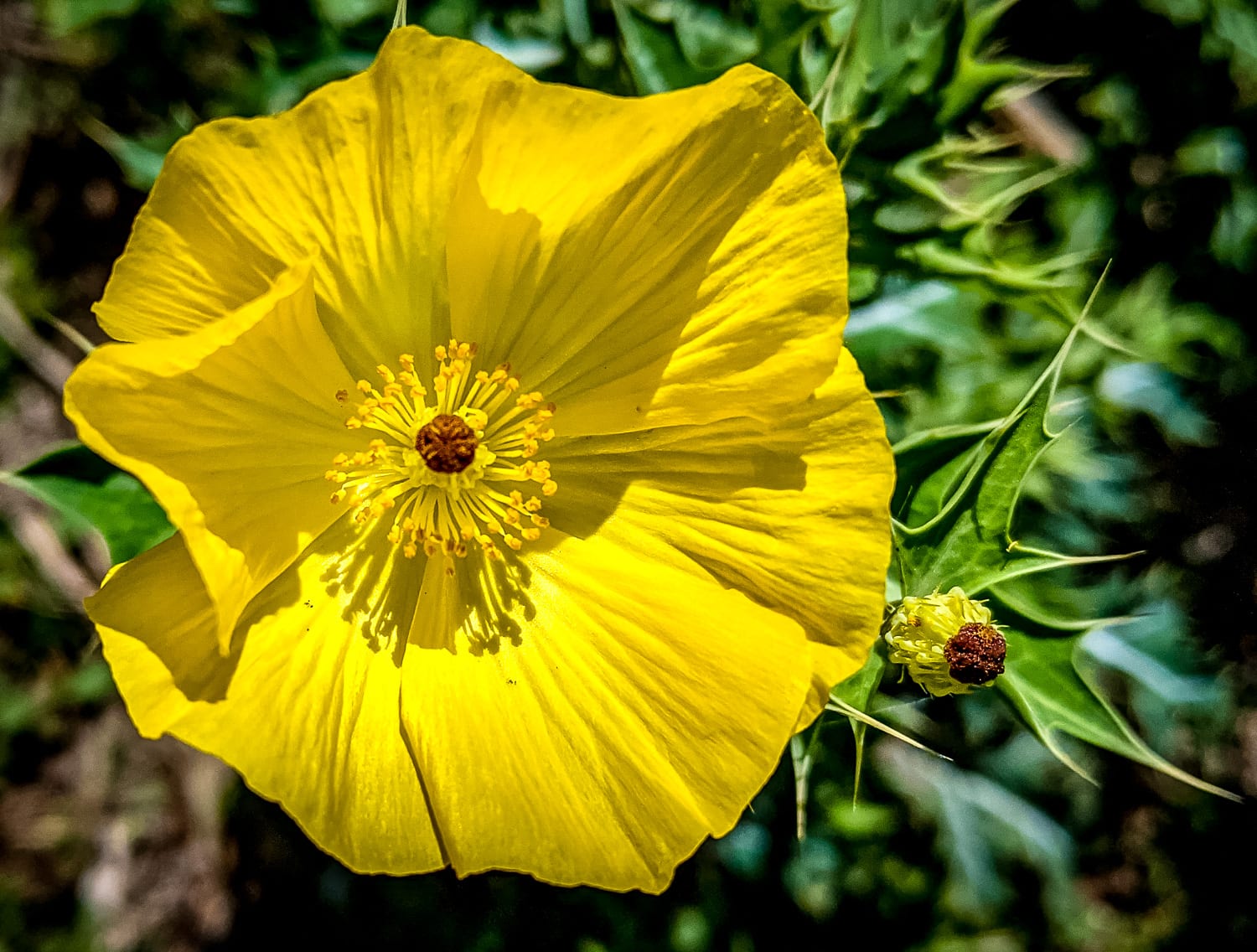

Prickly poppies, scientifically known as Argemone species, are a genus of flowering plants belonging to the poppy family, Papaveraceae. They are native to the Americas, particularly in regions like the southwestern United States and Mexico, where they have adapted to thrive in arid and semi-arid conditions.
These plants are easily recognizable due to their distinctive features. They often grow to modest heights, with stems that are typically 1-2 feet tall and covered in sharp, needle-like spines. These spines provide a physical barrier against potential herbivores, giving the plant its common name.
The flowers of prickly poppies are also quite unique. They are usually bright yellow or orange, with a subtle fragrance that attracts pollinators like bees and butterflies. The petals are delicate and papery, contrasting sharply with the robust and spiny stems.
Pros of Prickly Poppies
- Remarkable adaptability to arid environments
- Attractive flowers that enhance biodiversity
- Potential medicinal properties
Cons of Prickly Poppies
- Spines can be a nuisance for gardeners and hikers
- Potential invasiveness in certain regions
- May be harmful to livestock if ingested
Life Cycle and Adaptations
The life cycle of prickly poppies is a testament to their resilience and survival strategies. They are annual plants, meaning they complete their entire life cycle within a single growing season. This rapid growth and reproduction are key adaptations for their harsh environments.
Seed Germination and Early Growth
Prickly poppy seeds require specific conditions to germinate. They need a period of cold stratification, which mimics the winter conditions they would experience in their natural habitat. Once the conditions are right, the seeds quickly sprout, taking advantage of the brief window of opportunity in their arid environments.
Flowering and Pollination
As the plants grow, they develop their distinctive spiny stems and bright flowers. The flowers are a visual spectacle, drawing in pollinators with their vibrant colors and subtle fragrances. This is a critical stage for the plant’s survival, as successful pollination ensures the production of viable seeds for the next generation.
Seed Production and Dispersal
After pollination, the flowers wither, and the plant focuses its energy on seed production. The seeds are typically small and black, and they are contained within a capsule-like structure. When the seeds are mature, the capsule splits open, releasing the seeds.
The seeds have a unique dispersal mechanism. They are equipped with small, hair-like structures that allow them to be carried by the wind. This wind-dispersal strategy ensures the seeds can travel long distances, potentially finding more favorable conditions for germination and growth.
Medicinal and Cultural Significance
Prickly poppies have a long history of traditional use and cultural significance. Indigenous communities in the Americas have utilized various Argemone species for their medicinal properties. The seeds and leaves are known to contain alkaloids with potential therapeutic benefits, including pain relief and anti-inflammatory effects.
However, it’s important to note that these plants also contain toxic compounds, and improper use can lead to harmful side effects. Therefore, prickly poppies should only be used under the guidance of traditional healers or medical professionals with expertise in their applications.
Conservation and Environmental Impact

While prickly poppies have adapted to thrive in arid conditions, their presence can also have environmental impacts. In some regions, they have become invasive, outcompeting native plant species and altering the natural balance of ecosystems.
On the other hand, their deep root systems can help prevent soil erosion in arid landscapes, and their presence can provide food and habitat for various wildlife species, contributing to local biodiversity.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Identifying Prickly Poppies
- Look for spiny stems and branches.
- Check for bright yellow or orange flowers with delicate petals.
- Examine the leaves, which are typically lobed or deeply divided.
- Feel the texture - prickly poppies have a rough, spiny feel.
- Observe the plant's habitat - they thrive in arid and sunny conditions.
Conclusion
The prickly poppy is a botanical marvel, showcasing the incredible diversity and resilience of the plant kingdom. Its unique adaptations and survival strategies make it a fascinating subject of study for botanists and nature lovers alike. Whether you encounter it in the wild or in a botanical garden, the prickly poppy is sure to leave a lasting impression with its intriguing life cycle and remarkable beauty.
Are prickly poppies dangerous to humans or animals?
+While the spines can cause minor irritation if touched, the real danger lies in the plant’s potential toxicity. Prickly poppies contain alkaloids that can be harmful if ingested. Livestock and pets should be kept away from these plants, and humans should avoid consuming any parts of the plant.
Can prickly poppies be grown in home gardens?
+Yes, prickly poppies can be cultivated in home gardens, but with caution. They require well-drained soil and plenty of sunlight. However, due to their spines and potential invasiveness, it’s essential to choose the right location and consider wearing gloves when handling them.
What are some traditional uses of prickly poppies in indigenous cultures?
+Indigenous communities have used prickly poppies for various purposes, including as a pain reliever, anti-inflammatory, and even as a treatment for certain skin conditions. However, it’s important to approach these traditional practices with caution and under the guidance of experienced healers.
Are there any conservation efforts focused on prickly poppies?
+Yes, conservation efforts are underway to protect and study prickly poppies, particularly in regions where they are native. These efforts aim to understand their ecological role, promote sustainable use, and prevent the loss of their genetic diversity.