Unleash Your Creativity with Plant Cell Coloring
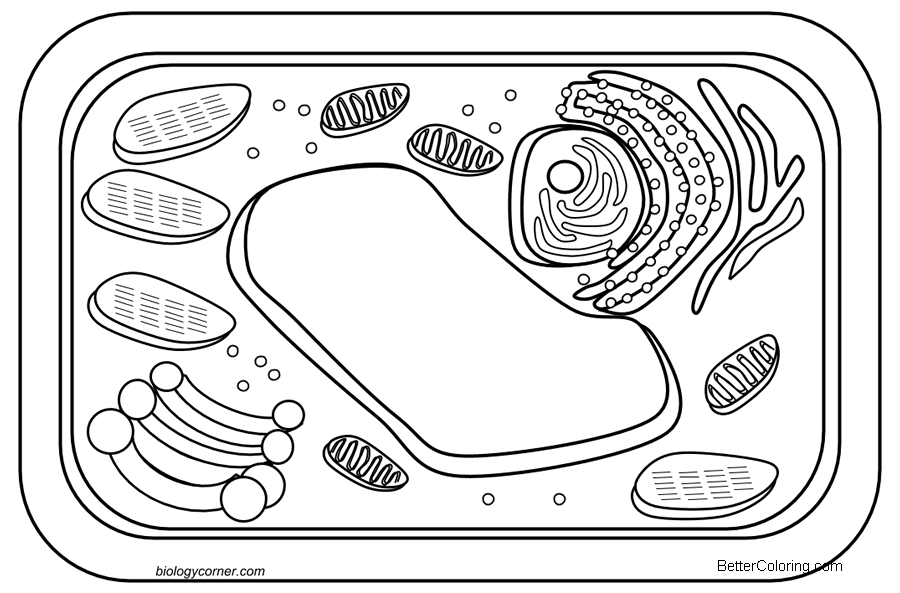
It’s time to dive into the fascinating world of plant cells and unleash your artistic side with a unique coloring activity that will not only spark your creativity but also deepen your understanding of these microscopic marvels. Plant cells, with their intricate structures and diverse functions, offer a captivating canvas for artistic exploration.
Get ready to explore the hidden beauty of plant cells, as we take a journey through the wonders of coloring, combining science and art in a way that will leave you with a newfound appreciation for the microscopic world.
The Intriguing World of Plant Cells

Plant cells, the building blocks of the green kingdom, are far more complex than one might initially think. Beyond their role in photosynthesis, plant cells showcase a remarkable array of specialized structures and functions that contribute to the overall health and vitality of plants.
Cell Wall:
A rigid yet flexible structure that provides support and protection, the cell wall is composed of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate. It acts as a barrier, preventing the cell from bursting due to turgor pressure, and also plays a crucial role in defining the shape and structure of the plant.
Chloroplasts:
These organelles are the powerhouses of photosynthesis, containing the pigment chlorophyll, which gives plants their characteristic green color. Chloroplasts capture sunlight and convert it into chemical energy through a series of complex reactions, ultimately providing the energy needed for plant growth and development.
Vacuole:
A large, water-filled sac that serves as a storage depot for various substances, the vacuole is crucial for maintaining the cell’s turgidity and overall structure. It also plays a role in waste disposal and can even contain pigments that contribute to the plant’s color.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER):
A network of membranes that extends throughout the cell, the ER is involved in the synthesis, modification, and transport of various molecules. It comes in two forms: smooth ER, which is involved in lipid synthesis and metabolism, and rough ER, which is studded with ribosomes and is crucial for protein synthesis.
Ribosomes:
Small, granular structures that float freely in the cytoplasm or are attached to the rough ER, ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. They read the genetic code carried by messenger RNA (mRNA) and translate it into a specific sequence of amino acids, thereby playing a vital role in the cell’s ability to produce the proteins it needs.
Mitochondria:
Often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell, mitochondria are responsible for generating the energy currency of the cell, ATP (adenosine triphosphate). They do this through a process called cellular respiration, which involves the breakdown of glucose and other molecules to release energy.
Golgi Apparatus:
A stack of flattened sacs, the Golgi apparatus is involved in the sorting, packaging, and distribution of various molecules, including proteins and lipids. It plays a crucial role in the cell’s ability to transport substances to their correct destinations.
Lysosomes:
Small, membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes, lysosomes are responsible for breaking down waste materials and cellular debris. They also play a role in the recycling of cellular components, ensuring the cell’s health and efficiency.
Nucleus:
The command center of the cell, the nucleus houses the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and directs the cell’s activities. It is responsible for controlling protein synthesis, cell growth, and reproduction.
Coloring Plant Cells: A Creative Journey
Coloring plant cells offers a unique opportunity to explore the intricate details of these microscopic structures and to express your creativity in a scientifically inspired way. It’s a journey that combines the precision of scientific observation with the freedom of artistic expression, resulting in a deeply satisfying and educational experience.
Choosing Your Medium:
The choice of coloring medium is a crucial step in this process. From traditional pencils and colored pens to watercolors and digital tools, the options are vast. Each medium offers a different experience, allowing you to experiment and find the one that best suits your artistic style and preferences.
Understanding Color Theory:
To create an accurate and aesthetically pleasing representation of plant cells, a basic understanding of color theory is essential. This includes knowledge of color mixing, color harmony, and the use of complementary colors to create depth and contrast.
Exploring Color Variations:
Plant cells offer a rich palette of colors, from the vibrant green of chloroplasts to the deep purple of certain cell wall components. By experimenting with different shades and hues, you can capture the true beauty of these microscopic structures and create a visually stunning representation.
Adding Textural Elements:
To bring your plant cell artwork to life, consider adding textural elements. This could involve using different shading techniques to depict the three-dimensional nature of cell structures, or incorporating patterns and textures to represent the intricate details of the cell wall or ER.
Incorporating Artistic Styles:
Coloring plant cells provides an opportunity to explore various artistic styles. From realistic depictions that faithfully represent the microscopic world to more abstract interpretations that emphasize form and color, the possibilities are endless.
The Educational Benefits of Coloring Plant Cells
Beyond its artistic merits, coloring plant cells offers a wealth of educational benefits. It provides a hands-on approach to learning about cell structures and functions, fostering a deeper understanding of the microscopic world.
Enhancing Scientific Understanding:
By engaging with plant cells in a creative way, students and enthusiasts can develop a more intuitive grasp of cell biology. The process of coloring requires a careful study of cell structures, leading to a deeper understanding of their functions and interactions.
Promoting Visual Learning:
Visual learning is a powerful tool for understanding complex concepts. Coloring plant cells provides a visual aid that helps to reinforce the knowledge gained through traditional study methods. It allows learners to associate the abstract with the concrete, making the learning experience more engaging and memorable.
Encouraging Creative Thinking:
The creative process involved in coloring plant cells stimulates the imagination and encourages creative thinking. It provides an outlet for self-expression and can foster a deeper connection with the subject matter, leading to a more engaged and passionate learning experience.
Developing Fine Motor Skills:
The precision required in coloring plant cells, especially when working with intricate details, helps to develop fine motor skills. This is particularly beneficial for younger learners, as it supports the development of hand-eye coordination and dexterity.
A Unique Blend of Art and Science
Coloring plant cells offers a unique blend of artistic expression and scientific exploration. It provides a fun and engaging way to learn about the microscopic world, fostering a deeper appreciation for the intricate beauty of plant cells.
By combining the precision of scientific observation with the freedom of artistic expression, this activity offers a holistic learning experience that caters to a wide range of learning styles and interests.
So, whether you’re an aspiring artist, a biology enthusiast, or simply someone looking for a creative outlet, unleashing your creativity with plant cell coloring is a journey that promises to be both educational and immensely rewarding.
Get your coloring tools ready, and let’s embark on this colorful exploration of the microscopic world!


