The Easy Guide to Filtering Pivot Tables

Are you overwhelmed by the sheer volume of data you need to analyze and filter on a daily basis? Pivot tables are a powerful tool in Microsoft Excel that can help you quickly summarize and analyze large datasets. However, knowing how to effectively filter and manipulate pivot tables can be a game-changer, saving you time and effort in your data analysis journey.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of pivot table filtering, exploring various techniques and best practices. Whether you're a seasoned data analyst or a beginner looking to enhance your Excel skills, this article will provide you with the knowledge and confidence to tackle any pivot table filtering challenge.
Understanding Pivot Table Filtering

Pivot tables are an invaluable asset when it comes to analyzing and presenting data in a structured manner. They allow you to dynamically summarize and organize large datasets, making it easier to identify patterns, trends, and insights. However, the true power of pivot tables lies in their filtering capabilities, which enable you to focus on specific subsets of data, refine your analysis, and make informed decisions.
Why Filter Pivot Tables?
Filtering pivot tables offers numerous benefits. It allows you to:
- Focus on relevant data: By applying filters, you can quickly narrow down your dataset to specific criteria, such as a particular date range, product category, or customer segment. This helps you analyze and visualize only the data that matters, reducing clutter and improving clarity.
- Compare and contrast: Filters enable you to compare different segments of your data side by side. For example, you can analyze sales performance by region, product type, or customer demographic, gaining valuable insights into trends and variations.
- Identify anomalies and outliers: Filtering can help you identify unusual patterns or outliers in your data. By isolating specific criteria, you can uncover potential issues, errors, or opportunities that may not be apparent in the raw dataset.
- Enhance data visualization: With filtered pivot tables, you can create dynamic and interactive visualizations, such as charts and graphs, that update automatically as you apply different filters. This enables you to present your analysis in a visually appealing and impactful manner.
Mastering the Art of Pivot Table Filtering
Now that we understand the importance of filtering pivot tables, let’s explore the various techniques and best practices to become a filtering expert.
Step 1: Create Your Pivot Table
Before we dive into filtering, ensure you have a pivot table set up with your desired data fields. If you’re new to pivot tables, here’s a quick guide to creating one:
- Select the data range you want to analyze.
- Go to the “Insert” tab in Excel and click on the “PivotTable” button.
- Choose whether you want to insert the pivot table into a new worksheet or an existing one.
- Drag and drop the fields you want to include in your pivot table into the appropriate areas (rows, columns, values, filters). This will create the initial layout of your pivot table.
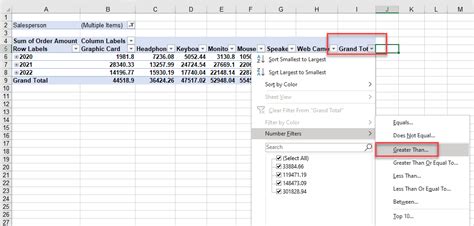
Step 2: Apply Filters to Your Pivot Table
Once you have your pivot table set up, it’s time to add filters. Filters allow you to control which data is displayed in your pivot table. Here’s how to apply filters:
- Select a cell within your pivot table.
- Go to the “Analyze” tab in Excel’s ribbon and click on the “Filter” button.
- A filter dropdown menu will appear for each field in your pivot table. Click on the arrow next to the field you want to filter.
- Choose the criteria you want to filter by. Excel offers various options, including selecting specific items, using checkboxes, entering custom values, or using date filters.
- As you apply filters, your pivot table will automatically update to display only the data that meets your criteria.
Advanced Filtering Techniques
Excel provides several advanced filtering techniques that can help you refine your analysis further. Let’s explore some of these techniques:
1. Multiple Filters
You can apply multiple filters to your pivot table to narrow down your analysis even further. Simply repeat the filtering process for each field you want to filter. For example, you can filter by product category and then apply an additional filter for a specific date range.
2. Filter by Dates
Filtering by dates is a common and powerful technique. Excel provides a user-friendly interface for filtering by date ranges. When you click on the filter dropdown for a date field, you’ll see options to select specific dates, use relative date ranges (e.g., “Last Month,” “This Year”), or create custom date ranges.
3. Filter by Top/Bottom Values
Excel allows you to filter your pivot table to show only the top or bottom values based on a specific field. For example, you can display the top 10 products by sales revenue or the bottom 5 customers by order frequency. This technique is particularly useful for identifying high-performing or underperforming segments of your data.
4. Filter by Values or Conditions
You can also filter your pivot table based on specific values or conditions. For instance, you can filter to show only records where the sales amount is greater than a certain threshold or where the customer’s age is within a particular range. This flexibility allows you to analyze your data from different angles and gain deeper insights.
5. Slicers
Slicers are a visual filtering tool in Excel that allows you to create interactive filters for your pivot table. They provide a user-friendly way to apply and adjust filters quickly. You can create slicers for multiple fields, and as you select or deselect options on the slicer, your pivot table will update instantly. Slicers are particularly useful when presenting data to others, as they offer a dynamic and intuitive filtering experience.
Working with Filtered Data
Once you’ve applied filters to your pivot table, you can perform various operations on the filtered data. Here are some common tasks you might want to perform:
- Calculations: You can perform calculations on the filtered data, such as calculating the sum, average, or count of a specific field. This allows you to analyze and derive meaningful insights from the filtered subset of your data.
- Data Analysis: With filtered data, you can conduct further analysis, such as comparing different segments, identifying trends, or running statistical calculations. Excel provides a range of tools, including pivot charts and data analysis add-ins, to assist you in your analysis.
- Data Visualization: Create compelling visualizations, such as charts, graphs, or dashboards, based on your filtered data. This helps you communicate your findings and insights effectively to stakeholders or decision-makers.
Best Practices for Pivot Table Filtering
To ensure you make the most of your pivot table filtering capabilities, here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Start with a Well-Structured Dataset: Ensure your data is clean, organized, and free from errors. This will make it easier to create accurate pivot tables and apply filters effectively.
- Understand Your Data: Take the time to understand your dataset and the relationships between different fields. This knowledge will guide you in selecting the appropriate fields for filtering and analysis.
- Use Meaningful Field Names: Choose descriptive and meaningful names for your pivot table fields. This will make it easier to identify and select the correct fields when applying filters.
- Utilize Multiple Filters: Don’t be afraid to apply multiple filters to your pivot table. This allows you to drill down into your data and analyze specific subsets, uncovering valuable insights.
- Combine Filters with Calculations: Take advantage of Excel’s calculation capabilities by performing calculations on your filtered data. This can help you derive more meaningful metrics and insights from your analysis.
- Visualize Your Data: Create visually appealing charts and graphs based on your filtered data. Visual representations can make complex data more accessible and easier to understand for yourself and others.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While pivot table filtering is a powerful tool, you may encounter some common issues along the way. Here are a few troubleshooting tips to help you overcome potential challenges:
- Filter Not Updating: If your pivot table filter is not updating as expected, ensure you have selected the correct cell within the pivot table before applying the filter. Also, check if you have any hidden or filtered rows or columns that may be affecting the filter’s behavior.
- Incorrect Filter Results: If your filter is not producing the expected results, double-check your filter settings and criteria. Ensure you have selected the correct field and applied the appropriate filter options.
- Slow Performance: Large datasets or complex pivot tables can sometimes lead to slow performance when applying filters. Consider optimizing your data by removing unnecessary rows or columns, using data compression techniques, or breaking down your analysis into smaller segments.
Advanced Filtering Techniques with Excel Functions

Excel offers a wide range of functions and formulas that can enhance your pivot table filtering capabilities. Here are a few advanced techniques to explore:
- VLOOKUP: The VLOOKUP function can be used to retrieve specific values from your dataset based on a lookup value. This function is particularly useful when you need to filter or analyze data based on specific criteria that may not be directly available in your pivot table fields.
- COUNTIF and SUMIF: These functions allow you to count or sum values in your dataset based on specific conditions. For example, you can use COUNTIF to count the number of records that meet a certain criteria, such as sales above a certain threshold.
- INDEX and MATCH: The INDEX and MATCH combination is a powerful technique for retrieving values from a dataset based on specific criteria. It can be used to filter and analyze data in a more flexible and dynamic manner.
Conclusion: Elevate Your Data Analysis with Pivot Table Filtering
Pivot table filtering is a valuable skill for any data analyst or Excel user. By mastering the techniques and best practices outlined in this guide, you’ll be able to unlock the full potential of your data analysis and make more informed decisions. Remember to start with a well-structured dataset, understand your data, and utilize multiple filters to drill down into specific insights.
With pivot table filtering, you can efficiently analyze and visualize your data, identify trends, and present your findings in a compelling manner. So, embrace the power of pivot tables, and let your data analysis soar to new heights!
How do I create a pivot table in Excel?
+To create a pivot table in Excel, follow these steps: Select the data range you want to analyze. Go to the “Insert” tab and click on the “PivotTable” button. Choose where you want to insert the pivot table. Drag and drop the fields into the appropriate areas (rows, columns, values, filters) to create the initial layout.
What are some best practices for pivot table filtering?
+Some best practices for pivot table filtering include starting with a well-structured dataset, understanding your data, using meaningful field names, utilizing multiple filters, combining filters with calculations, and visualizing your data with charts and graphs.
Can I filter pivot tables based on multiple criteria?
+Yes, you can apply multiple filters to your pivot table. Simply repeat the filtering process for each field you want to filter. This allows you to narrow down your analysis and focus on specific subsets of data.