Get Your Pivot Table Dates Right
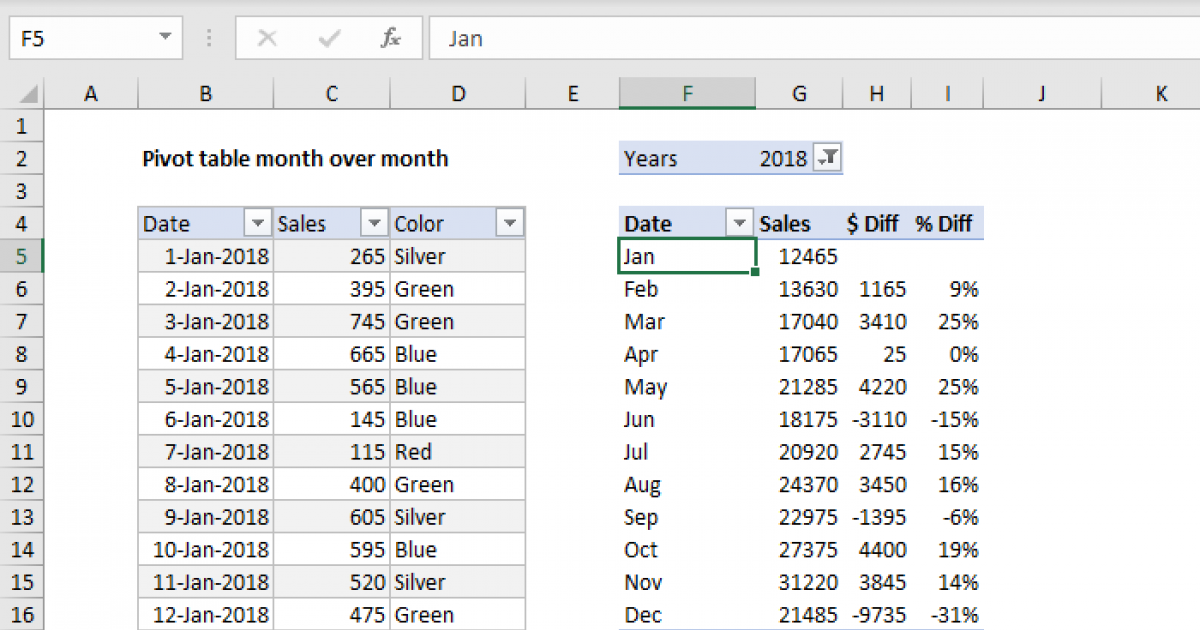
In the world of data analysis and reporting, pivot tables are an invaluable tool for professionals across various industries. However, one common challenge that analysts often encounter is correctly managing dates in pivot tables. Accurate date formatting and manipulation are crucial for generating meaningful insights and ensuring the integrity of your data. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of working with dates in pivot tables, offering practical solutions and best practices to help you master this essential aspect of data analysis.
The Significance of Dates in Pivot Tables
Dates serve as a foundational element in many datasets, especially those involving time-based information such as sales data, customer behavior, or financial records. When constructing pivot tables, the way you handle dates can significantly impact the accuracy and usefulness of your analysis. Incorrect date formatting or calculations can lead to misinterpretations and inaccurate conclusions, potentially affecting business decisions.
Common Challenges with Date Handling

When working with dates in pivot tables, several challenges may arise:
- Date Format Consistency: Ensuring that all dates in your dataset are in a consistent format is crucial. Mismatched date formats can lead to errors in calculations and sorting.
- Calculations and Formulas: Performing calculations on dates, such as finding the difference between two dates or determining the fiscal year, requires careful consideration and often involves using specific functions.
- Grouping and Aggregation: Grouping data by dates, especially when dealing with granular time periods like days, weeks, or months, can be complex. It’s essential to ensure that the grouping is accurate and aligns with your analysis goals.
- Handling Missing or Inconsistent Data: Datasets often contain missing or incomplete date information. Effective strategies are needed to handle such gaps without compromising the integrity of your analysis.
Best Practices for Date Management in Pivot Tables
Standardize Date Formats
Before creating your pivot table, ensure that all date values in your dataset are in a standardized format. Commonly used date formats include YYYY-MM-DD, MM/DD/YYYY, or DD/MM/YYYY. Consistency is key; make sure all dates adhere to the same format to avoid potential errors.
Utilize Date Functions
Familiarize yourself with date-related functions in your spreadsheet software. For instance, in Microsoft Excel, functions like DATE, YEAR, MONTH, DAY, and NETWORKDAYS can be invaluable for calculating and manipulating dates. Similarly, in Google Sheets, functions like DATEVALUE, YEAR, MONTH, and WEEKDAY offer powerful date-handling capabilities.
Group Dates Effectively
When grouping data by dates, consider the level of granularity required for your analysis. For instance, if you’re analyzing sales trends, grouping by months might be sufficient. However, for more detailed insights, you might need to group by weeks or even days. Ensure that the grouping intervals align with your business needs and the nature of your data.
| Grouping Interval | Description |
|---|---|
| Year | Ideal for high-level trend analysis and comparing annual performance. |
| Quarter | Useful for examining seasonal patterns and comparing performance across quarters. |
| Month | Commonly used for tracking monthly sales, expenses, or website traffic. |
| Week | Provides detailed insights into weekly patterns, especially for time-sensitive industries. |
| Day | Essential for analyzing daily fluctuations, such as in e-commerce or financial data. |

Handle Missing or Inconsistent Data
Datasets often contain gaps or inconsistencies in date information. Here are some strategies to address this:
- Data Cleaning: Manually review and clean your dataset to identify and rectify any obvious errors or missing values.
- Imputation Techniques: Consider using imputation methods to fill in missing date values. This could involve estimating values based on the average of nearby dates or using a specific formula.
- Data Validation: Implement data validation rules to ensure that dates entered into your dataset are valid and in the expected format.
Advanced Date Handling Techniques
Calculating Fiscal Years
In many organizations, financial data is analyzed based on fiscal years, which may not align with the calendar year. To calculate fiscal years accurately, you can use custom functions or formulas. For example, in Excel, you might use the DATE function to determine the fiscal year based on a specific start date.
Working with Date Intervals
When analyzing time-based data, understanding date intervals is crucial. Date intervals refer to the difference between two dates, often expressed in years, months, or days. Functions like DATEDIF in Excel or DATE_DIFF in Google Sheets can help calculate these intervals accurately.
Creating Custom Date Groups
Sometimes, standard date groupings like years, quarters, or months might not align with your specific analysis needs. In such cases, you can create custom date groups. For instance, you might want to group data by half-year periods or specific seasons. This can be achieved by using conditional formatting or custom functions to categorize dates as per your requirements.
Tips for Troubleshooting Date Issues

Despite your best efforts, you may encounter date-related errors or inconsistencies in your pivot tables. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Check Date Formats: Ensure that all dates in your dataset are in a consistent format. Mismatched date formats can lead to unexpected results.
- Review Formulas: Double-check the formulas or functions you’ve used to manipulate dates. A simple typo or incorrect reference can cause errors.
- Use Error-Checking Tools: Utilize error-checking features in your spreadsheet software to identify and resolve potential issues.
- Test with Sample Data: Before applying your pivot table settings to a large dataset, test them on a smaller sample to ensure accuracy.
Future Considerations: Dynamic Date Handling
As data analysts, we often work with dynamic datasets that are regularly updated. To ensure that your pivot tables remain accurate and up-to-date, consider implementing dynamic date handling techniques. This involves using formulas or macros that automatically update your pivot tables whenever new data is added or existing data is modified.
Conclusion: Mastering Date Handling for Effective Analysis
Date handling in pivot tables is a critical skill for data analysts and professionals working with time-based data. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your pivot tables provide accurate and meaningful insights. Remember, accurate date formatting, consistent grouping, and effective handling of missing data are the keys to unlocking the full potential of your analysis.
FAQ
How can I ensure date consistency across my dataset?
+To maintain date consistency, standardize the format of all date values in your dataset. Use a single format, such as YYYY-MM-DD, and ensure that all dates adhere to this format. This practice minimizes errors and simplifies date calculations.
What are some common date-related functions in Excel and Google Sheets?
+In Excel, key date functions include DATE, YEAR, MONTH, DAY, and NETWORKDAYS. These functions help manipulate and calculate dates. Similarly, in Google Sheets, functions like DATEVALUE, YEAR, MONTH, and WEEKDAY offer similar capabilities.
How do I calculate fiscal years in my pivot table?
+To calculate fiscal years, you can use custom functions or formulas. For instance, in Excel, you might use the DATE function along with a specified start date for your fiscal year. This allows you to determine the fiscal year for any given date in your dataset.



