How to Read Pie Charts with Fractions
Pie charts are a popular and intuitive way to visualize data, often used to represent proportions and percentages. However, reading and interpreting pie charts can be a bit tricky, especially when they involve fractions. This guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of how to effectively read and analyze pie charts with fractions, helping you extract valuable insights from data presentations.
Understanding Pie Charts and Fractions

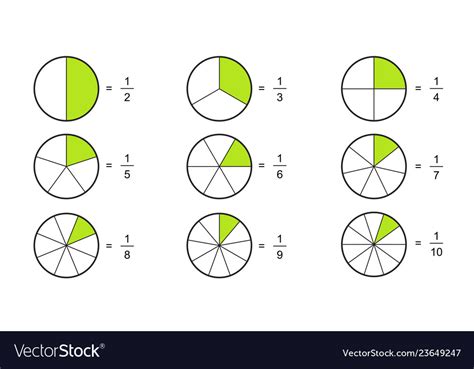
Pie charts are circular diagrams divided into segments, where each segment represents a particular category or data point. The size of each segment corresponds to the proportion or percentage it represents in the whole dataset. Fractions, on the other hand, are numerical values that express parts of a whole, typically in the form of a/b, where a is the numerator (the part) and b is the denominator (the whole). When fractions are used in pie charts, they provide a more detailed breakdown of the data, often offering a precise representation of proportions.
Key Techniques for Reading Pie Charts with Fractions

To effectively read and interpret pie charts with fractions, consider the following techniques:
1. Identifying Segments and Their Fractions
Start by examining each segment of the pie chart. Look for labels or values that indicate the category or data point represented by the segment. Alongside or within the segment, you should find the corresponding fraction. For instance, you might see a segment labeled “Apples” with the fraction 3⁄8 written inside it.
2. Understanding the Whole and Its Fraction
Pie charts with fractions often have a designated segment or label that represents the whole. This segment is typically marked as “Total” or “Whole”, and its fraction will be 1, indicating that it represents the entire dataset. Understanding the whole helps you grasp the context and scale of the fractions in the other segments.
3. Converting Fractions to Percentages
While fractions provide precise information, percentages are often easier to interpret and compare. To convert fractions to percentages, you can multiply the fraction by 100. For example, if a segment has a fraction of 3⁄8, the percentage it represents is 37.5% (3⁄8 * 100 = 37.5%). This conversion allows you to compare different segments more intuitively.
4. Calculating Absolute Values
If the pie chart provides the total number of items or the total value represented by the whole, you can calculate the absolute values for each segment. Multiply the fraction by the total to find the absolute value. For instance, if the whole represents 16 items and a segment has a fraction of 3⁄8, the absolute value for that segment is 6 (16 * 3⁄8 = 6).
5. Analyzing Proportions and Relationships
One of the strengths of pie charts with fractions is their ability to highlight proportions and relationships between different categories. Compare the sizes of the segments and their corresponding fractions to understand the relative importance of each category. Look for segments with larger fractions or percentages, as they indicate a more significant portion of the whole.
| Category | Fraction | Percentage | Absolute Value (Total: 50) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apples | 3/8 | 37.5% | 18.75 |
| Bananas | 2/8 | 25% | 12.5 |
| Oranges | 1/8 | 12.5% | 6.25 |
| Grapes | 2/8 | 25% | 12.5 |
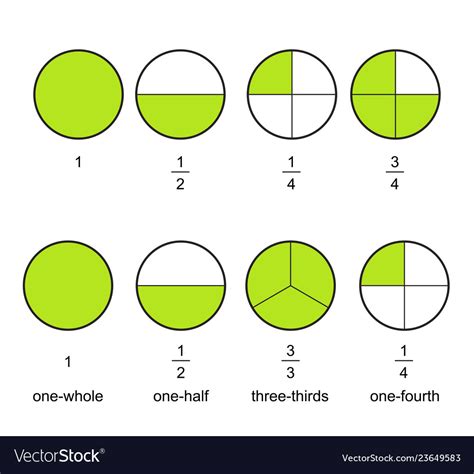
6. Comparing Multiple Pie Charts
Sometimes, you might encounter multiple pie charts representing different datasets or categories. When comparing these charts, pay attention to the scales and fractions used. Ensure that the fractions or percentages are consistent across charts to facilitate accurate comparisons. Look for similarities and differences in the patterns and proportions depicted.
Practical Example: Analyzing Student Grades
Let’s consider a practical scenario: analyzing student grades in a mathematics class. The teacher has created a pie chart to visualize the distribution of grades, using fractions to represent the proportions of students achieving different grades.
In this pie chart, each segment represents a grade range, and the fraction inside each segment indicates the proportion of students who achieved that grade. For instance, the segment labeled "A" has a fraction of 1/4, meaning 25% of the students received an "A" grade.
By examining the chart, we can quickly identify that 75% of the students (the sum of the fractions for "B" and "C" grades) received a grade of "B" or "C". This provides valuable insights into the overall performance of the class and can help the teacher identify areas where additional support might be needed.
Conclusion: Mastery of Pie Charts with Fractions
Reading and interpreting pie charts with fractions is a valuable skill, enabling you to extract detailed insights from data visualizations. By understanding the relationship between fractions and percentages, you can analyze proportions and make meaningful comparisons. With practice, you’ll become adept at deciphering the stories told by pie charts, whether in academic settings, business reports, or everyday data presentations.
How can I compare fractions in pie charts effectively?
+To compare fractions in pie charts, it’s best to convert them to percentages. This simplifies the comparison process and allows you to quickly identify the relative sizes of different segments. Multiply each fraction by 100 to convert it to a percentage.
Are pie charts with fractions more accurate than those with percentages?
+Pie charts with fractions can provide more precise representations of proportions, especially when dealing with small datasets or when the data needs to be divided into many categories. However, for ease of interpretation and comparison, pie charts with percentages are often preferred, as they are more intuitive for most audiences.
Can I convert percentages back to fractions in a pie chart?
+Absolutely! To convert a percentage back to a fraction, divide the percentage by 100. For example, if a segment has a percentage of 25%, the corresponding fraction is 1⁄4. This conversion is useful when you want to maintain precision or perform further calculations.