Download the Periodic Table PDF Now
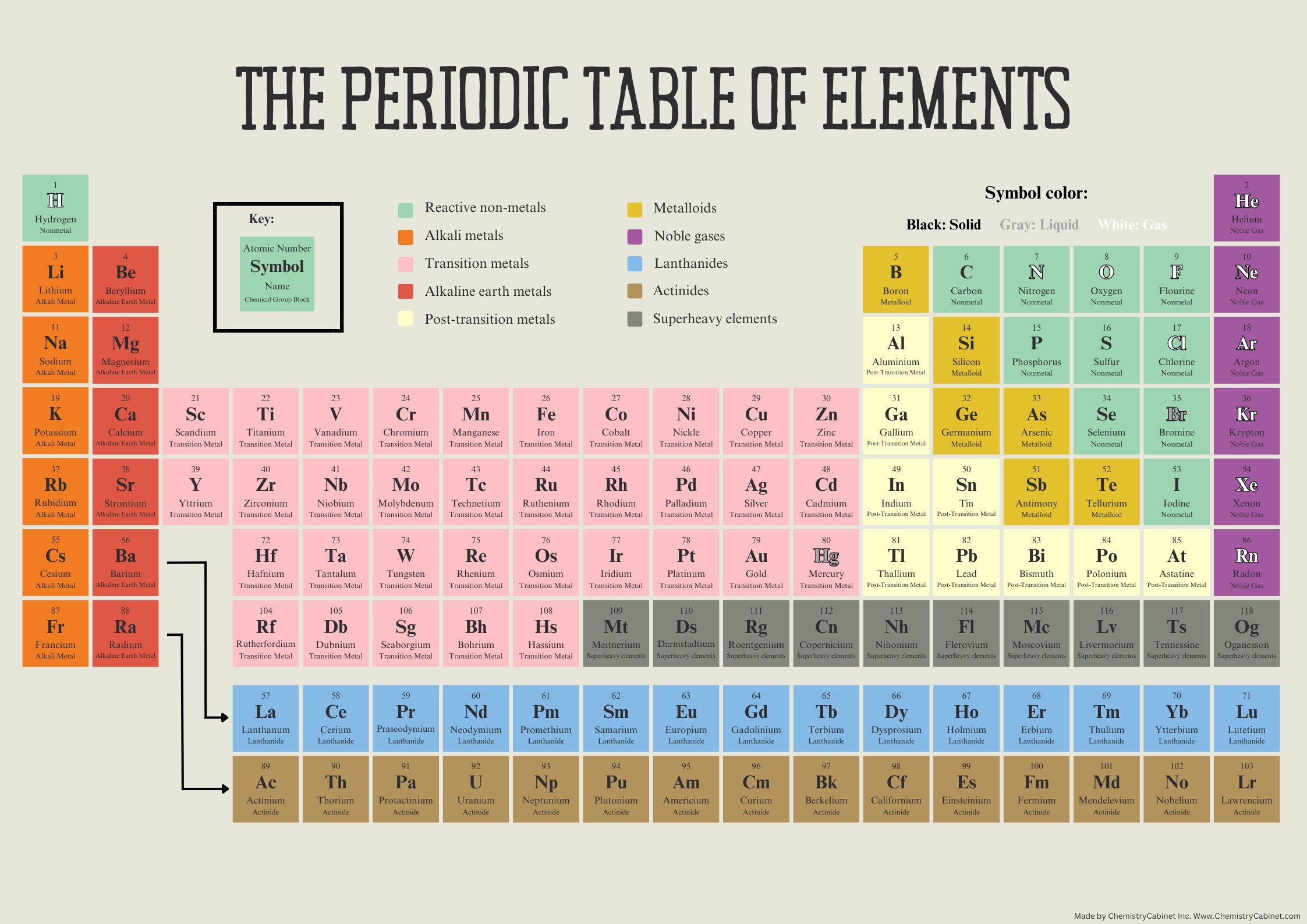
The Periodic Table: A Visual Guide to the Building Blocks of Our Universe

Step into the fascinating world of chemistry, where elements come alive and the Periodic Table reigns supreme. This comprehensive guide will unveil the secrets and wonders of this iconic chart, providing you with an immersive journey through the elements that shape our universe. From its humble beginnings to its modern-day complexity, get ready to explore the Periodic Table like never before!
The Evolution of the Periodic Table
The story of the Periodic Table is a testament to human curiosity and scientific discovery. It all began in the mid-19th century when a Russian chemist, Dmitri Mendeleev, sought to organize the known elements into a logical system. Mendeleev’s vision was revolutionary, as he recognized patterns and trends in the properties of elements, leading to the creation of the first Periodic Table.
Over time, as more elements were discovered and our understanding of atomic structure deepened, the Periodic Table evolved. Today, it stands as a testament to the progress of chemistry, showcasing a vast array of elements, each with its unique properties and characteristics.
Unraveling the Secrets of the Table
The Periodic Table is more than just a collection of elements; it’s a powerful tool that reveals the underlying principles of chemistry. Each element, represented by its symbol and atomic number, holds a wealth of information. Here’s a glimpse into what this visual masterpiece can teach us:
Periodic Trends: As you move across and down the table, you’ll notice distinct patterns in the properties of elements. For instance, atomic radius tends to increase as you go down a group, while ionization energy decreases. These trends provide valuable insights into the behavior of elements and their reactions.
Chemical Families: The Periodic Table groups elements into families, or groups, based on their similar properties. For example, the alkali metals, located on the leftmost column, share characteristics like high reactivity and the ability to form positive ions. Understanding these families helps chemists predict the behavior of unknown elements.
Atomic Structure: The table’s layout provides a visual representation of the electron configuration of each element. By studying the arrangement of electrons in different energy levels, chemists can explain the stability, reactivity, and bonding behavior of elements.
Exploring the Elements
Now, let’s delve deeper into the world of elements and uncover some fascinating facts:
Hydrogen (H): The simplest and most abundant element in the universe, hydrogen is a key component of water and a vital energy carrier. Its unique properties make it a focus of research for clean energy solutions.
Carbon ©: Known as the building block of life, carbon forms the backbone of organic compounds. Its ability to form diverse bonds and structures has led to the incredible complexity of living organisms.
Oxygen (O): Vital for respiration and essential for life, oxygen is also highly reactive. It plays a crucial role in combustion and is a key component of the air we breathe.
Gold (Au): A precious metal with a long history of fascination, gold is renowned for its beauty and resistance to corrosion. Its unique properties have made it valuable for jewelry, electronics, and even medical applications.
The Impact of the Periodic Table
The Periodic Table’s influence extends far beyond the confines of chemistry laboratories. Its principles and insights have revolutionized industries, shaped technological advancements, and even inspired artistic endeavors. Here are some real-world applications:
Materials Science: Chemists and engineers rely on the Periodic Table to design and develop new materials with specific properties. From superstrong alloys for aerospace to biocompatible materials for medical implants, the table guides innovation.
Environmental Science: Understanding the properties of elements is crucial for addressing environmental challenges. For instance, knowledge of heavy metals and their toxicity helps scientists develop strategies for pollution control and remediation.
Forensic Chemistry: The Periodic Table plays a vital role in forensic investigations. By analyzing the elements present in evidence, forensic chemists can uncover critical clues, identify substances, and solve complex crimes.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Using the Periodic Table
For those new to the world of chemistry, here’s a simple guide to navigating and utilizing the Periodic Table:
Familiarize Yourself: Start by exploring the layout and organization of the table. Notice the groups, periods, and blocks that categorize elements.
Locate Elements: Practice finding specific elements by their symbol or atomic number. This skill is essential for referencing element properties and characteristics.
Understand Trends: Study the patterns and trends across the table. Look for variations in atomic radius, ionization energy, or electronegativity as you move through different regions.
Explore Families: Learn about the different chemical families and their characteristic properties. This knowledge will help you predict the behavior of elements and understand their roles in chemical reactions.
Apply in Practice: Use the Periodic Table as a tool for problem-solving and chemical analysis. Whether it’s balancing equations, predicting reaction outcomes, or designing experiments, the table will be your trusted companion.
Final Thoughts
The Periodic Table is not merely a static chart; it’s a dynamic representation of the building blocks of our universe. Its evolution and ongoing discoveries continue to inspire curiosity and drive scientific progress. By embracing the Periodic Table, we unlock a wealth of knowledge and the potential to create a better world.
Remember, the journey of discovery is ongoing, and the Periodic Table stands as a beacon, guiding us through the wonders of chemistry. So, embrace the elements, explore their secrets, and let your curiosity fuel your passion for science!
How many elements are currently known and included in the Periodic Table?
+As of my last update in January 2023, there are 118 known elements officially recognized and included in the Periodic Table. However, ongoing research and discovery may lead to the addition of new elements in the future.
Can you explain the significance of the different colors used in the Periodic Table?
+The colors used in some versions of the Periodic Table are often employed to categorize elements based on their physical state at room temperature. For instance, metals are typically represented in shades of gray or silver, while non-metals might be colored in various hues. This visual aid helps distinguish between different types of elements at a glance.
What is the longest-named element on the Periodic Table, and why does it have such a lengthy name?
+The longest-named element on the Periodic Table is currently ununtrium (Uut), with an atomic number of 113. Its name derives from the temporary systematic element name, which combines the numerical value of its atomic number with the suffix “-ium” to indicate a metallic element. The lengthy name is a placeholder until the element is officially named by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), following thorough review and confirmation of its discovery.
Are there any elements that are considered rare or valuable, and why?
+Yes, several elements are considered rare or valuable due to their limited availability, unique properties, or specific applications. For example, platinum (Pt) and gold (Au) are highly valued for their resistance to corrosion and use in jewelry and electronics. Similarly, rare earth elements like neodymium (Nd) and dysprosium (Dy) are essential for modern technologies, such as permanent magnets and hybrid car batteries.



