Unveiling the Secrets of Periodic Chemistry
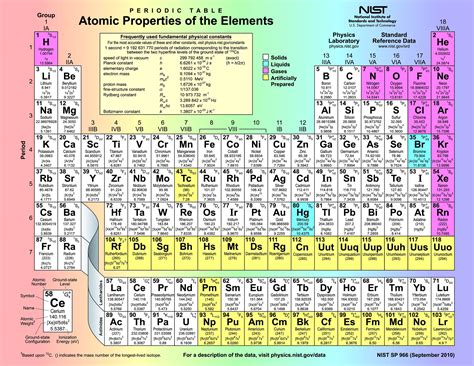
The world of chemistry is an intricate tapestry woven with the threads of elements, each possessing unique properties and behaviors. At the heart of this tapestry lies the periodic table, a masterpiece of scientific organization that reveals the secrets of the elements and their relationships. In this exploration, we delve into the fascinating realm of periodic chemistry, uncovering the underlying principles and phenomena that shape our understanding of the chemical universe.
The Historical Evolution of the Periodic Table

The concept of organizing elements is not a modern invention; it has evolved over centuries, with early chemists recognizing patterns and similarities in the behavior of different substances. One of the earliest attempts to classify elements was made by the ancient Greeks, who believed in the concept of the four elements: earth, water, air, and fire. While their understanding was simplistic, it laid the foundation for future exploration.
Fast forward to the 19th century, and we witness the groundbreaking work of Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist who is often credited with the creation of the modern periodic table. Mendeleev’s genius lay in his ability to arrange the known elements based on their atomic weights, creating a table that not only organized existing knowledge but also predicted the properties of undiscovered elements. This predictive power is a testament to the elegance and accuracy of his system.
The Periodic Table: A Dynamic Blueprint
The periodic table is more than just a static arrangement of elements; it is a dynamic blueprint that reflects the fundamental principles of chemistry. Each row, or period, represents a new energy level, or shell, of electrons, while the columns, or groups, denote elements with similar electronic configurations and, consequently, similar chemical properties.
Imagine the periodic table as a vast cosmic map, where each element is a celestial body, and the table itself is a cosmic compass. The elements are not static entities but rather dynamic players in a grand chemical symphony, with their properties and behaviors determined by their position in this cosmic map.
Unlocking the Secrets: A Journey into Periodicity
The true power of the periodic table lies in its ability to reveal patterns and trends in the properties of elements. As we traverse the table, we encounter a multitude of secrets waiting to be unveiled:
Atomic Radius: Elements within a group share similar atomic radii, with the size of the atom increasing as we move down a group. This trend is a direct consequence of the increasing number of electron shells.
Ionization Energy: The energy required to remove an electron from an atom, known as ionization energy, generally increases as we move from left to right across a period. This phenomenon is attributed to the increasing nuclear charge, which attracts electrons more strongly.
Electronegativity: A measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond, electronegativity also follows a trend across the table. Elements on the right side of the table tend to be more electronegative, while those on the left are less so.
Chemical Reactivity: The periodic table provides a roadmap to chemical reactivity. Elements in the same group often exhibit similar chemical behaviors, while those in different groups can react in unique and fascinating ways.
A Case Study: The Noble Gases
The noble gases, located in group 18 of the periodic table, are a testament to the predictive power of periodic trends. These elements, including helium, neon, argon, and xenon, are renowned for their stability and lack of reactivity. This behavior can be attributed to their complete outer electron shells, which make them extremely reluctant to engage in chemical reactions.
Pros of Noble Gases:
- Exceptional stability
- Inertness in chemical reactions
- Widely used in lighting and insulation
Cons of Noble Gases:
- Limited reactivity makes them challenging to study
- High cost of extraction and purification
Future Trends: Expanding Horizons

The periodic table is a living document, constantly evolving as new elements are discovered and our understanding of existing ones deepens. In recent years, the focus has shifted to the exploration of superheavy elements, those with atomic numbers greater than 100. These elements, created in laboratories through particle accelerators, pose fascinating questions about the limits of the periodic table and the nature of matter itself.
Conclusion: A Chemical Odyssey
In this journey through the secrets of periodic chemistry, we have scratched the surface of a vast and complex field. The periodic table is not just a tool for organization but a key to unlocking the mysteries of the chemical world. As we continue to explore and discover, the secrets of periodic chemistry will continue to inspire and guide us, fueling our curiosity and pushing the boundaries of scientific knowledge.
What is the significance of the periodic table in modern chemistry?
+The periodic table is a fundamental tool in modern chemistry, providing a systematic organization of elements based on their properties. It allows chemists to predict and understand the behavior of elements, aiding in the development of new materials and technologies. Additionally, it serves as a visual representation of the underlying principles of atomic structure and chemical reactivity.
How do scientists use the periodic table to predict chemical behavior?
+Scientists utilize the periodic table to predict chemical behavior by analyzing the trends in element properties. For example, elements in the same group tend to have similar chemical properties due to their identical valence electron configurations. This knowledge allows chemists to make informed predictions about the reactivity and behavior of elements they haven’t studied extensively.
Are there any elements that don’t fit the periodic trends?
+While the periodic table provides a robust framework for understanding element behavior, there are a few exceptions. Some elements, particularly those with higher atomic numbers, exhibit unique properties that deviate from the expected trends. These deviations are often attributed to the complex interplay of quantum mechanics and the electronic structure of these elements.
What are some practical applications of understanding periodic trends?
+Understanding periodic trends has numerous practical applications. For instance, in the field of materials science, knowledge of element properties can guide the development of new materials with specific characteristics. In environmental chemistry, it aids in understanding the behavior of pollutants and their interactions with different elements. Additionally, in medicine, it plays a role in the design of pharmaceutical compounds and drug delivery systems.


