Unveiling the Secrets of Water Heater Components
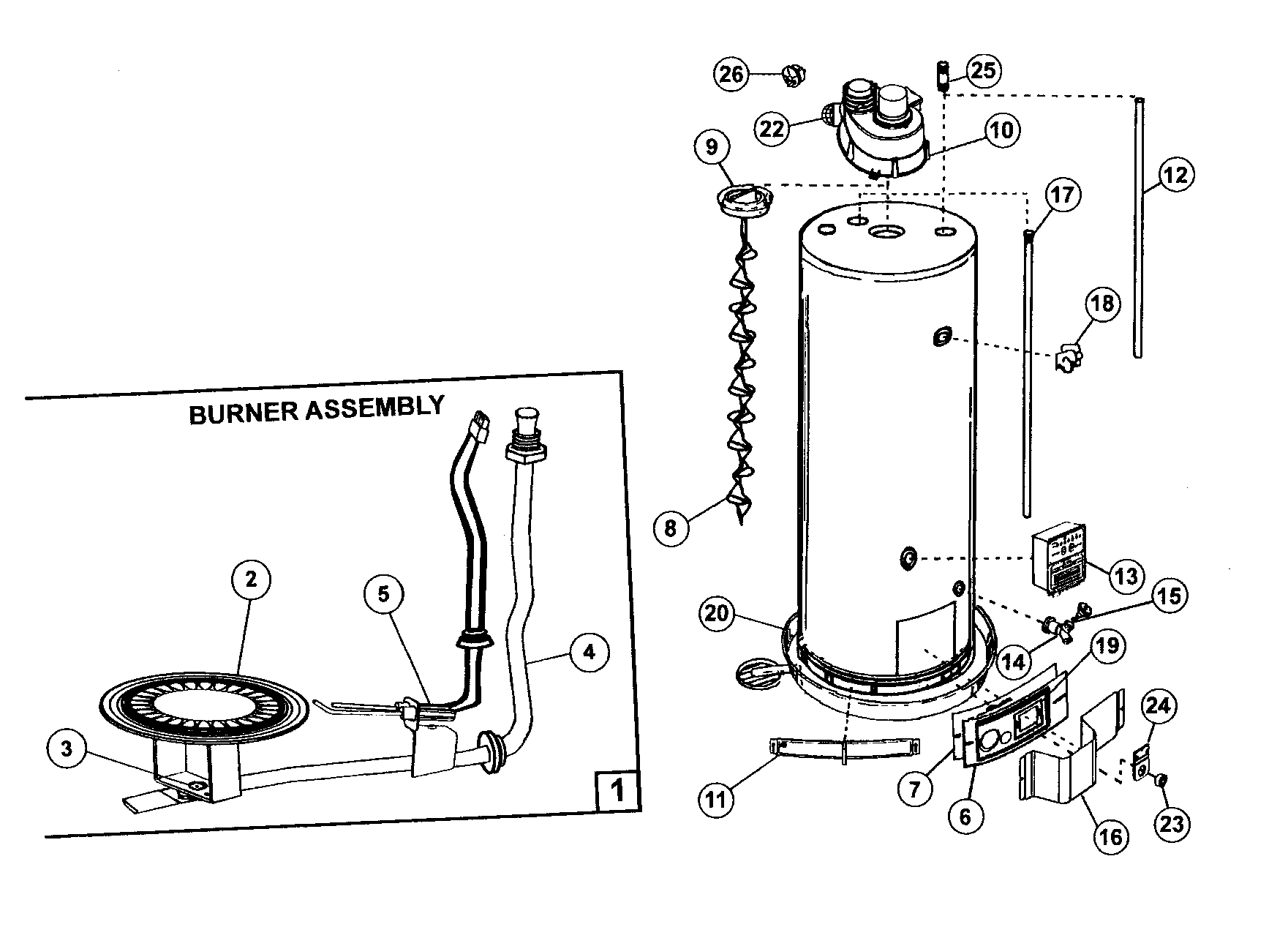
A Deep Dive into the Core Functionality of Water Heaters

Water heaters, often overlooked, are vital appliances that provide us with hot water, an essential aspect of modern living. Yet, few understand the intricate workings behind this everyday convenience. In this article, we will lift the lid on the inner mechanisms, exploring the components that make water heaters such reliable and efficient devices.
The Heart of the Heater: An Exploration of Key Components
The Heating Element
At the core of any water heater is its heating element. This crucial component is responsible for transferring heat energy to the water, raising its temperature to the desired level. Typically, these elements are made from durable metals like stainless steel or copper, ensuring they can withstand the constant exposure to hot water and potential mineral deposits.
There are two primary types of heating elements: electric and gas. Electric elements, often found in residential water heaters, use electrical resistance to generate heat. They are simple in design, easy to replace, and highly efficient. Gas heating elements, on the other hand, use burners to ignite a flame, which then heats the water. While they may be more complex in design, gas elements offer faster heating and are often more cost-effective for larger applications.
The Tank: A Reservoir of Hot Water
The tank is the unsung hero of water heaters. It serves as a reservoir, storing heated water until it is needed. Typically constructed from steel, the tank is coated with a glass lining to protect it from corrosion and ensure its longevity.
The size of the tank is a critical consideration, as it determines the volume of hot water available at any given time. For residential use, tanks ranging from 40 to 60 gallons are common, while commercial applications may require much larger capacities.
Thermostats: The Temperature Regulators
Thermostats are the unsung heroes of water heaters, quietly regulating the temperature of the water to ensure it remains consistent and safe. These devices are integral to the system, ensuring the water is heated to the desired temperature and preventing it from becoming scalding hot.
Modern thermostats offer precise temperature control, often with digital displays and easy-to-use interfaces. Some advanced models even feature vacation modes, allowing users to temporarily lower the water temperature when the heater is not in regular use, saving energy and reducing costs.
Anode Rods: Sacrificial Protectors
Anode rods, often referred to as sacrificial anodes, are a crucial component of water heaters, particularly those with tanks. These rods, typically made from magnesium or aluminum, are designed to corrode instead of the tank itself, thus preventing the tank from rusting and extending its lifespan.
Over time, anode rods will degrade and need to be replaced. Regular maintenance checks should include an inspection of the anode rod to ensure it is still in good condition.
Dip Tubes: Directing Water Flow
Dip tubes are an essential component of water heaters, guiding cold water into the tank’s lower section, where it is heated. This strategic placement ensures efficient heating, as cold water entering the bottom of the tank displaces the heated water, which rises to the top, ready for use.
Pressure Relief Valves: Safety First
Pressure relief valves are critical safety features in water heaters. These valves are designed to open and release pressure if it exceeds a certain threshold, preventing potential explosions or other hazardous situations. Regular testing of these valves is essential to ensure they are functioning correctly.
Maintenance and Longevity
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the longevity and efficiency of water heaters. Beyond checking the anode rod and pressure relief valve, other maintenance tasks include flushing the tank to remove sediment buildup, inspecting the heating element for corrosion or damage, and ensuring all connections are secure and free from leaks.
Pros
- Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of water heaters.
- Well-maintained heaters are more energy-efficient, reducing operating costs.
Cons
- Maintenance requires specialized knowledge and tools.
- Neglecting maintenance can lead to costly repairs or early heater replacement.
Emerging Technologies: The Future of Water Heating
The water heater industry is continually evolving, with new technologies offering improved efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced convenience.
Tankless water heaters, for instance, are gaining popularity due to their on-demand heating capabilities, eliminating the need for a storage tank. These systems heat water only when required, reducing energy waste and providing an endless supply of hot water.
Solar water heaters are another innovative solution, harnessing the power of the sun to heat water. These systems offer significant environmental benefits and can reduce energy costs, particularly in regions with abundant sunlight.
Conclusion: The Unseen Complexity of Water Heaters
Water heaters, despite their humble appearance, are complex machines, with a myriad of components working in harmony to provide us with hot water. From the heating element to the tank, thermostat, and beyond, each part plays a crucial role in ensuring this essential service.
As we’ve explored, regular maintenance and an understanding of these components can significantly extend the lifespan of water heaters, while emerging technologies offer exciting possibilities for the future. So, the next time you step into a hot shower, spare a thought for the intricate workings behind this everyday luxury.



