Master Excel: The Ultimate Guide to Partial Matches
Excel, a powerhouse tool for data manipulation and analysis, offers a wide range of functions and features to streamline complex tasks. Among these, the ability to perform partial matches is an invaluable skill for data professionals. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and techniques to master partial matching in Excel, enhancing your data management prowess.
Understanding Partial Matches in Excel

Partial matching in Excel refers to the process of finding and manipulating data based on specific criteria or patterns within a dataset. It allows you to identify and work with subsets of data that match certain conditions, even if the match is not exact.
For instance, imagine you have a large spreadsheet containing customer information, including their names and email addresses. You want to filter and analyze data for customers whose names start with "John" and whose email addresses contain "@gmail.com". This is where partial matching comes into play, enabling you to quickly retrieve the desired subset of data.
The Power of Excel’s Partial Matching Functions
Excel provides a range of functions specifically designed for partial matching, offering flexibility and precision in data manipulation. Let’s explore some of the key functions and their applications:
- LEFT, MID, and RIGHT Functions: These functions extract a specified number of characters from the left, middle, or right side of a text string, respectively. For example, if you have a list of product codes and need to extract the first three characters, you can use the LEFT function. This is particularly useful when you need to identify patterns within a larger string.
- FIND and SEARCH Functions: These functions locate a specific substring within a text string. The FIND function is case-sensitive, while the SEARCH function is not, making it more versatile. For instance, if you want to find the position of a specific word within a sentence, these functions come in handy.
- LEN Function: The LEN function returns the length of a text string, counting the number of characters. It is often used in conjunction with other functions to perform conditional formatting or data validation.
- CONCATENATE Function: As the name suggests, this function combines multiple text strings into one. It is valuable when you need to merge data from different columns or create custom text strings based on specific conditions.
- SUBSTITUTE Function: The SUBSTITUTE function replaces specific text within a string with new text. It is particularly useful when you need to clean up or standardize data, such as replacing hyphens with spaces or removing special characters.
Practical Application: Filtering and Analyzing Data
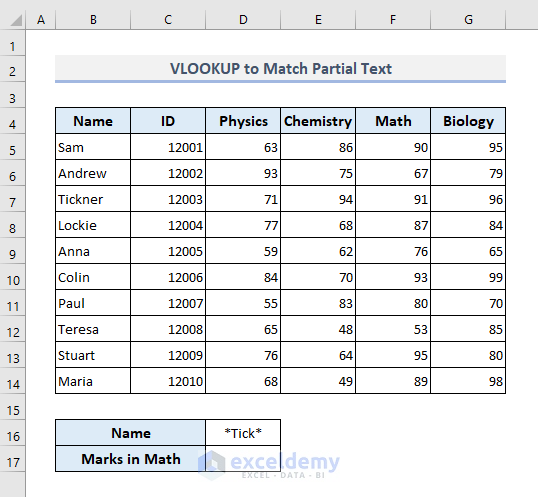
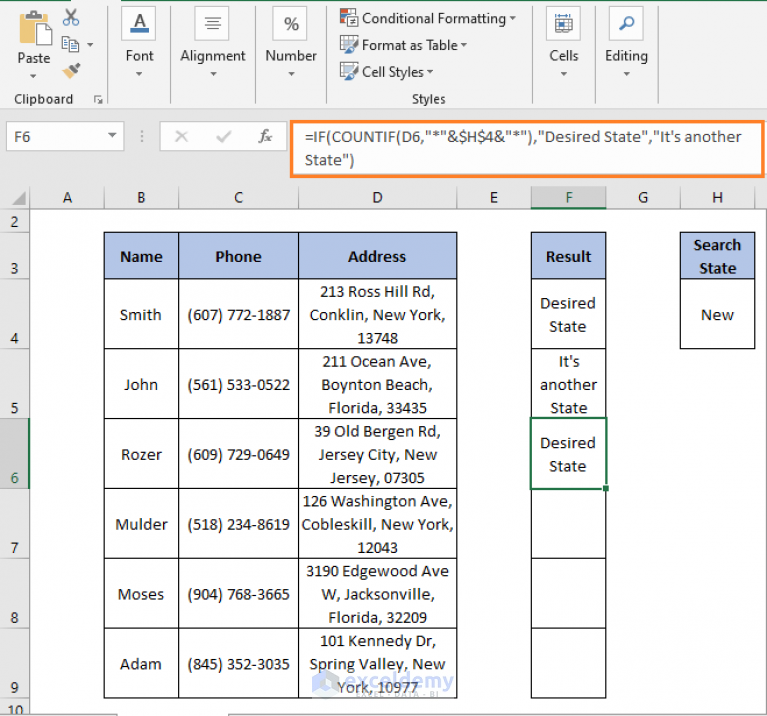
Let’s delve into a practical scenario to understand how partial matching functions can be applied in real-world data analysis.
Consider a scenario where you are working with a dataset containing information about various products, including their names, categories, and prices. Your task is to identify and analyze products that fall into a specific category, say "Electronics", and have prices above a certain threshold, for instance, $500.
Using Excel's partial matching functions, you can achieve this with ease. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Create a Filter: Start by selecting the dataset and applying a filter. Go to the Data tab and click on Filter to activate the filtering feature.
- Filter by Category: In the filter dropdown for the "Category" column, choose the "Text Filters" option and select "Begins With". Enter "Electronics" to filter for products in the "Electronics" category.
- Filter by Price: Similarly, filter the "Price" column by selecting the "Number Filters" option and choosing "Greater Than". Enter the threshold value, say $500, to filter for products above this price.
- Apply the Filters: Click OK to apply the filters, and Excel will display only the products that meet both conditions: belonging to the "Electronics" category and having a price above $500.
- Analyze the Data: With the filtered data, you can now perform various analyses, such as calculating the total revenue from these high-end electronic products or identifying the most popular items in this category.
Tips for Efficient Partial Matching
To optimize your partial matching skills in Excel, consider these expert tips:
- Use Named Ranges: Assign names to your data ranges to make your formulas more readable and maintainable. For instance, you can name a range of product prices as "ProductPrices" for easier reference.
- Utilize Conditional Formatting: Excel's conditional formatting feature allows you to visually highlight cells that meet specific criteria. This can be especially useful for quickly identifying patterns or anomalies in your data.
- Combine Functions: Excel's functions can be chained together to create powerful formulas. For example, you can use the FIND function within an IF statement to check for the presence of a specific substring and perform different actions based on the result.
- Master the Formula Bar: The formula bar is your friend when working with complex formulas. It allows you to see and edit formulas easily, making it simpler to debug and refine your calculations.
Advanced Techniques: Mastering Text Manipulation
While the basic partial matching functions are powerful, Excel offers a host of advanced techniques for more intricate text manipulation.
Text Manipulation Functions
Excel provides a range of functions specifically designed for text manipulation, enabling you to transform and refine your data. Let’s explore some of these functions:
- UPPER, LOWER, and PROPER Functions: These functions allow you to convert text to uppercase, lowercase, or proper case, respectively. They are invaluable for standardizing and cleaning up data, especially when dealing with user-generated content.
- TRIM Function: The TRIM function removes extra spaces from a text string, ensuring consistent formatting. This is particularly useful when you receive data from various sources and need to ensure uniformity.
- VALUE Function: The VALUE function converts a text representation of a number into an actual numeric value. It is handy when you need to perform calculations on data that was initially entered as text.
- CLEAN Function: The CLEAN function removes non-printable characters from text, ensuring clean and readable data. This function is especially useful when working with data imported from external sources.
- REPT Function: The REPT function repeats a text string a specified number of times. It is useful for creating custom text patterns or generating repeated data for testing purposes.
Combining Text and Data
Excel also provides functions to combine text and data, creating dynamic and informative reports. The CONCAT function, introduced in Excel 2016, is a powerful tool for this purpose. It allows you to join text from multiple cells into a single cell, with optional delimiters to separate the text.
For instance, you can use the CONCAT function to combine a customer's first name, last name, and email address into a single cell, creating a comprehensive contact record.
Performance and Efficiency
As your Excel skills advance, it’s essential to consider performance and efficiency. Here are some best practices to ensure your Excel workbooks run smoothly, even with large datasets:
- Optimize Formulas: Review your formulas regularly to ensure they are as efficient as possible. Avoid unnecessary calculations and use relative references whenever possible.
- Utilize Table Functions: Excel's table functions, such as SUMIFS and COUNTIFS, are optimized for performance and can significantly speed up your calculations.
- Avoid Volatile Functions: Volatile functions, like NOW and RAND, recalculate every time Excel recalculates the workbook. Use them sparingly and consider alternative approaches for better performance.
- Use Data Validation: Data validation can prevent errors and ensure data integrity. It allows you to set rules for acceptable data, such as requiring a specific format or limiting the range of values.
Future Implications and Advanced Analytics

As data professionals, it’s crucial to stay ahead of the curve and explore emerging trends in data analysis. Here’s a glimpse into the future of data analysis with Excel and some advanced techniques to consider:
Power Query and Power Pivot
Excel’s Power Query and Power Pivot add-ins offer powerful data transformation and analysis capabilities. Power Query enables you to connect to various data sources, transform and clean data, and load it into Excel for further analysis. Power Pivot, on the other hand, allows you to perform complex data modeling and create sophisticated data models.
PivotTables and PivotCharts
PivotTables and PivotCharts are Excel’s dynamic data analysis tools. They allow you to summarize, analyze, and visualize large datasets with ease. With PivotTables, you can quickly rearrange and filter data, while PivotCharts provide visual representations of your data, making it easier to identify trends and patterns.
Data Visualization and Dashboards
Excel’s data visualization capabilities have advanced significantly, allowing you to create professional-looking dashboards and reports. With features like conditional formatting, charts, and Sparklines, you can transform your data into visually appealing and informative representations.
Data Modeling and Power BI
For more advanced data modeling and analysis, Microsoft’s Power BI platform is an excellent choice. Power BI integrates seamlessly with Excel, allowing you to connect, transform, and visualize your data in powerful ways. It offers a range of features, including interactive dashboards, advanced data modeling, and natural language queries.
Conclusion: Excel’s Role in Data Analytics
Excel remains a cornerstone tool for data professionals, offering a vast array of functions and features for data manipulation and analysis. By mastering partial matching and advanced text manipulation techniques, you can unlock the full potential of Excel and streamline your data analysis workflows.
As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, Excel's capabilities will continue to evolve, ensuring that data professionals have the tools they need to stay ahead of the curve. With Excel's flexibility and power, the possibilities for data analysis are endless.
FAQ
How can I improve the performance of my Excel workbooks with large datasets?
+To optimize performance, consider using Excel’s table functions like SUMIFS and COUNTIFS, which are designed for speed. Additionally, review your formulas for efficiency and avoid unnecessary calculations. Utilize data validation to ensure data integrity and prevent errors.
What are some best practices for efficient data validation in Excel?
+When using data validation, ensure that you set clear and specific rules for acceptable data. This could include limiting data to a specific format, range of values, or even requiring a certain data type. Data validation helps maintain data integrity and prevents errors.
How can I create dynamic and interactive dashboards in Excel?
+Excel offers a range of tools for creating dynamic dashboards. Utilize PivotTables and PivotCharts to summarize and visualize your data. Additionally, leverage conditional formatting and Sparklines to create visually appealing and informative representations of your data.