A Comprehensive Guide to Palestine's Geography
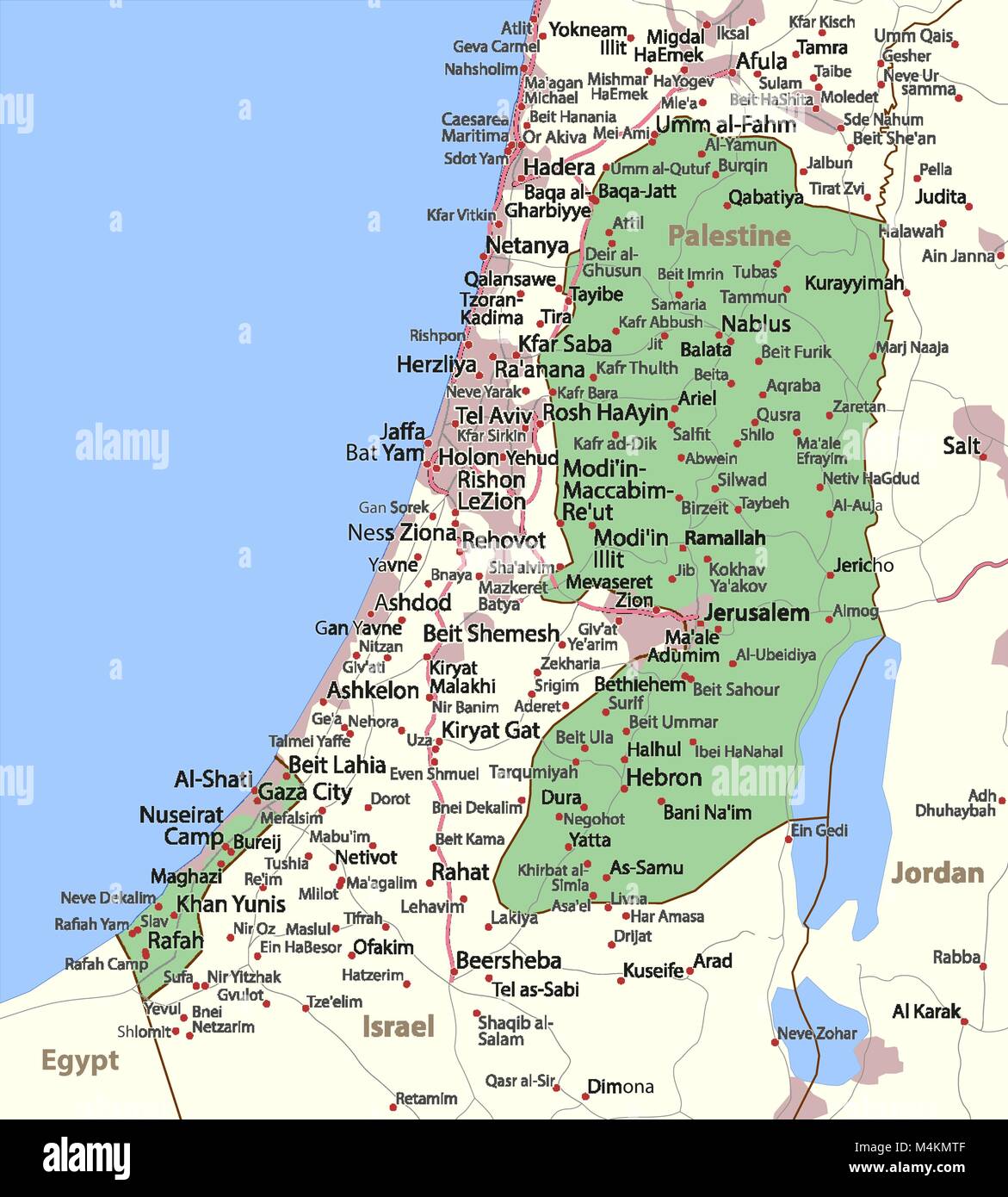
The land of Palestine, with its rich history and cultural significance, offers a captivating exploration of diverse landscapes and unique geographical features. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricate tapestry of Palestine’s geography, shedding light on its varied terrains, natural wonders, and the ways in which its geographical attributes have shaped the region’s identity.
The Topography of Palestine: A Mosaic of Terrains
Palestine presents a mosaic of landscapes, from the fertile coastal plains and rolling hills to the rugged mountains and arid deserts. The country’s topography is a study in contrasts, offering a diverse range of environments that support an array of ecosystems and human settlements.
At the heart of Palestine’s geographical diversity lies the Jordan Rift Valley, a profound geological feature that stretches from the Hula Valley in the north to the Dead Sea and beyond. This rift valley, part of the larger Jordan-Dead Sea Rift, showcases dramatic changes in elevation and has played a pivotal role in the region’s history and cultural development.
The Jordan Rift Valley is characterized by its steep slopes, deep valleys, and a unique microclimate that supports a diverse range of plant and animal life. It is a significant habitat for many species, including some that are endemic to the region, making it a vital area for conservation and ecological research.
"The Jordan Rift Valley is a geological wonder, offering a window into the Earth's history and the forces that shape our planet. It is a testament to the power of nature and the resilience of the life that thrives within its boundaries." - Dr. Maya Haroun, Geologist
Beyond the rift valley, Palestine’s terrain includes the rugged mountains of the West Bank, which rise majestically and offer breathtaking views. These mountains, with their rocky outcrops and lush valleys, have long served as a strategic advantage, providing natural defenses and shaping the region’s military history.
The coastal plains of Palestine, stretching along the Mediterranean Sea, offer a stark contrast to the mountainous interiors. These plains, with their fertile soils and mild climate, have supported human settlements and agricultural activities for millennia. The ancient cities of Gaza, Jaffa, and Caesarea, among others, testify to the rich history and cultural significance of Palestine’s coastal regions.
Natural Wonders: Palestine’s Ecological Treasures
Palestine is blessed with an array of natural wonders, from pristine beaches and dramatic cliffs to unique geological formations and biodiverse ecosystems. These natural treasures not only enhance the country’s beauty but also contribute significantly to its ecological importance and tourism potential.
One of the most renowned natural wonders of Palestine is the Dead Sea, a hypersaline lake situated at the lowest point on Earth. The Dead Sea, with its unique properties and therapeutic benefits, has attracted visitors and researchers from around the globe. Its high salinity makes it a challenging environment for most life forms, yet it supports a range of specialized microorganisms and has a profound impact on the local climate and ecosystem.
"The Dead Sea is a geological marvel, a living laboratory where we can study the Earth's processes and the resilience of life. It is a reminder of the delicate balance between nature and humanity, and the importance of preserving our natural treasures." - Prof. Ibrahim Abu El-Haija, Ecologist
In addition to the Dead Sea, Palestine boasts several national parks and nature reserves that protect its diverse ecosystems. The Wadi Qelt Nature Reserve, for instance, is a haven for wildlife, with its lush oasis-like environment and dramatic cliffs. It is home to a range of plant and animal species, including the iconic ibex, a symbol of resilience in this arid landscape.
Palestine’s coastal areas, too, offer unique natural wonders. The Mediterranean Sea, with its pristine beaches and vibrant marine life, provides a haven for recreational activities and a vital habitat for marine species. The beaches of Gaza and Jaffa, in particular, have long been cherished for their beauty and have played a significant role in the region’s cultural and recreational life.
Human-Geography Interface: Shaping the Landscape and Society
The geography of Palestine has profoundly influenced the region’s human settlement patterns, cultural development, and social dynamics. The interplay between the natural environment and human activities has shaped the unique character of Palestinian society and its distinctive cultural practices.
The mountainous regions of Palestine, with their strategic locations and challenging terrain, have long been centers of defense and resistance. The rugged landscapes have provided natural strongholds and have played a pivotal role in the region’s military history. The iconic city of Jerusalem, nestled among the Judean Mountains, is a prime example of how geographical features have influenced the course of history and shaped the cultural identity of the region.
In contrast, the fertile coastal plains and river valleys have supported agricultural activities and human settlements for millennia. The ancient cities of Palestine, such as Gaza and Nablus, were established along trade routes and water sources, taking advantage of the region’s rich agricultural potential. The development of irrigation systems and the cultivation of crops have not only sustained the population but have also influenced the cultural practices and culinary traditions of Palestine.
Palestine’s Geography: A Cultural and Historical Lens
The geographical attributes of Palestine have been intimately tied to its cultural and historical development. The country’s diverse landscapes, from the rugged mountains to the fertile plains, have provided the backdrop for a rich tapestry of human stories, cultural traditions, and historical events.
The historical significance of Palestine’s geographical features is evident in its ancient cities and archaeological sites. Jerusalem, with its holy sites and ancient walls, stands as a testament to the region’s religious and cultural importance. The city’s geographical location, perched atop the Judean Mountains, has made it a focal point of historical events and a symbol of cultural and religious convergence.
Other ancient cities, such as Bethlehem and Hebron, also bear witness to the region’s rich historical heritage. These cities, with their ancient walls, religious sites, and archaeological treasures, provide a window into the past and offer a deeper understanding of the cultural and historical dynamics that have shaped Palestine.
Conclusion: A Land of Geographical Diversity and Significance
Palestine’s geography is a complex tapestry, offering a diverse range of landscapes, natural wonders, and cultural significance. From the dramatic Jordan Rift Valley to the lush coastal plains and rugged mountains, Palestine presents a unique and captivating study in geographical contrasts.
The interplay between the natural environment and human activities has shaped the region’s history, culture, and society. Palestine’s geographical attributes have influenced its settlement patterns, cultural practices, and even its political dynamics. Understanding Palestine’s geography provides a deeper appreciation of the region’s complexity and the unique role it plays in the broader Middle East.
As we explore Palestine’s geographical diversity, we uncover not only the physical attributes of the land but also the rich cultural and historical narratives that have unfolded within its boundaries. Palestine’s geography is a living testament to the interconnectedness of nature and humanity, and a reminder of the enduring significance of this land.
Palestine's geography offers a captivating study in contrasts, from the dramatic Jordan Rift Valley to the lush coastal plains. The interplay between nature and humanity has shaped the region's history, culture, and society, making Palestine a land of unique geographical and cultural significance.
What is the Jordan Rift Valley and why is it significant in Palestine’s geography?
+The Jordan Rift Valley is a profound geological feature that stretches through Palestine and beyond. It is a significant habitat for diverse plant and animal life and has played a pivotal role in the region’s history and cultural development. The rift valley’s unique microclimate and dramatic changes in elevation have made it a vital area for conservation and a testament to the power of nature.
How has Palestine’s geography influenced its human settlement patterns and cultural practices?
+Palestine’s geography has shaped its human settlement patterns and cultural practices in profound ways. The mountainous regions, with their strategic locations and challenging terrain, have long been centers of defense and resistance, influencing the region’s military history. The fertile coastal plains and river valleys, on the other hand, have supported agricultural activities and human settlements for millennia, influencing cultural practices and culinary traditions.
What are some of Palestine’s most renowned natural wonders and how do they contribute to its ecological significance?
+Palestine boasts several natural wonders, including the Dead Sea, a hypersaline lake with unique properties and therapeutic benefits. The Dead Sea is a challenging environment for most life forms but supports specialized microorganisms and has a profound impact on the local climate and ecosystem. Other natural wonders, such as the Wadi Qelt Nature Reserve and the Mediterranean Sea’s pristine beaches, enhance Palestine’s ecological importance and tourism potential.
How does Palestine’s geography relate to its historical and cultural heritage?
+Palestine’s geographical attributes are intimately tied to its historical and cultural heritage. The country’s diverse landscapes, from the rugged mountains to the fertile plains, have provided the backdrop for a rich tapestry of human stories, cultural traditions, and historical events. Ancient cities like Jerusalem, Bethlehem, and Hebron bear witness to the region’s rich historical heritage and offer a deeper understanding of the cultural and historical dynamics that have shaped Palestine.



