Understanding Sugar Levels During Pregnancy

A Comprehensive Guide to Sugar Levels and Pregnancy
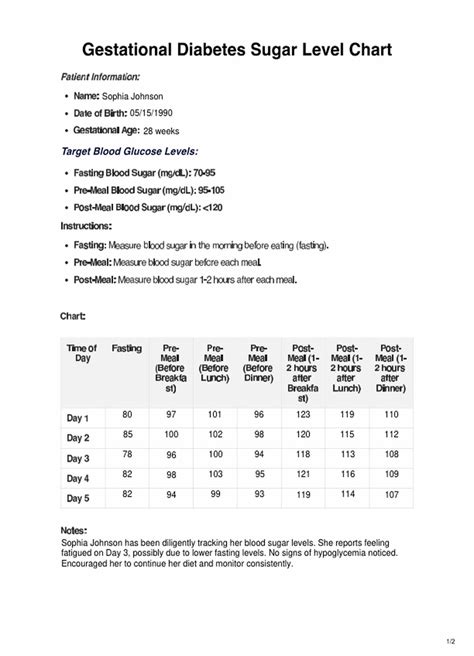
The journey of pregnancy is a fascinating and transformative experience, and it often comes with a unique set of health considerations. One crucial aspect that expectant mothers and healthcare providers carefully monitor is blood sugar levels. Managing glucose is not just about maintaining energy levels; it’s a vital part of ensuring a healthy pregnancy and birth. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of sugar levels during pregnancy, exploring the why, how, and what-if scenarios.
"Understanding and managing blood sugar levels during pregnancy is like navigating a complex puzzle. It requires precision, awareness, and a tailored approach for each unique individual."
The Importance of Sugar Regulation During Pregnancy
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is essential for overall health, but it takes on a new level of significance during pregnancy. Here’s why:
Fetal Development: Stable glucose levels are crucial for the healthy growth and development of the fetus. Imbalances can lead to complications, impacting the baby’s organ development and overall health.
Pregnancy-Related Conditions: Gestational diabetes is a condition unique to pregnancy, where blood sugar levels become challenging to manage. Early detection and management are vital to prevent complications like macrosomia (excessive birth weight) and preeclampsia.
Maternal Health: High blood sugar can increase the risk of pregnancy-induced hypertension and other maternal health issues. It’s also associated with an increased likelihood of C-section deliveries.
Long-Term Health: Managing sugar levels during pregnancy can have lasting benefits, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases later in life.
The Science Behind Blood Sugar Levels
To grasp the importance of sugar regulation, it’s essential to understand the science behind blood sugar levels:
Glucose: This simple sugar is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. It’s derived from carbohydrates in our diet and is vital for bodily functions.
Insulin: Produced by the pancreas, insulin is a hormone that regulates glucose levels in the blood. It enables cells to absorb glucose, thus maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Blood Sugar Levels: These fluctuate throughout the day, influenced by meals, activity levels, and hormones. Optimal blood sugar levels for pregnant women are generally lower than non-pregnant individuals due to the body’s increased sensitivity to insulin.
Gestational Diabetes: This condition occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels effectively during pregnancy. It typically develops in the second or third trimester and affects about 10% of pregnancies.
Detecting and Monitoring Sugar Levels
Detecting and monitoring sugar levels during pregnancy is a multi-faceted process:
Glucose Screening: Typically conducted between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy, this involves a glucose tolerance test. The woman drinks a glucose solution, and her blood sugar levels are measured before and after to assess her body’s response.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): This advanced technology uses a small sensor placed under the skin to continuously track blood sugar levels. It provides real-time data, offering a more comprehensive understanding of sugar fluctuations.
Home Glucose Testing: Some women, especially those at higher risk for gestational diabetes, may be advised to monitor their blood sugar levels at home. This involves using a glucose meter to prick the finger and obtain a blood sample for testing.
Ketone Testing: In cases of severe glucose imbalances, ketone testing may be recommended. Ketones are produced when the body burns fat for energy, and high levels can indicate a serious condition called diabetic ketoacidosis.
Managing Sugar Levels for a Healthy Pregnancy
Effective management of sugar levels during pregnancy involves a holistic approach:
Dietary Adjustments: A balanced diet is key. Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates. Avoid excessive sugar and refined carbohydrates.
Exercise and Activity: Regular physical activity helps regulate blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily, such as walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight during pregnancy is essential. Excessive weight gain can increase the risk of gestational diabetes and other complications.
Medications and Insulin: In some cases, oral medications or insulin injections may be prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels. These should be taken as directed by a healthcare provider.
Stress Management: Stress can impact blood sugar levels. Incorporate relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or prenatal massage to help manage stress effectively.
Case Study: Emma’s Journey with Gestational Diabetes
Let’s consider the real-life story of Emma, a 32-year-old woman who was diagnosed with gestational diabetes during her second pregnancy:
Emma, an active and healthy woman, was surprised when her routine glucose screening indicated high blood sugar levels. Further testing confirmed gestational diabetes.
With the guidance of her healthcare team, Emma implemented a strict dietary plan, focusing on low-glycemic index foods and regular, balanced meals. She also started monitoring her blood sugar levels at home and adjusted her diet accordingly.
Emma’s commitment to her health paid off. With a combination of dietary changes, regular exercise, and close monitoring, she successfully managed her gestational diabetes. Her baby was born healthy, and Emma’s own long-term health prospects were greatly improved.
Looking Ahead: Future Trends and Developments
The field of gestational diabetes management is evolving, with new research and technologies constantly emerging:
Advanced CGM Technology: Continuous glucose monitoring is becoming more accessible and accurate, offering real-time data to help women manage their sugar levels more effectively.
Precision Nutrition: Personalized dietary plans, tailored to each woman’s unique needs and preferences, are being developed to optimize sugar regulation during pregnancy.
Telehealth and Digital Solutions: Remote monitoring and digital health platforms are making it easier for women to manage their sugar levels from home, with real-time access to healthcare professionals.
Expert Perspective: Dr. Olivia Green, Endocrinologist
"The management of gestational diabetes has evolved significantly in recent years. With advancements in technology and a deeper understanding of the condition, we can now offer more precise and effective care to pregnant women."
Practical Tips for Expectant Mothers
Here are some practical tips for expectant mothers to help manage sugar levels during pregnancy:
Eat Regular Meals: Aim for 3 balanced meals and 2-3 healthy snacks per day. Avoid skipping meals, as this can lead to blood sugar spikes.
Focus on Whole Foods: Opt for fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit processed foods and added sugars.
Stay Active: Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best exercises for you.
Monitor Sugar Levels: If advised by your doctor, use a glucose meter to track your blood sugar levels. Follow the recommended testing schedule and keep a record of the results.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent dehydration.
Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques and prioritize self-care to reduce stress levels, which can impact blood sugar control.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in managing sugar levels during pregnancy:
Prenatal Care: Regular prenatal visits are essential for monitoring blood sugar levels and overall health. These visits provide an opportunity to discuss concerns and receive guidance.
Education and Support: Healthcare providers should offer comprehensive education on sugar management, including dietary advice, exercise recommendations, and stress management techniques.
Continuous Monitoring: For women at higher risk or with diagnosed gestational diabetes, frequent monitoring is necessary. Healthcare providers should provide the necessary tools and guidance for effective self-monitoring.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the signs of high blood sugar during pregnancy?
+Signs of high blood sugar during pregnancy may include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and nausea. However, these symptoms can also be attributed to normal pregnancy changes, so it's essential to have your blood sugar levels tested by a healthcare professional.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can gestational diabetes affect my baby's health?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes, unmanaged gestational diabetes can lead to various complications for the baby, including excessive birth weight (macrosomia), low blood sugar levels after birth, and an increased risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes later in life. However, with proper management, these risks can be significantly reduced.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How often should I monitor my blood sugar levels if I have gestational diabetes?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>The frequency of blood sugar monitoring depends on the severity of your gestational diabetes and your healthcare provider's recommendations. Generally, it's advised to check your blood sugar levels 4-6 times a day, including before and after meals, and sometimes at bedtime.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Are there any specific dietary guidelines for managing gestational diabetes?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes, a balanced diet is crucial for managing gestational diabetes. Focus on lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index. Limit sugary foods and refined carbohydrates. Your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can provide a personalized meal plan.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can exercise help manage gestational diabetes?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Absolutely! Regular physical activity can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and prenatal yoga are generally safe during pregnancy. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any exercise routine.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Conclusion

Understanding and managing sugar levels during pregnancy is a complex but rewarding process. It requires a holistic approach, combining dietary adjustments, regular exercise, and close monitoring. With the guidance of healthcare professionals and a commitment to healthy habits, expectant mothers can ensure a healthy pregnancy and set the stage for a lifetime of well-being for both themselves and their little ones.



