The Step-by-Step Guide to Adding a User

Adding a user to a system or platform is a common task for administrators and IT professionals. It involves a series of steps to ensure the new user can access the necessary resources securely and efficiently. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the process of adding a user, covering everything from initial planning to final verification. By following these steps, you'll be able to streamline the user onboarding process and enhance the overall user experience.
Step 1: Gather User Information and Requirements
Before adding a user, it’s crucial to collect the necessary details and understand their specific requirements. Here’s what you need to gather:
- User Details: Obtain the user’s full name, email address, and any other relevant identification information.
- Access Rights: Determine the level of access the user requires. This could include permissions for specific applications, networks, or resources.
- User Preferences: Gather any preferences the user may have, such as language settings, time zone, or customization options.
- Security Considerations: Assess any security measures needed, such as multi-factor authentication or specific password policies.
Step 2: Create the User Account
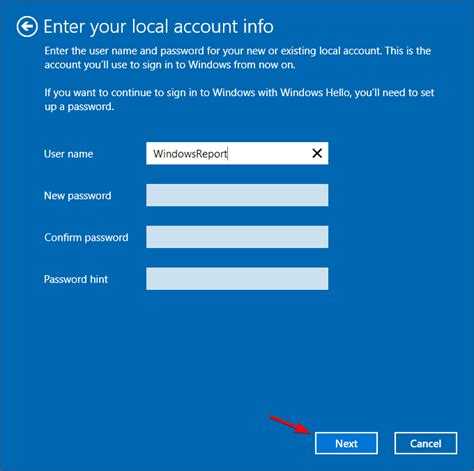
With the required information in hand, it’s time to create the user account. Follow these steps:
- Choose the Appropriate Platform: Select the system or platform where the user will be added. This could be an operating system, a network, or a specific application.
- Access the User Management Interface: Log in to the administrative panel or control panel of the chosen platform. This is where you’ll create and manage user accounts.
- Add User Details: Input the user’s information, including their name, email, and any other required fields. Ensure accuracy to avoid future issues.
- Assign Access Rights: Based on the user’s requirements, assign the appropriate access rights and permissions. This step is critical to ensure the user can perform their tasks securely.
- Set Initial Credentials: Generate or assign initial login credentials, such as a temporary password. It’s essential to communicate these credentials to the user securely.
Step 3: Configure User Settings and Preferences
Once the user account is created, customize it to meet the user’s preferences and requirements:
- Language and Locale: Set the user’s preferred language and locale to ensure a personalized experience. This includes language settings for the user interface and any locale-specific adjustments.
- Time Zone: Select the appropriate time zone for the user. This ensures accurate timestamps and schedule management.
- Customizations: Allow the user to customize their profile, interface, or workspace according to their preferences. This could include themes, color schemes, or personal avatars.
- Security Settings: Review and adjust any security settings based on the user’s needs. This may involve enabling or disabling specific security features or configuring multi-factor authentication.
Step 4: Provide User Training and Support
Adding a user is not just about creating an account; it’s about ensuring the user can effectively utilize the system. Here’s how to provide training and support:
- User Manuals and Guides: Create comprehensive documentation or provide access to existing user manuals. These resources should cover basic functionality, troubleshooting tips, and frequently asked questions.
- Onboarding Tutorials: Develop interactive tutorials or videos that guide new users through the platform’s key features and functionalities. This hands-on approach accelerates the learning curve.
- Support Channels: Establish dedicated support channels, such as a help desk or a dedicated email address, where users can seek assistance. Ensure prompt responses to build user confidence.
- Feedback and Improvement: Encourage users to provide feedback on their experience. This feedback loop helps identify areas for improvement and enhances the overall user experience.
Step 5: Verify User Access and Security
After completing the previous steps, it’s crucial to verify the user’s access and ensure security:
- Test Access: Have the user log in to the system and verify their access to the required resources. Ensure they can navigate the platform and perform their intended tasks.
- Security Audit: Conduct a security audit to ensure the user’s account adheres to security policies and best practices. This includes checking password strength, access logs, and any other relevant security measures.
- User Feedback: Gather feedback from the user regarding their experience during the onboarding process. Address any concerns or issues promptly to ensure a smooth transition.
Step 6: Regularly Monitor and Update User Accounts
Adding a user is not a one-time task; it requires ongoing maintenance and updates. Here’s how to manage user accounts effectively:
- Regular Reviews: Schedule periodic reviews of user accounts to ensure they remain up-to-date and aligned with the user’s evolving needs. This includes updating access rights, preferences, and security measures.
- Password Management: Encourage users to regularly update their passwords and follow strong password practices. Implement password expiration policies to maintain security.
- Access Revocation: When a user’s role or responsibilities change, promptly adjust their access rights accordingly. This prevents unauthorized access and ensures data security.
- Account Deactivation: If a user leaves the organization or no longer requires access, deactivate their account promptly. This step helps maintain data integrity and reduces security risks.
Conclusion
Adding a user is a critical process that requires careful planning and execution. By following this step-by-step guide, you can ensure a seamless and secure user onboarding experience. Remember, each step is interconnected, and attention to detail is crucial. With a well-structured approach, you’ll be able to efficiently manage user accounts and provide a positive user experience.
What are some common challenges when adding a user, and how can they be overcome?
+Common challenges include inaccurate user information, insufficient access rights, and delayed communication. To overcome these, ensure proper data collection, consult with relevant teams for access requirements, and maintain open lines of communication throughout the process.
How often should user accounts be reviewed and updated?
+User accounts should be reviewed and updated at least annually, or more frequently if there are significant changes in the user’s role or responsibilities. Regular reviews help maintain security and ensure users have the necessary access to perform their tasks effectively.
What are some best practices for user training and support?
+Best practices include providing clear and concise documentation, offering interactive tutorials, and establishing prompt support channels. Additionally, encourage users to explore the platform on their own, as this can enhance their familiarity and confidence.