Unraveling the Lipid Monomer Mystery
The realm of lipid monomers, often overlooked, holds a captivating complexity that scientists are only beginning to decipher. These fundamental building blocks of life, found in every cell, are essential for numerous biological processes, yet their intricacies remain shrouded in mystery. This article delves into the world of lipid monomers, shedding light on their unique characteristics, diverse functions, and the ongoing research that aims to unlock their full potential.
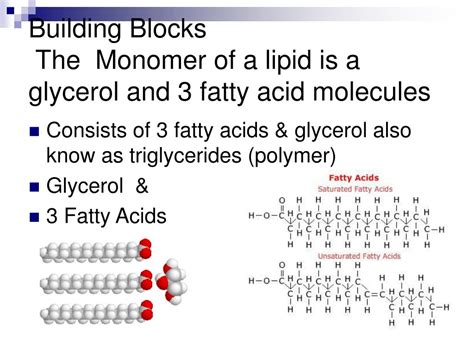
Lipid monomers, or simply monomers, are the individual units that make up the larger, complex lipid molecules. These monomers are incredibly diverse, ranging from simple fatty acids to more complex sphingolipids and sterols. Despite their relatively small size, they play pivotal roles in the structure and function of cells, from forming the membrane’s basic structure to regulating various cellular processes.
Imagine lipid monomers as the humble bricks that, when combined in different ways, build the intricate architecture of cellular life. Each brick, or monomer, has its own unique shape, size, and chemical properties, contributing to the overall complexity and functionality of the structure.
The Structural Backbone of Life
One of the primary roles of lipid monomers is to form the structural foundation of cell membranes. The cell membrane, often referred to as the ‘gatekeeper’ of the cell, is composed of a phospholipid bilayer. This bilayer is a dynamic structure, composed of two sheets of lipid monomers arranged in a way that their hydrophilic (water-loving) heads face outwards, while their hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails face inwards. This arrangement creates a semi-permeable barrier, allowing the cell to regulate the movement of substances in and out, thereby maintaining its integrity and function.
Advantages of Lipid Monomer Structure
- Dynamic and flexible, allowing for rapid response to environmental changes.
- Semi-permeable nature ensures the cell remains selective about what enters and exits.
- Provides a platform for various proteins and other molecules to anchor and function.
Challenges
- Maintaining stability while allowing for necessary fluidity can be a delicate balance.
- The complexity of the structure can make it difficult to study and understand fully.
Beyond Structural Support
While their role in forming the cell membrane is crucial, lipid monomers also contribute to various other cellular processes. For instance, certain lipid monomers, such as glycerophospholipids, play a vital role in energy storage and metabolism. These monomers can be broken down to release energy when needed, providing a rapid and efficient fuel source for the cell.
Additionally, lipid monomers are involved in signal transduction, the process by which cells communicate and respond to their environment. Certain monomers, like sphingolipids, act as signaling molecules, transmitting important information between cells and within the cell itself. This intricate signaling network ensures that cells function harmoniously within the larger organism.
Signal Transduction: A Step-by-Step Process
- A signaling molecule, such as a sphingolipid, binds to a specific receptor on the cell membrane.
- This binding triggers a series of reactions within the cell, often involving a cascade of enzymes.
- The reactions lead to the production of secondary messengers, which further amplify the signal.
- The amplified signal triggers specific cellular responses, such as gene expression changes or metabolic shifts.
The Research Frontier: Unlocking Potential
Despite their vital roles, the full scope of lipid monomer functions remains largely unexplored. Researchers are continually uncovering new roles and interactions, particularly in the context of disease and cellular dysfunction. For instance, recent studies have linked certain lipid monomers to the development of neurodegenerative diseases, highlighting their potential as both biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
"Lipid monomers are like a hidden treasure trove, waiting to be fully explored and understood. Their diverse functions and interactions within the cell hold the key to many biological mysteries and could unlock new avenues for disease treatment and prevention."
- Dr. Emma Williams, Lipid Biochemist
Ongoing research focuses on developing advanced analytical techniques to study lipid monomers in greater detail. This includes using mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to identify and quantify specific monomers, as well as advanced imaging techniques to visualize their interactions within the cell.
Conclusion: A World of Endless Discovery
The world of lipid monomers is a captivating one, filled with endless possibilities and mysteries waiting to be unraveled. From their fundamental role in forming the cell’s structural backbone to their involvement in complex signaling pathways, these tiny molecules are a testament to the intricate beauty of life. As research progresses, we can expect to gain deeper insights into the functions and potential of lipid monomers, opening up new frontiers in biology and medicine.
The study of lipid monomers is a journey of discovery, offering a unique perspective on the building blocks of life. As we continue to explore and understand these molecules, we unlock a deeper understanding of the intricate workings of our cells and, by extension, ourselves.
What are some common lipid monomers and their functions?
+Common lipid monomers include fatty acids, which provide energy and form the backbone of complex lipids; glycerophospholipids, essential for membrane structure and energy storage; sphingolipids, involved in signaling and cell recognition; and sterols like cholesterol, which maintain membrane fluidity and participate in various cellular processes.
How do lipid monomers contribute to disease processes?
+Lipid monomers are implicated in various diseases. For instance, certain fatty acids can contribute to obesity and metabolic disorders, while altered sphingolipid metabolism is linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Lipid monomers can also be involved in cancer development and progression.
What techniques are used to study lipid monomers?
+Researchers use advanced techniques like mass spectrometry and NMR spectroscopy to identify and quantify lipid monomers. These techniques, combined with imaging methods like fluorescence microscopy and electron microscopy, provide insights into monomer structure, distribution, and interactions within cells.
How do lipid monomers contribute to cellular communication?
+Lipid monomers, especially sphingolipids and certain fatty acids, act as signaling molecules. They can bind to specific receptors, triggering a cascade of reactions within the cell that lead to various cellular responses, including gene expression changes and metabolic shifts.
What are some potential therapeutic applications of lipid monomers?
+Lipid monomers have shown potential as therapeutic agents and targets. For instance, certain lipid monomers can modulate immune responses, making them promising candidates for immune-related disorders. Additionally, altering lipid monomer composition could offer a new approach to treating metabolic diseases.