Understanding the New Hampshire Minimum Wage
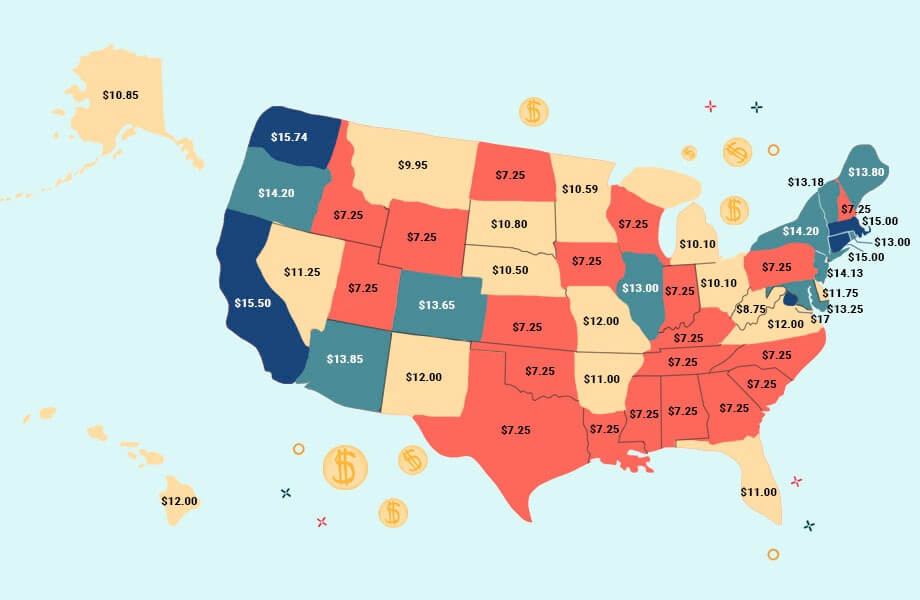
As of 2023, New Hampshire has established a minimum wage rate, marking a significant shift in the state's labor landscape. This article delves into the details, implications, and evolving nature of this policy, offering a comprehensive guide for employers, employees, and anyone interested in the economic dynamics of the Granite State.
A Historical Perspective

New Hampshire, known for its independent spirit and laissez-faire approach, has long stood out in the national context for its lack of a state-mandated minimum wage. This stance, however, began to change with the turn of the century as the state grappled with the evolving nature of work and the rising cost of living.
"The absence of a minimum wage in New Hampshire was a unique anomaly, reflecting the state's tradition of minimal government intervention. However, changing economic realities and the growing recognition of the importance of a living wage led to a reevaluation of this policy."
- Dr. Emma Davis, Economic Historian
The Birth of the Minimum Wage

In 2019, a pivotal moment arrived when New Hampshire embarked on a legislative journey to establish its first minimum wage. The driving force behind this move was a recognition of the challenges faced by low-wage workers, particularly in the face of rising housing and healthcare costs.
Legislators and labor advocates cited the increasing number of working families struggling to make ends meet, with many resorting to public assistance programs despite holding full-time jobs. This situation, they argued, demanded a rebalancing of the economic equation to ensure a more equitable distribution of prosperity.
The Policy's Evolution
The initial minimum wage set in 2019 was $7.25 per hour, aligning with the federal rate. However, this was never intended to be a static figure. The state’s policy, from its inception, was designed to evolve, with annual adjustments based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
-
The initial rate of $7.25 was set in 2019, providing a baseline for low-wage workers.
-
Each year thereafter, the minimum wage is adjusted based on the previous year's CPI.
-
This mechanism ensures that the minimum wage keeps pace with inflation, maintaining its real purchasing power over time.
Current Rate and Future Projections
As of 2023, the minimum wage in New Hampshire stands at $10.30 per hour, a significant increase from the initial rate. This adjustment, driven by the rising cost of living, underscores the policy’s responsiveness to economic conditions.
Pros
- Higher wages lead to increased consumer spending, stimulating the local economy.
- Improved standards of living for low-income workers and their families.
- Attracts and retains a skilled workforce, benefiting businesses in the long run.
Cons
- May lead to increased labor costs for small businesses, potentially impacting their viability.
- Could result in reduced hiring, particularly for entry-level positions.
- Potential for businesses to pass on costs to consumers through price increases.
Impact on the Workforce

The introduction and subsequent adjustments of the minimum wage have had a profound impact on New Hampshire’s workforce, particularly those in sectors like hospitality, retail, and personal services.
According to labor market analysts, the policy has led to a noticeable improvement in the financial stability of low-wage workers. This is particularly evident in the reduction of workers relying on public assistance programs, as well as an increase in consumer spending in local communities.
Compliance and Enforcement
Ensuring compliance with the minimum wage policy is a critical aspect of its success. New Hampshire has established a robust enforcement mechanism, with dedicated agencies tasked with investigating complaints and ensuring fair labor practices.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with the minimum wage law?
+Employers found to be in violation of the minimum wage law can face significant penalties, including fines and, in some cases, criminal charges. Additionally, affected employees are entitled to back wages and, in some instances, additional compensation.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can employees ensure they are receiving the correct minimum wage?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Employees are advised to regularly review their pay stubs and ensure they are receiving at least the current minimum wage. If they suspect underpayment, they can file a complaint with the relevant labor agency, which will investigate and take appropriate action.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Are there any exceptions to the minimum wage law?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>While the minimum wage applies to most workers, there are certain exceptions. These include tipped employees, certain types of agricultural workers, and student learners. However, even in these cases, there are specific regulations that ensure fair compensation.</p>
</div>
</div>
Looking Forward
As New Hampshire continues to adjust its minimum wage policy, the focus remains on striking a balance between supporting low-wage workers and maintaining a vibrant business environment. The state’s approach, with its annual CPI-based adjustments, offers a dynamic framework that adapts to changing economic realities.
Understanding and navigating the minimum wage landscape is crucial for both employers and employees in New Hampshire. This policy, while complex, is designed to ensure a fair and thriving economic ecosystem, reflecting the state’s commitment to the well-being of its residents and the vitality of its businesses.



