Unraveling the Mystery of Meter's Abbreviation
Meter, a fundamental unit of measurement, is often represented by an intriguing abbreviation. This abbreviation, a simple yet powerful symbol, has become a cornerstone in various scientific and engineering disciplines. The story behind this symbol is a fascinating journey through history and precision, offering a glimpse into the meticulous world of metrology.
The meter's abbreviation is a testament to the evolution of scientific notation, serving as a universal language for accurate measurement across diverse fields.
Historical Evolution: From ‘Mètre’ to ’m’

The journey of the meter’s abbreviation began with its French roots. The term ‘mètre’, adopted in 1795 by the French Academy of Sciences, was a new measure for length, intended to replace the arbitrary and inconsistent units of the past. The original definition of the meter was based on the circumference of the Earth, with one meter equaling one ten-millionth of the distance from the North Pole to the equator.
However, this definition was challenging to standardize, leading to the adoption of a more practical reference. In 1889, the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) defined the meter as the distance between two lines on a prototype meter bar, made of a platinum-iridium alloy. This physical standard ensured a more precise and consistent meter across laboratories.
Despite the change in definition, the abbreviation for meter remained consistent. The initial ’M’ was later shortened to ’m’ to avoid confusion with the SI prefix ‘mega’ (M), which represents a factor of one million. This simplification, adopted universally, has become an iconic symbol in the scientific community.
The Significance of the Abbreviation ’m’

The abbreviation ’m’ for meter is more than just a convenient shorthand. It represents a standardized unit of measurement, ensuring consistent communication and understanding across various fields. Whether in physics, engineering, or even everyday life, the meter is a fundamental unit for expressing lengths, distances, and dimensions.
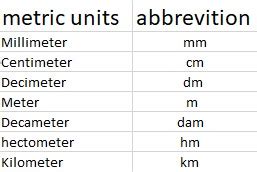
The simplicity of the ’m’ abbreviation belies its critical role in scientific and engineering calculations. It forms the basis for more complex units, such as the kilometer (km) and the millimeter (mm), which are derived from the meter. This hierarchy of units, built upon the meter, facilitates precise measurements and calculations, enabling advancements in technology, architecture, and countless other disciplines.
Standardization and Global Acceptance
The meter’s abbreviation, ’m’, is part of the International System of Units (SI), the modern form of the metric system. SI is the most widely used system of measurement, recognized and adopted by the majority of countries worldwide. Its universal acceptance ensures that scientists, engineers, and professionals can communicate and collaborate effectively, regardless of their geographical location or cultural background.
The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) plays a crucial role in maintaining the SI system and ensuring its accuracy. They define and maintain the standards for all SI units, including the meter. Their efforts contribute to the consistent and precise use of the meter’s abbreviation, fostering a global language of measurement.
Practical Applications and Real-World Impact
The meter’s abbreviation is not just an abstract concept; it has tangible implications in our daily lives. From measuring the length of a room to the distance of a marathon, the meter is a familiar unit of measurement. In construction, architecture, and engineering, precise measurements are crucial for ensuring safety and functionality.
In scientific research, the meter plays a pivotal role. Whether studying the behavior of particles in physics, analyzing the properties of materials in chemistry, or observing celestial objects in astronomy, the meter is a fundamental unit of measurement. The precision and consistency provided by the ’m’ abbreviation contribute to the accuracy and reproducibility of scientific experiments and observations.
Future Trends and Innovations

While the meter’s abbreviation has remained consistent, the future of measurement holds exciting possibilities. With advancements in technology, new methods of measurement are being developed, offering even greater precision and accuracy. Laser interferometry, for example, allows for measurements at the sub-nanometer level, far beyond the capabilities of traditional meter bars.
As technology evolves, the definition and application of the meter may also evolve. However, the core principle of standardization and universal acceptance will likely remain, ensuring that the meter’s abbreviation continues to serve as a cornerstone of measurement across disciplines.
Conclusion
The meter’s abbreviation, ’m’, is a powerful symbol, representing the evolution of measurement and the quest for precision. From its French origins to its global acceptance, the meter has become an indispensable unit of measurement, underpinning countless scientific and engineering advancements. As we continue to push the boundaries of knowledge and technology, the meter’s abbreviation will remain a constant, a reliable reference for accurate measurement.
What is the history behind the meter’s abbreviation ’m’?
+The meter’s abbreviation ’m’ has its roots in the French term ‘mètre’, adopted by the French Academy of Sciences in 1795. The original definition of the meter was based on the circumference of the Earth, with one meter equaling one ten-millionth of this distance. Later, the definition was standardized using a prototype meter bar, made of platinum-iridium alloy. To avoid confusion with the SI prefix ‘mega’ (M), the abbreviation was shortened to ’m’, which has since become a universal symbol for the meter.
Why is the meter’s abbreviation important in scientific and engineering fields?
+The meter’s abbreviation ’m’ is crucial as it represents a standardized unit of measurement. This standardization ensures consistent communication and understanding across various scientific and engineering disciplines. The meter forms the basis for more complex units and is fundamental in precise measurements and calculations, driving advancements in technology and research.
How is the meter’s abbreviation used in everyday life?
+The meter’s abbreviation ’m’ is a familiar unit of measurement in our daily lives. From measuring the length of a room to the distance of a marathon, the meter is a practical and essential unit. In fields like construction, architecture, and engineering, precise measurements are crucial, and the meter plays a vital role in ensuring safety and functionality.
What are the future trends and innovations in measurement related to the meter’s abbreviation?
+While the meter’s abbreviation ’m’ remains consistent, future advancements in technology are expected to bring about new methods of measurement. Laser interferometry, for instance, allows for incredibly precise measurements at the sub-nanometer level. These innovations may lead to further evolution in the definition and application of the meter, but the principle of standardization and universal acceptance is likely to endure.



