The Ultimate Guide to Spanish Maps
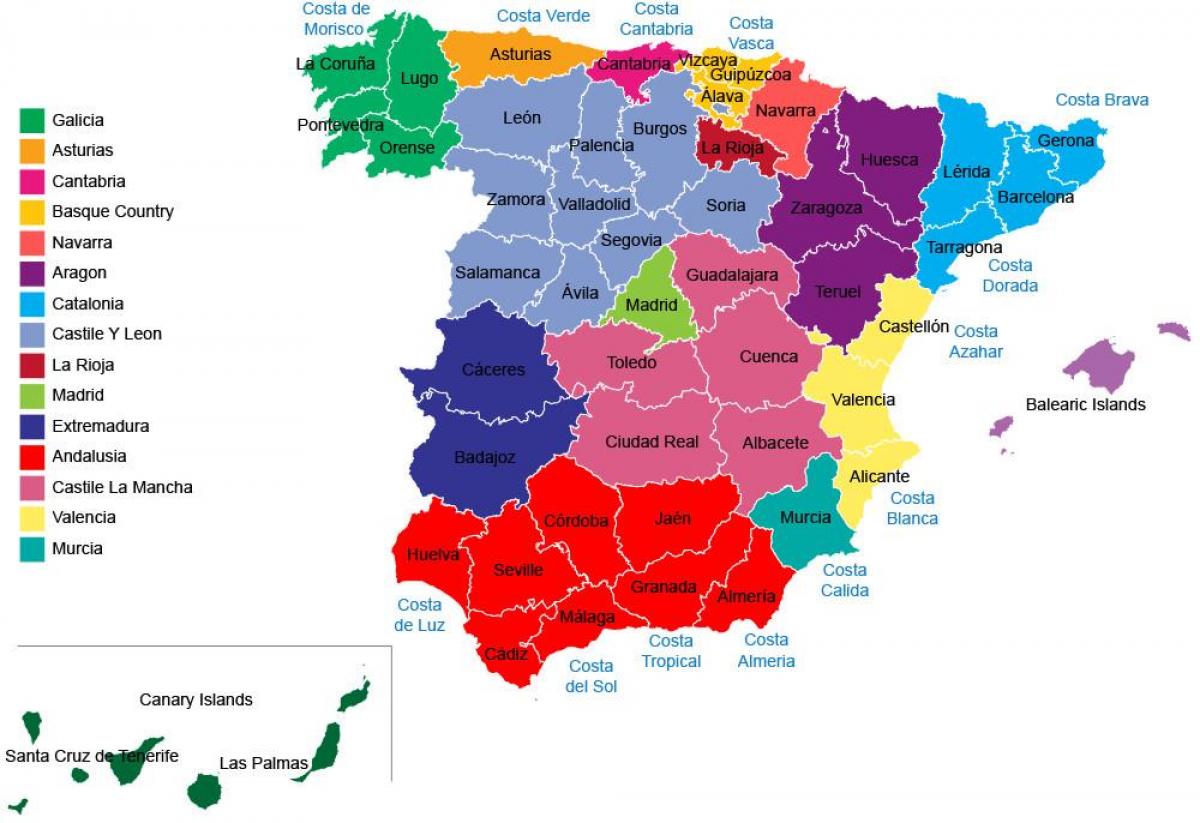
Unveiling the intricate tapestry of Spain's geography, this guide offers a comprehensive journey through Spanish maps, their historical evolution, and their modern-day applications. From ancient cartographic traditions to the cutting-edge technology of the present, we explore the stories and significance these maps hold.
The Ancient Origins of Spanish Cartography
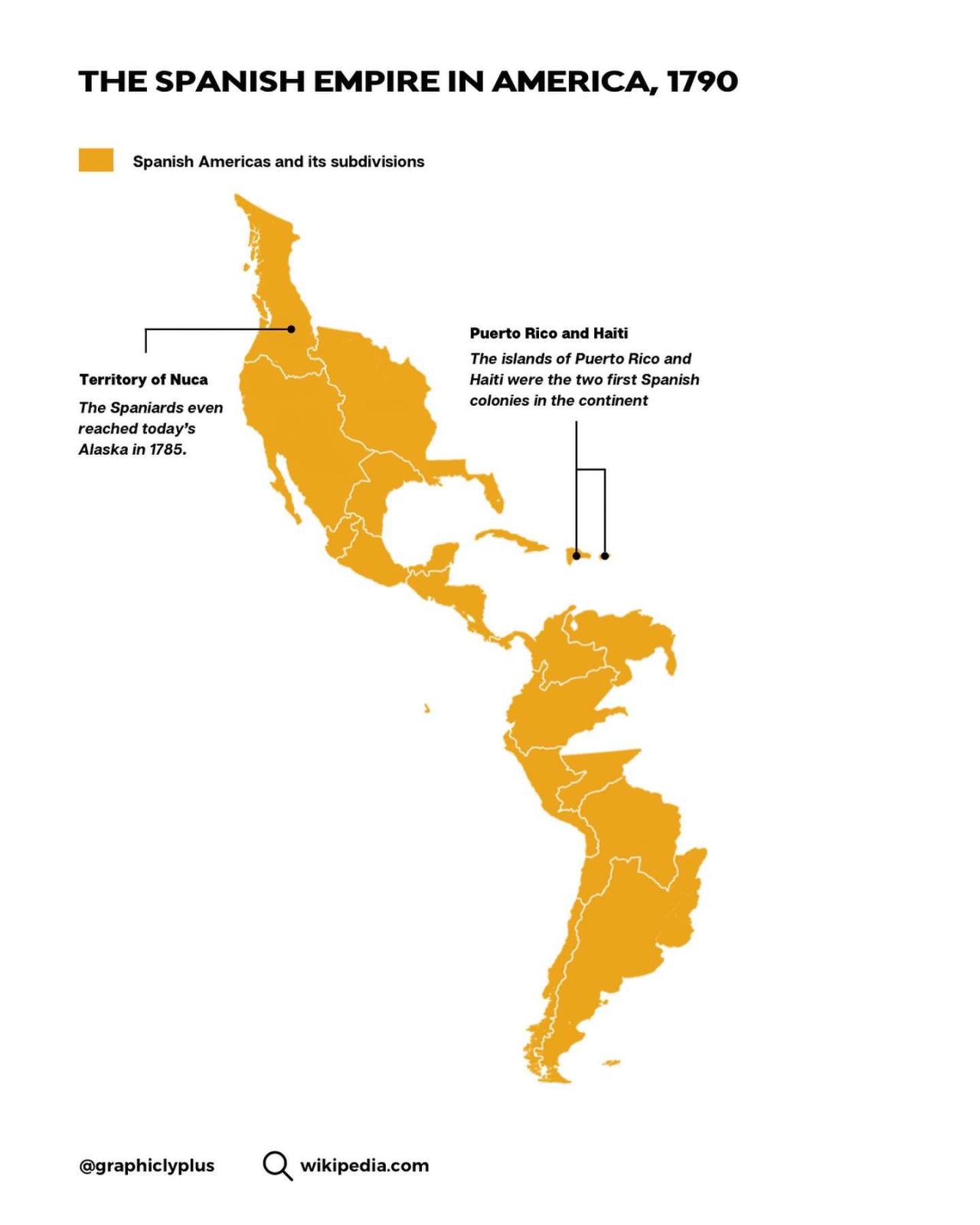
The roots of Spanish mapmaking can be traced back to the rich cultural tapestry of ancient civilizations that once flourished on the Iberian Peninsula. The Phoenicians, Greeks, and Romans all left their mark on the region, contributing to the early development of cartographic practices. These ancient maps, often adorned with intricate details and artistic flourishes, served not only as navigational tools but also as cultural artifacts reflecting the worldviews of their creators.
One notable example is the Tabula Peutingeriana, a 13th-century copy of a Roman road map that depicts the extensive network of roads and settlements across the Roman Empire, including the Iberian Peninsula. This ancient document provides a fascinating glimpse into the Roman understanding of geography and their mastery of land transportation.
Medieval Cartography and the Golden Age of Spain

The Middle Ages witnessed a remarkable flourishing of cartographic skills in Spain, largely influenced by the cultural exchange between Christian, Muslim, and Jewish communities. This period saw the creation of intricate portolan charts, used by sailors to navigate the Mediterranean and beyond. These charts, with their distinctive compass roses and intricate coastal details, were among the most advanced navigational tools of their time.
Pros of Medieval Spanish Cartography
- Highly accurate coastal representations, aiding in safe navigation.
- Integration of cultural knowledge, reflecting diverse perspectives.
- Advancements in nautical science and instrument development.
Cons of Medieval Spanish Cartography
- Limited inland detail, focusing primarily on coastal areas.
- Lack of standardized symbols and conventions.
- Rarity and exclusivity, with maps often being closely guarded secrets.
The Renaissance and Beyond: Technological Advancements
The Renaissance brought about a revolution in cartographic techniques, with the introduction of printing presses allowing for the widespread dissemination of maps. Spanish cartographers played a significant role in this era, contributing to the development of more accurate and detailed maps. The 16th century saw the emergence of notable figures like Diego Gutiérrez, whose maps of the Americas were among the most advanced of their time, offering new insights into the geography of the New World.
The Golden Age of Spanish Cartography
The 17th and 18th centuries, often referred to as the Golden Age of Spain, were a period of remarkable cartographic achievement. Spanish mapmakers, often employed by the royal court, created exquisite maps that combined artistic excellence with scientific precision. These maps, often featuring intricate engravings and colorful illustrations, not only served practical purposes but also became prized possessions and symbols of national pride.
Modern Applications: From Tourism to Technology
In the modern era, Spanish maps have evolved to meet the diverse needs of a globalized world. From detailed road maps for tourists exploring the country’s rich cultural heritage to advanced GIS (Geographic Information Systems) used in urban planning and environmental management, Spanish cartography has adapted to new technologies and applications.
Modern Mapmaking: A Step-by-Step Process
- Data Collection: Utilizing advanced GPS and remote sensing technologies, cartographers gather a wealth of geographic data.
- Processing and Analysis: This data is then processed and analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies.
- Map Design: With the data ready, cartographers employ their artistic skills to create visually appealing and informative maps.
- Publishing and Dissemination: Finally, maps are made accessible through various mediums, including online platforms, printed materials, and interactive digital formats.
The Future of Spanish Cartography

Looking ahead, the future of Spanish cartography is poised for exciting developments. With the continued advancement of technology, we can expect to see even more sophisticated maps, incorporating real-time data and interactive features. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms may further revolutionize the field, enabling more accurate predictions and analyses.
How have Spanish maps evolved over time?
+Spanish maps have evolved from ancient, hand-drawn representations to modern, digital masterpieces. The journey has been marked by technological advancements, with each era contributing unique advancements and insights.
What is the significance of portolan charts in Spanish cartography?
+Portolan charts, with their intricate coastal details, played a crucial role in maritime navigation during the Middle Ages. They represented the culmination of cultural exchange and advanced nautical science, becoming indispensable tools for sailors exploring the Mediterranean and beyond.
How do modern Spanish maps impact tourism and urban planning?
+Modern Spanish maps, with their detailed representations of roads, attractions, and landmarks, are invaluable tools for tourists exploring the country. Additionally, advanced GIS maps are used in urban planning, helping cities manage growth, infrastructure, and environmental challenges.
What role does technology play in the future of Spanish cartography?
+Technology will continue to shape the future of Spanish cartography, with advancements in data collection, processing, and visualization. The integration of AI and machine learning may further enhance the accuracy and interactivity of maps, revolutionizing the field.
From ancient traditions to modern innovations, Spanish maps offer a captivating journey through time and space. As we continue to explore and navigate the world, the evolution of cartography in Spain serves as a testament to human ingenuity and our enduring fascination with understanding our place in the world.



