5 Facts About Loose Areolar Connective Tissue

Fact 1: The Origin of Loose Areolar Connective Tissue
Loose areolar connective tissue, often referred to as “areolar tissue,” is a fascinating and vital component of our bodies. This unique type of connective tissue forms a delicate network throughout our tissues, providing support, protection, and a means of communication between different cell types. Its name, “areolar,” originates from the Latin word “areola,” meaning “small open space,” which perfectly describes its appearance under a microscope.
Fact 2: Unique Cellular Composition
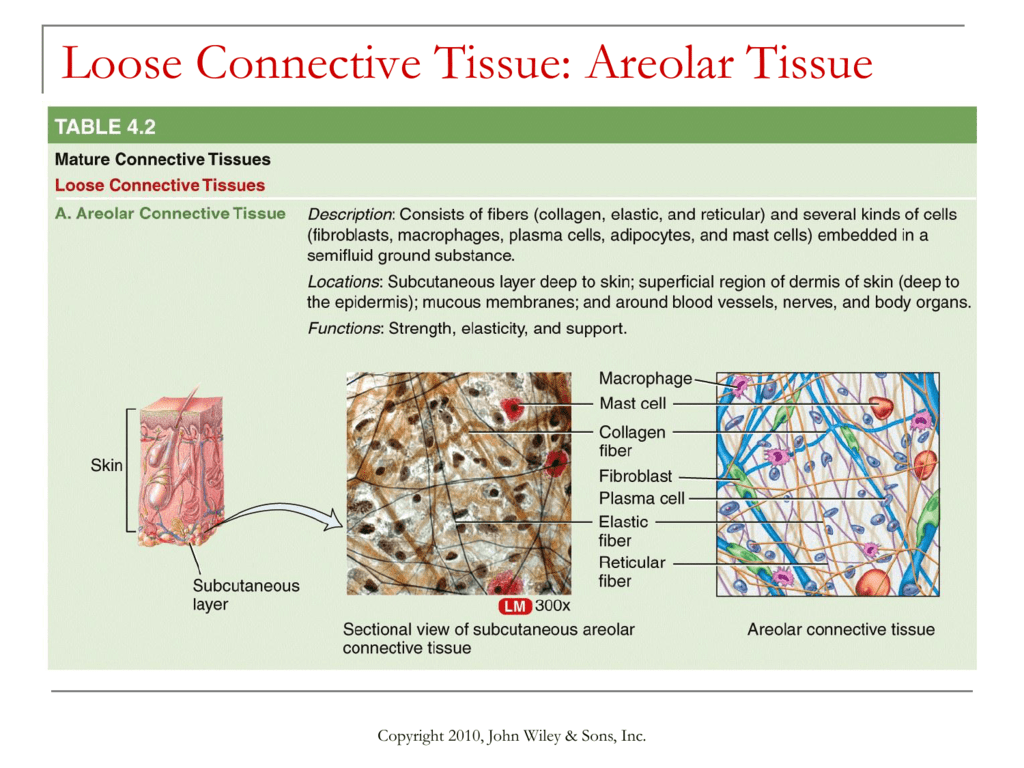
What sets loose areolar connective tissue apart is its cellular makeup. Unlike other connective tissues, it contains a diverse array of cell types, each with specific functions. The primary cells include fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, and adipocytes. Fibroblasts are the master builders, producing collagen and other fibers to give the tissue its structural integrity. Macrophages act as the tissue’s guardians, engulfing foreign particles and cellular debris. Mast cells, with their ability to release histamine, play a crucial role in immune responses and inflammation. Adipocytes, or fat cells, are responsible for energy storage and insulation.
Fact 3: A Versatile Matrix
The matrix of loose areolar connective tissue is incredibly versatile and adaptable. It consists of a gel-like substance called ground substance, which is rich in proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans. This gel-like matrix provides a fluid environment for cells to move and interact, facilitating the exchange of nutrients and waste products. Additionally, the ground substance acts as a shock absorber, cushioning and protecting the tissues and organs it surrounds.
Fact 4: Crucial Role in Wound Healing
Loose areolar connective tissue plays a pivotal role in wound healing. When our skin or other tissues are injured, this tissue springs into action. Fibroblasts migrate to the wound site, producing collagen fibers to close the gap and initiate the healing process. Macrophages clear away damaged cells and debris, creating a clean environment for healing. Mast cells release substances that attract immune cells and promote inflammation, a necessary step in the healing cascade. The flexibility and adaptability of loose areolar connective tissue make it an essential component of the body’s repair system.
Fact 5: Connections and Communication
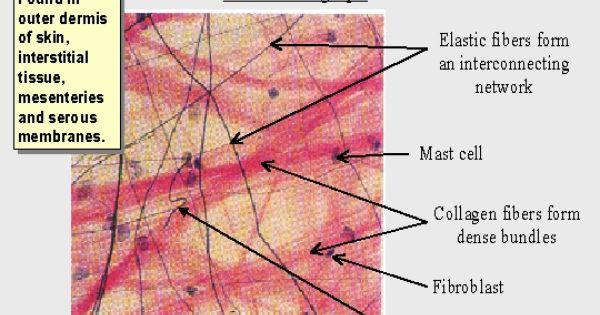
One of the most intriguing aspects of loose areolar connective tissue is its ability to facilitate communication between different cell types and tissues. It acts as a conduit, allowing signals to travel between cells, organs, and the nervous system. This intricate network of connections ensures that our bodies function as a harmonious whole. For example, nerve endings in the tissue can detect changes in pressure or temperature, providing sensory feedback to the brain.
The Pros and Cons of Loose Areolar Connective Tissue
- Pros: Provides essential support and protection to organs and tissues, facilitates cell communication, and plays a vital role in wound healing.
- Cons: Can become damaged or inflamed due to injury, infection, or disease, potentially leading to impaired function and chronic pain.
What is the primary function of loose areolar connective tissue?
+Loose areolar connective tissue serves multiple functions, including providing support and protection to organs and tissues, facilitating cell communication, and playing a crucial role in wound healing. Its adaptability and diverse cellular composition make it a vital component of our body’s structure and function.
Can loose areolar connective tissue be damaged, and what are the implications?
+Yes, loose areolar connective tissue can be damaged due to injury, infection, or certain diseases. When damaged, it may lead to impaired function, inflammation, and potentially chronic pain. In severe cases, it can affect the overall integrity and function of the affected tissues or organs.
How does loose areolar connective tissue contribute to overall health and well-being?
+Loose areolar connective tissue plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. Its support and protection of organs and tissues ensure their proper functioning. Additionally, its role in wound healing and cell communication helps our bodies respond to injuries and maintain homeostasis.
What are some common conditions or diseases that can affect loose areolar connective tissue?
+Loose areolar connective tissue can be affected by various conditions and diseases, including arthritis, fibromyalgia, connective tissue disorders, and certain autoimmune diseases. These conditions can lead to inflammation, pain, and impaired function of the affected tissues.