The Amazing Areolar Connective Tissue

Areolar connective tissue, often referred to as the “fibrous friend,” is an unsung hero in the intricate tapestry of our bodies. This ubiquitous tissue, found throughout our anatomical landscape, plays a crucial role in maintaining structural integrity and facilitating bodily functions. Its diverse nature and adaptability make it a fascinating subject of exploration, revealing the intricacies of our physiological design.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of areolar connective tissue, uncovering its unique characteristics, functions, and significance in human physiology. From its microscopic structure to its macroscopic impact, we will explore why this tissue is indeed amazing and essential to our overall health and well-being.
Areolar connective tissue is the body's Swiss Army knife, equipped with a versatile toolkit to handle a myriad of tasks. Its adaptability and functionality are a testament to the brilliance of biological design.
Microscopic Marvels: The Composition of Areolar Connective Tissue
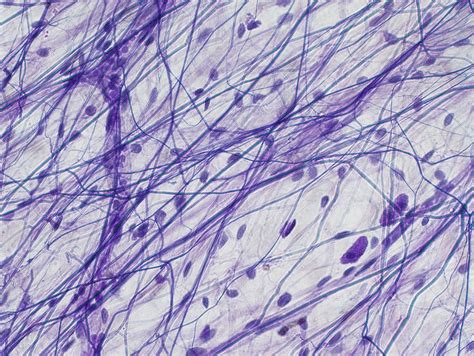
At the microscopic level, areolar connective tissue is a complex network of cells and fibers, each playing a critical role in its overall function. The primary components include:
Fibroblasts: These are the master builders of connective tissue. Fibroblasts are responsible for producing the fibers and ground substance that give areolar tissue its structure and elasticity. They are also key players in the healing process, migrating to sites of injury to initiate repair.
Collagen Fibers: Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, and for good reason. These strong, flexible fibers provide tensile strength to the tissue, allowing it to withstand stretching and pulling forces. Collagen fibers are arranged in a crisscross pattern, providing stability and support.
Elastic Fibers: Complementing the collagen fibers are elastic fibers, which add elasticity and resilience to the tissue. These fibers allow the tissue to stretch and recoil, facilitating movement and flexibility.
Ground Substance: This gel-like matrix surrounds the cells and fibers, providing a lubricated environment that allows for smooth movement and protection. It consists of proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans, which bind water and contribute to the tissue’s fluidity and shock-absorbing properties.
Versatile Functions: The Roles of Areolar Connective Tissue

The unique composition of areolar connective tissue enables it to perform a diverse range of functions, contributing to the overall health and functionality of various organs and systems. Here are some of its key roles:
Support and Cushioning: Areolar tissue provides structural support to organs, preventing them from collapsing under their own weight. Its gel-like ground substance acts as a cushion, absorbing shocks and protecting delicate tissues from damage.
Flexibility and Movement: The elastic fibers in areolar tissue allow for smooth, flexible movement. This is particularly important in areas like the skin, where it enables stretching and contraction during activities like breathing and exercise.
Nutrient Delivery: The vascular nature of areolar tissue means it is well-supplied with blood vessels. This facilitates the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to surrounding cells, ensuring they receive the sustenance they need to function optimally.
Immune Response: Areolar tissue contains various immune cells, such as macrophages and lymphocytes, which are crucial in mounting an immune response against pathogens. These cells patrol the tissue, identifying and eliminating foreign invaders.
Wound Healing: In the event of injury, areolar tissue plays a vital role in the healing process. Fibroblasts migrate to the site of injury, producing collagen and other fibers to repair damaged tissue. Its vascular nature also ensures a steady supply of nutrients and immune cells to aid in healing.
Areolar Connective Tissue in Action: Real-World Applications
The impact of areolar connective tissue extends beyond the microscopic level, with its functions influencing our everyday lives and overall health. Here are some real-world examples of its importance:
Skin Elasticity: The elastic fibers in areolar tissue are crucial for maintaining skin elasticity. As we age, these fibers can become less effective, leading to wrinkles and saggy skin. Understanding the role of areolar tissue can inform strategies for maintaining youthful skin.
Joint Mobility: Areolar tissue is found in the synovial membranes of joints, providing cushioning and facilitating smooth movement. In conditions like arthritis, the inflammation and degradation of this tissue can lead to reduced mobility and pain.
Wound Care: In wound healing, the role of areolar tissue is paramount. By understanding its functions, healthcare professionals can develop more effective wound care strategies, promoting faster and more efficient healing.
Organ Support: Areolar tissue surrounds and supports vital organs, ensuring they remain in their correct position and function optimally. Its structural integrity is essential for the overall health and functionality of these organs.
Future Trends: Exploring the Potential of Areolar Connective Tissue
As our understanding of areolar connective tissue deepens, so too do the potential applications and innovations it could inspire. Here are some future trends and possibilities:
Regenerative Medicine: The ability of areolar tissue to repair and regenerate itself makes it a promising candidate for regenerative medicine. By harnessing its healing potential, researchers could develop therapies for a range of conditions, from skin injuries to organ failure.
Biomaterials: The unique composition of areolar tissue could inspire the development of new biomaterials for medical and engineering applications. These materials could be used in everything from tissue engineering to advanced wound dressings.
Personalized Medicine: Understanding an individual’s unique areolar tissue composition could lead to personalized medicine approaches. This could involve tailored treatments based on an individual’s tissue characteristics, optimizing healing and reducing adverse reactions.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Amazing Areolar Connective Tissue

Areolar connective tissue, with its diverse composition and functions, is a true hero of human physiology. From its microscopic structure to its macroscopic impact, it showcases the brilliance of biological design. By understanding and appreciating the role of this tissue, we can unlock new possibilities for healthcare, innovation, and a deeper understanding of our bodies.
As we continue to explore the wonders of areolar connective tissue, let us remember the importance of this often-overlooked tissue in maintaining our health and well-being. Its story is a testament to the beauty and complexity of the human body, a true masterpiece of nature’s design.
The areolar connective tissue, with its unique composition and multifaceted functions, is a true marvel of nature. Its versatility and adaptability make it a crucial component of our physiological symphony, deserving of our appreciation and admiration.
What is the primary function of areolar connective tissue?
+Areolar connective tissue serves a diverse range of functions, including providing structural support, facilitating movement, delivering nutrients, and participating in the immune response and wound healing. Its adaptability makes it essential for maintaining the health and functionality of various organs and systems.
How does areolar tissue contribute to skin elasticity?
+The elastic fibers in areolar tissue are crucial for maintaining skin elasticity. These fibers allow the skin to stretch and recoil, preventing wrinkles and saggy skin. However, as we age, these fibers can become less effective, leading to reduced skin elasticity.
What role does areolar tissue play in joint health?
+Areolar tissue is found in the synovial membranes of joints, providing cushioning and facilitating smooth movement. Its role is crucial in maintaining joint health and mobility. In conditions like arthritis, the degradation of areolar tissue can lead to reduced joint function and pain.
Can areolar tissue be regenerated?
+Yes, areolar tissue has the ability to regenerate and repair itself. This regenerative potential makes it a promising candidate for regenerative medicine, with the potential to develop therapies for a range of conditions, from skin injuries to organ failure.
How does areolar tissue contribute to organ support and protection?
+Areolar tissue surrounds and supports vital organs, preventing them from collapsing under their own weight. Its gel-like ground substance acts as a cushion, absorbing shocks and protecting delicate tissues from damage. This structural support is essential for the overall health and functionality of organs.