Understanding the Loanable Funds Market: 5 Key Insights

Introduction to the Loanable Funds Market

The loanable funds market is a crucial component of any economy, shaping the flow of capital and influencing a range of economic activities. At its core, this market determines the availability and cost of funds for borrowers, impacting everything from personal finances to large-scale business investments. As such, a comprehensive understanding of this market’s dynamics is essential for both individual decision-making and broader economic policy formulation.
In this article, we delve into five key insights that shed light on the loanable funds market, offering a nuanced perspective on its inner workings and broader implications. By exploring these insights, we aim to empower readers with the knowledge to navigate this market effectively and make informed choices that align with their financial goals.
The Equilibrium in Loanable Funds
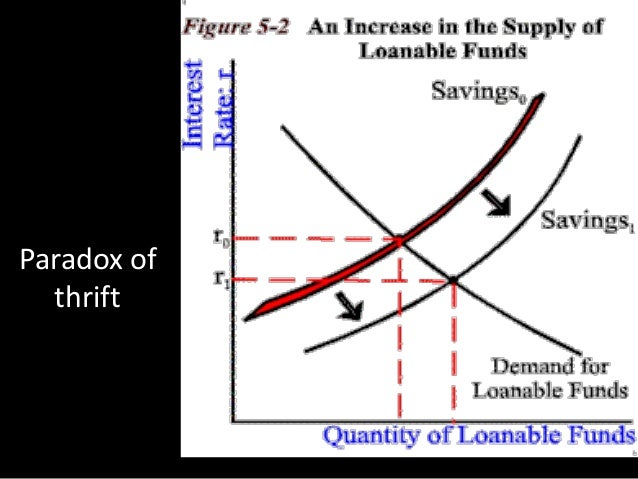
The concept of equilibrium in the loanable funds market is fundamental to understanding its dynamics. In a state of equilibrium, the market interest rate aligns with the intersection of the supply and demand curves for loanable funds. This equilibrium interest rate ensures that the market’s demand for funds is met by the available supply, creating a balance that stabilizes the market.
However, this equilibrium is not static; it can shift due to various factors. An increase in the demand for loanable funds, for instance, could be driven by expanding business activities or rising consumer spending. On the other hand, a surge in supply might occur as a result of higher savings rates or a decline in investment opportunities. These shifts can lead to disequilibrium, necessitating adjustments in the interest rate to restore balance.
Supply of Loanable Funds: Savings and Investments
The supply of loanable funds originates primarily from two sources: household savings and institutional investments. Household savings, derived from personal income and often directed into savings accounts or investment vehicles, represent a significant portion of the loanable funds pool. On the institutional side, investments from businesses, governments, and financial institutions contribute to the supply, driven by their need to allocate capital efficiently.
The level of savings and investment activities can be influenced by a range of factors, including income levels, economic confidence, and the availability of attractive investment opportunities. A robust economy, for example, may encourage higher savings rates and increased investment, thereby expanding the supply of loanable funds. Conversely, economic downturns can lead to reduced savings and investment, constricting the supply.
Demand for Loanable Funds: Borrowing Activities
The demand for loanable funds is driven by the borrowing activities of households, businesses, and governments. For households, borrowing may be necessitated by large purchases such as homes or vehicles, or by the need to consolidate existing debts. Businesses, on the other hand, borrow to finance expansion, acquire new assets, or cover operational expenses. Governments may borrow to fund public projects, manage budget deficits, or address emergency situations.
The level of demand for loanable funds is influenced by various economic factors. A thriving economy may lead to increased borrowing as businesses expand and households have greater financial confidence. Conversely, economic downturns can reduce borrowing activities as businesses and households become more cautious. Interest rates also play a significant role, with lower rates generally stimulating borrowing and higher rates suppressing demand.
The Role of Interest Rates in Market Dynamics
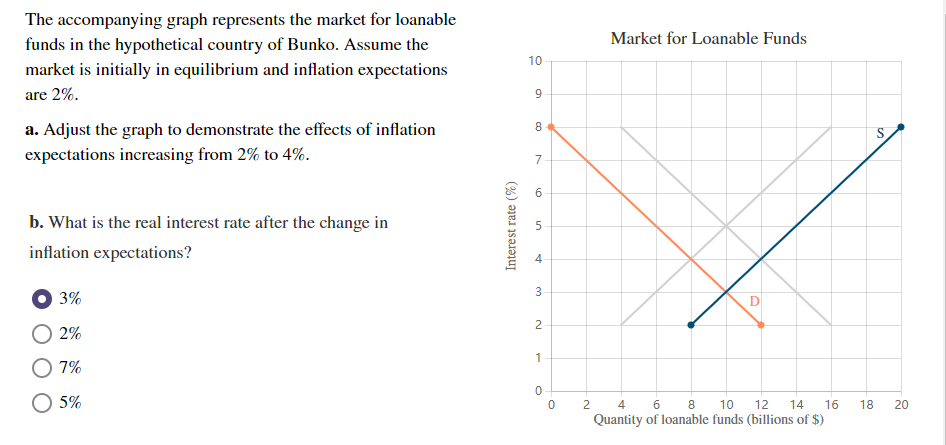
Interest rates are a critical determinant in the loanable funds market, influencing both the supply and demand of funds. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes more attractive, leading to increased demand for loanable funds. Conversely, high interest rates can deter borrowing, as the cost of funds becomes prohibitive.
Interest rates also impact the supply side. When rates are high, investors are incentivized to seek out higher-yielding investment opportunities, increasing the supply of loanable funds. Conversely, low interest rates may reduce the incentive to save or invest, potentially decreasing the supply of loanable funds. The interplay between interest rates and market dynamics is complex, with central banks and monetary policy playing a significant role in managing these relationships.
Market Efficiency and its Impact on Borrowers and Lenders
Market efficiency in the loanable funds market is crucial for ensuring that funds are allocated optimally. In an efficient market, borrowers and lenders interact in a way that maximizes the benefits for both parties. Borrowers obtain funds at competitive interest rates, while lenders earn returns that reflect the risk associated with their loans.
However, market inefficiencies can arise due to various factors, including information asymmetry, transaction costs, and regulatory barriers. These inefficiencies can result in suboptimal fund allocation, where borrowers may face higher borrowing costs or have difficulty accessing funds, while lenders may earn lower returns or face higher default risks.
Enhancing Market Efficiency: The Role of Financial Intermediaries
Financial intermediaries, such as banks and other lending institutions, play a critical role in enhancing the efficiency of the loanable funds market. These intermediaries act as a bridge between borrowers and lenders, facilitating the flow of funds and providing valuable services such as loan origination, credit evaluation, and risk management.
By leveraging their expertise and resources, financial intermediaries can reduce transaction costs, improve information asymmetry, and mitigate risks. This, in turn, can lead to a more efficient market, benefiting both borrowers and lenders. Financial intermediaries also provide a range of financial products and services, such as savings accounts, loans, and investment opportunities, further enhancing market efficiency and accessibility.
Conclusion: Navigating the Loanable Funds Market
In conclusion, the loanable funds market is a dynamic and complex environment, shaped by a multitude of factors. By understanding the key insights outlined in this article, individuals and businesses can make more informed decisions when navigating this market. Whether it’s borrowing for personal or business needs, investing surplus funds, or understanding the broader economic implications, a comprehensive understanding of the loanable funds market is essential.
As we’ve explored, the equilibrium in loanable funds, the interplay between supply and demand, the role of interest rates, and the importance of market efficiency all contribute to the intricate dynamics of this market. By staying informed and proactive, individuals and businesses can position themselves to capitalize on opportunities and navigate challenges effectively.