Understanding the Difference: Lead Time vs Cycle Time
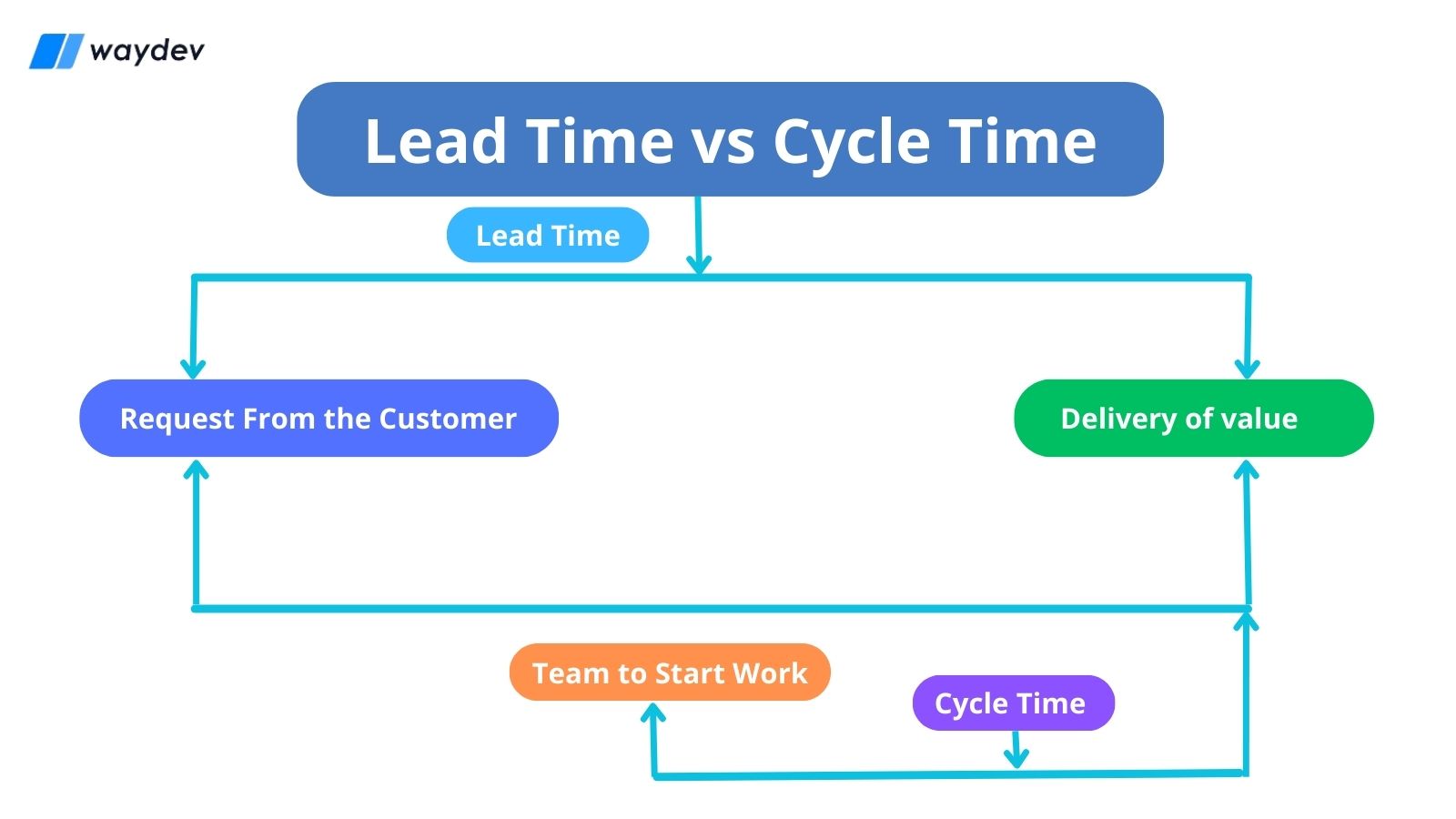
In the realm of project management and process optimization, two key metrics that often come into play are lead time and cycle time. While they may seem similar at first glance, these terms refer to distinct aspects of a project's timeline and understanding their differences is crucial for effective planning and performance evaluation.
Lead time and cycle time are essential concepts for any business or organization aiming to enhance productivity, reduce bottlenecks, and deliver products or services more efficiently. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of these metrics, their implications, and how they can be leveraged to drive operational excellence.
Defining Lead Time
Lead time is a term frequently used in project management, supply chain, and lean manufacturing contexts. It represents the total time elapsed from the initiation of a process or task to its completion, encompassing all stages, including those that may not be under direct control.
For instance, in the case of manufacturing a product, lead time would start from the moment the raw materials are ordered and end when the finished product is delivered to the customer. This time frame includes not only the actual production process but also the time taken for material procurement, quality checks, and transportation.
In simpler terms, lead time is the entire duration a customer or stakeholder has to wait for a product or service to be delivered, from start to finish. It is a comprehensive metric that considers the entire value stream of a process.
Components of Lead Time
- Queue Time: This refers to the time a task or order spends waiting to be processed. It is often a result of limited resources or bottlenecks in the system.
- Processing Time: The actual time taken to complete a task or process a request. This is the active work time and does not include breaks or idle periods.
- Move Time: The time taken to physically move a product or component from one stage to another. This could include transportation or the time spent in transit.
- Inspection Time: Time allocated for quality checks and inspections to ensure the product meets the required standards.
Lead time is a critical metric for businesses as it directly impacts customer satisfaction and the overall efficiency of operations. A longer lead time can lead to delays in delivery, increased costs, and potential loss of business opportunities.
Understanding Cycle Time

Cycle time, on the other hand, focuses on the active work time within a process. It measures the duration from the commencement of a task to its completion, excluding any waiting or idle periods. In essence, cycle time represents the efficiency of the process itself, without considering external factors.
For example, in a software development project, cycle time would be the time taken to develop a specific feature, from coding to testing and deployment. It does not include the time the feature spent in the backlog or the time taken for approval processes.
Cycle time is a vital metric for process optimization as it helps identify areas where resources can be allocated more effectively and where bottlenecks may be causing delays. By optimizing cycle time, businesses can improve their overall productivity and reduce the time taken to deliver value to customers.
Key Differences and Implications
| Metric | Definition | Key Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Time | Total time from process initiation to completion, including all stages. |
|
| Cycle Time | Time taken for active work on a task, excluding waiting or idle periods. |
|

Understanding the distinction between lead time and cycle time is crucial for businesses to set realistic expectations, optimize their processes, and deliver value to customers more effectively. By analyzing and managing these metrics, organizations can gain insights into their operations, identify areas for improvement, and ultimately enhance their overall performance.
Real-World Examples and Analysis
To illustrate the practical applications of lead time and cycle time, let's consider a fast-food restaurant scenario. In this context, lead time would represent the time a customer waits from placing an order to receiving their meal, including the time taken for order preparation, cooking, and serving.
On the other hand, cycle time would focus solely on the active work time, such as the time taken to cook a burger or prepare a salad. It would exclude the time the customer spends waiting in line to place their order or the time the food spends waiting to be served.
By analyzing these metrics, the restaurant management can identify areas for improvement. For instance, if the cycle time for cooking burgers is consistently high, they might invest in additional equipment or training to speed up the process. Meanwhile, if the lead time is excessive due to long queues, they might consider optimizing the ordering process or adding more staff during peak hours.
Optimizing Lead Time: Strategies and Techniques
- Value Stream Mapping: Visualize and analyze the entire process to identify areas of waste and inefficiency. This can help in streamlining the workflow and reducing lead time.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory Management: Implement JIT techniques to minimize the time spent on material procurement and reduce the queue time for tasks.
- Lean Manufacturing Principles: Adopt lean principles to eliminate waste, optimize processes, and reduce the overall lead time.
- Process Automation: Automate repetitive tasks to speed up the process and reduce human error, which can contribute to shorter lead times.
Improving Cycle Time: Best Practices
- Resource Optimization: Allocate resources effectively to balance workload and minimize idle time. This can involve cross-training staff or using technology to optimize resource allocation.
- Process Standardization: Establish clear, standardized processes to ensure efficiency and consistency. This can help in reducing variability in cycle times.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously analyze and improve processes to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Techniques like Kaizen can be employed for incremental improvements.
- Performance Measurement and Feedback: Regularly measure and analyze cycle times to identify trends and areas for improvement. Provide feedback to teams to encourage efficiency and motivate improvement.
By implementing these strategies and best practices, businesses can effectively manage their lead times and cycle times, leading to improved operational performance and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Future Implications and Trends
As businesses continue to prioritize efficiency and customer satisfaction, the effective management of lead time and cycle time will remain crucial. With the increasing focus on digital transformation and process automation, we can expect to see more advanced technologies being leveraged to optimize these metrics.
For instance, the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms can help in predicting lead times more accurately, especially in dynamic environments. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make real-time adjustments to processes, leading to significant improvements in lead time and cycle time.
Additionally, the concept of Agile methodologies is gaining traction in various industries, not just software development. Agile principles, such as iterative development and continuous improvement, can be applied to optimize cycle times and lead times in a wide range of processes.
Final Thoughts
In today's fast-paced business landscape, understanding and effectively managing lead time and cycle time is essential for any organization aiming to stay competitive. By grasping the nuances of these metrics and implementing strategies to optimize them, businesses can deliver products and services more efficiently, enhance customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive their success in the market.
How do lead time and cycle time impact customer satisfaction?
+Long lead times can lead to delays in delivery, impacting customer satisfaction. On the other hand, high cycle times can indicate inefficiencies in the process, which may also affect customer satisfaction as it can result in longer wait times for services or products.
Can lead time and cycle time be reduced simultaneously?
+Yes, it is possible to reduce both lead time and cycle time through strategic process improvements. However, it often requires a holistic approach to address various aspects of the process, including resource allocation, process standardization, and technology integration.
What role does technology play in optimizing lead time and cycle time?
+Technology plays a crucial role in optimizing lead time and cycle time. It can help in automating processes, providing real-time data and analytics, and enabling more efficient resource management. Advanced technologies like AI and ML can further enhance these optimization efforts.



