3 Ways Wireless Internet Is Telecommunication
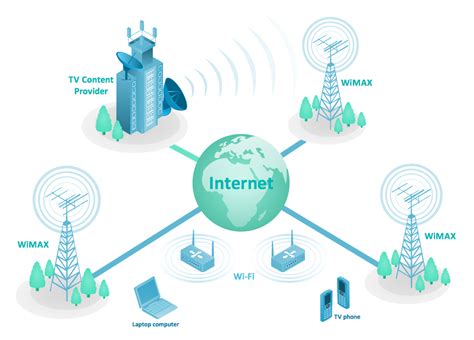
The rise of wireless internet technology has revolutionized the way we communicate and access information. It has become an integral part of our daily lives, powering our smartphones, laptops, and various connected devices. While we often associate wireless internet with the convenience of Wi-Fi and mobile networks, it plays a much larger role in the realm of telecommunication, contributing to the seamless flow of data and communication across the globe.
In this article, we will explore three distinct ways in which wireless internet is a pivotal component of the telecommunication industry, shaping the way we connect and interact in the digital age.
1. Wireless Broadband: The Foundation of Digital Communication
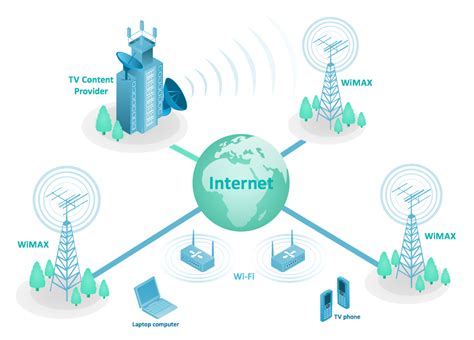
Wireless broadband technologies, such as 4G and 5G cellular networks, have become the backbone of modern telecommunication. These high-speed wireless connections enable the efficient transmission of data, voice, and multimedia content over long distances. They power our smartphones, providing us with seamless access to the internet, streaming services, and communication platforms.
The evolution of wireless broadband has been remarkable. From the early days of 2G networks, which primarily supported voice calls and basic data transfer, we have progressed to 4G LTE networks that offer lightning-fast data speeds, enabling us to stream high-definition videos and engage in video conferencing with ease. The latest 5G networks promise even greater speeds and low latency, opening up new possibilities for immersive experiences, autonomous vehicles, and the Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
| Generation | Speed | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| 2G | Up to 50 Kbps | Voice calls, SMS |
| 3G | Up to 2 Mbps | Mobile internet, video calls |
| 4G LTE | Up to 1 Gbps | HD streaming, mobile gaming |
| 5G | Up to 10 Gbps | VR/AR, IoT, autonomous cars |

The widespread adoption of wireless broadband has led to a significant shift in how we consume media and communicate. It has empowered individuals and businesses alike, enabling remote work, online education, and the seamless exchange of information across borders. With each generation of wireless technology, we move closer to a truly connected world, where communication barriers fade away.
Benefits of Wireless Broadband:
- High-speed data transfer for efficient communication.
- Enhanced connectivity for remote areas, bridging the digital divide.
- Support for a wide range of applications, from basic internet access to advanced IoT solutions.
2. Wi-Fi: Unlocking Wireless Freedom

Wi-Fi, a wireless networking technology based on the IEEE 802.11 standard, has become an indispensable part of our lives. It allows devices to connect to the internet without the need for physical cables, providing wireless freedom and flexibility.
The advent of Wi-Fi has transformed the way we interact with technology. It has enabled the proliferation of smart homes, where devices like thermostats, lighting systems, and security cameras can be controlled remotely. In businesses, Wi-Fi facilitates collaboration, with employees able to work seamlessly across different devices and locations. Public Wi-Fi hotspots have also become common, offering internet access to travelers and commuters.
Key Advantages of Wi-Fi:
- Wireless connectivity for multiple devices, promoting flexibility and convenience.
- Supports high-speed data transfer for streaming, online gaming, and cloud services.
- Enables the Internet of Things (IoT) by connecting a wide range of devices.
| Wi-Fi Standard | Speed | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 802.11b | Up to 11 Mbps | Basic internet access |
| 802.11g | Up to 54 Mbps | Video streaming, online gaming |
| 802.11n | Up to 600 Mbps | HD video streaming, large file transfers |
| 802.11ac | Up to 1 Gbps | 4K video streaming, VR/AR applications |
| 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) | Up to 10 Gbps | Ultra-high-speed applications, dense environments |
As Wi-Fi technology continues to evolve, we can expect even faster speeds and more efficient connections. The latest Wi-Fi 6 standard, for instance, promises to handle dense networks with improved performance, making it ideal for busy public spaces and large enterprises.
3. Satellite Communication: Connecting the World from Above
While terrestrial wireless technologies like cellular networks and Wi-Fi dominate our daily lives, satellite communication plays a crucial role in telecommunication, especially in remote and underserved areas.
Satellite communication systems utilize a network of artificial satellites orbiting the Earth to provide wireless connectivity. These satellites can transmit signals over vast distances, making them ideal for regions where laying physical cables is impractical or expensive. They are commonly used for television broadcasting, weather monitoring, and emergency communication services.
Applications of Satellite Communication:
- Television broadcasting, bringing live news and entertainment to remote areas.
- Weather monitoring and forecasting, helping meteorologists track storms and issue timely warnings.
- Emergency communication during natural disasters or in remote locations.
- Military communication for secure and reliable transmission of sensitive information.
The use of satellite communication is particularly vital for maritime and aviation industries. Ships and aircraft can maintain constant connectivity with ground stations, ensuring safety and efficient navigation. Additionally, satellite phones and networks provide a reliable means of communication in regions with limited or no terrestrial network coverage.
As we look to the future, advancements in satellite technology, such as the deployment of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellations, promise to bring high-speed internet access to even the most remote corners of the globe. This has the potential to revolutionize communication and access to information for underserved communities.
How does wireless internet compare to wired connections in terms of speed and reliability?
+Wireless internet, especially with the latest 5G and Wi-Fi 6 technologies, can offer speeds comparable to or even surpassing wired connections. However, wired connections generally provide more consistent and reliable performance, as they are less susceptible to interference and signal degradation. The choice between wireless and wired depends on factors like the specific use case, location, and desired level of stability.
What are the security concerns associated with wireless internet, and how can they be addressed?
+Wireless networks can be more vulnerable to unauthorized access and cyberattacks compared to wired networks. To enhance security, it’s crucial to use strong encryption protocols, regularly update firmware and software, employ robust authentication measures, and educate users about best practices for secure connectivity.
How is the Internet of Things (IoT) influenced by wireless internet technologies?
+Wireless internet is integral to the growth and success of IoT. It enables the connectivity of a vast array of devices, from smart home appliances to industrial sensors, allowing for remote monitoring, control, and data exchange. The low-power, wide-area network (LPWAN) technologies used in IoT often rely on wireless communication protocols like LoRa and Sigfox.



