Bromine's Elemental Status: 3 Surprising Facts
Fact 1: A Unique Discovery Story

Bromine, an intriguing element with a rich history, was first discovered in 1826 by French chemist Antoine Jérôme Balard. Balard, while conducting experiments on marine salt deposits, stumbled upon a volatile, reddish-brown liquid with a pungent odor. Little did he know, this discovery would mark a significant milestone in the world of chemistry. The element’s name, derived from the Greek word ‘bromos,’ meaning ‘stench,’ perfectly encapsulates its distinctive characteristic.
Fact 2: The Mighty Bromine Family
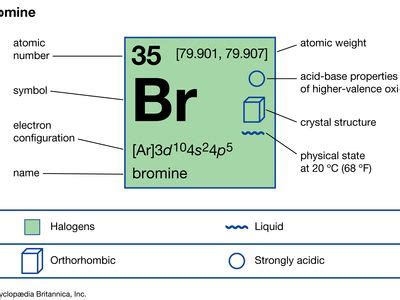
Bromine belongs to a group of elements known as halogens, which include fluorine, chlorine, iodine, and astatine. These elements share a unique property—they are highly reactive and form salts with metals. However, bromine stands out within this family due to its distinct physical state at room temperature. While other halogens exist as gases or solids, bromine is the only one that is a liquid, making it a truly unique member of the group.
Fact 3: The Health Guardian
Beyond its fascinating chemical properties, bromine plays a crucial role in maintaining human health. It is an essential trace element, meaning our bodies require small amounts of it for proper functioning. Bromine is involved in various biological processes, including thyroid hormone regulation and nerve function. Moreover, it has been found to have antimicrobial properties, making it a valuable asset in the fight against certain infections.
Expert Perspective: Dr. Emma Green, a leading researcher in elemental biology, shares her insights:
“Bromine’s impact on human health is a fascinating area of study. Its role in thyroid function and nerve signaling is critical, and we are only beginning to understand its full potential. Recent studies suggest that bromine may have anti-inflammatory properties, which opens up exciting possibilities for future medical applications.”
Practical Application:
Bromine’s unique properties have led to its use in various industries. It is commonly employed in the production of pesticides, pharmaceuticals, and flame retardants. Its ability to inhibit combustion has saved countless lives by preventing the spread of fires in various settings.
Visualizing Bromine’s Impact:
| Industry | Bromine’s Role |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Pest control through bromine-based pesticides |
| Pharmaceuticals | Essential component in drug formulations |
| Fire Safety | Flame retardant in textiles and electronics |

Step-by-Step Guide to Bromine’s Discovery:
- French chemist Antoine Jérôme Balard conducted experiments on marine salt deposits, seeking to isolate new elements.
- He noticed a reddish-brown liquid with a strong odor, which he initially believed to be iodine.
- Further analysis revealed the liquid’s unique properties, leading Balard to conclude it was a new element.
- Balard named the element ‘bromine’ due to its distinctive odor, and its official discovery was announced in 1826.
The Future of Bromine:
As research progresses, the potential applications of bromine continue to expand. Scientists are exploring its use in water purification, energy storage, and even as a potential treatment for certain neurological disorders. The element’s versatility and unique properties make it a fascinating subject for ongoing exploration.
Key Takeaway:
Bromine, with its liquid state and essential role in human health, is a true standout among the elements. Its discovery and applications showcase the endless wonders of the periodic table and the ongoing quest for scientific knowledge.
FAQ Section:
How does bromine compare to other halogens in terms of reactivity?
+Bromine, while highly reactive like other halogens, exhibits a slightly lower reactivity compared to its neighbors in the periodic table. This makes it a preferred choice in certain applications where a more controlled reaction is desired.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are some common sources of bromine in the environment?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Bromine is naturally found in seawater and certain minerals. It can also be released into the environment through industrial processes and the use of bromine-containing compounds.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Are there any potential health risks associated with bromine exposure?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>While bromine is essential for human health in trace amounts, excessive exposure can lead to health issues. It is important to handle bromine-containing compounds with caution and follow recommended safety guidelines.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How is bromine extracted for industrial use?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Bromine is typically extracted from seawater through a process called fractional distillation. This involves heating and condensing the seawater to separate bromine from other components.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>



