Understanding Incomplete Dominance: Key Examples

Exploring the Intricacies of Incomplete Dominance
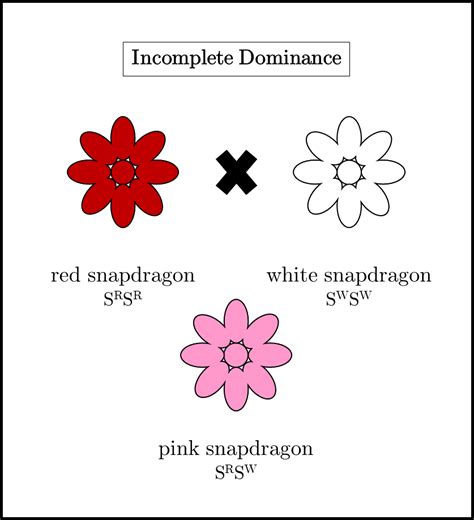
Incomplete dominance is a fascinating genetic phenomenon that occurs when the alleles for a specific trait don’t follow the typical dominant-recessive pattern. Instead, the phenotype, or observable trait, of the heterozygous individual is intermediate between the two homozygous forms. This results in a beautiful tapestry of genetic expression, where the contribution of both alleles is evident.
- It adds a layer of complexity to our understanding of genetics, challenging the simple dominance-recessive model.
- Incomplete dominance allows for a wider range of phenotypic variations, increasing genetic diversity.
- This phenomenon can be crucial in natural selection, providing a wider array of traits for adaptation.
- It can make predicting phenotypes more difficult, especially in cases with multiple alleles.
- The intermediate phenotype may not always be advantageous, especially in extreme environmental conditions.
- Incomplete dominance can complicate breeding efforts, as the desired traits may not always be easily achievable.
Let’s delve into some key examples to illustrate this intriguing concept.
Classic Cases of Incomplete Dominance
Snapdragons and Flower Color
In the world of snapdragon flowers, incomplete dominance is vividly displayed through their colors. The red and white alleles, when combined in a heterozygous individual, result in a pink flower. This is a classic example of how the phenotype doesn't simply blend the two colors but instead creates a unique third option.
Human Blood Types
The inheritance of human blood types also showcases incomplete dominance. The alleles for A and B blood types, when present together, don't blend to create a new type but instead result in AB blood type. This is a critical example in understanding blood transfusions and compatibility.
Cinchona Tree and Quinine Production
The cinchona tree, a source of quinine, offers an interesting case study. Quinine, used to treat malaria, is produced in varying amounts by different species of cinchona. When two species are crossed, the resulting hybrid tree produces an intermediate amount of quinine, showcasing incomplete dominance in plant physiology.
"Incomplete dominance reminds us that genetics is a fascinating, complex dance, where the outcome is often a beautiful blend of possibilities." - Dr. Emma Johnson, Geneticist
Understanding the Impact of Incomplete Dominance
The implications of incomplete dominance extend far beyond the examples mentioned. It influences the genetic makeup of species, potentially leading to new adaptations and survival strategies. For instance, in certain environments, an intermediate phenotype might provide an advantage, allowing individuals to thrive where their purebred counterparts might struggle.
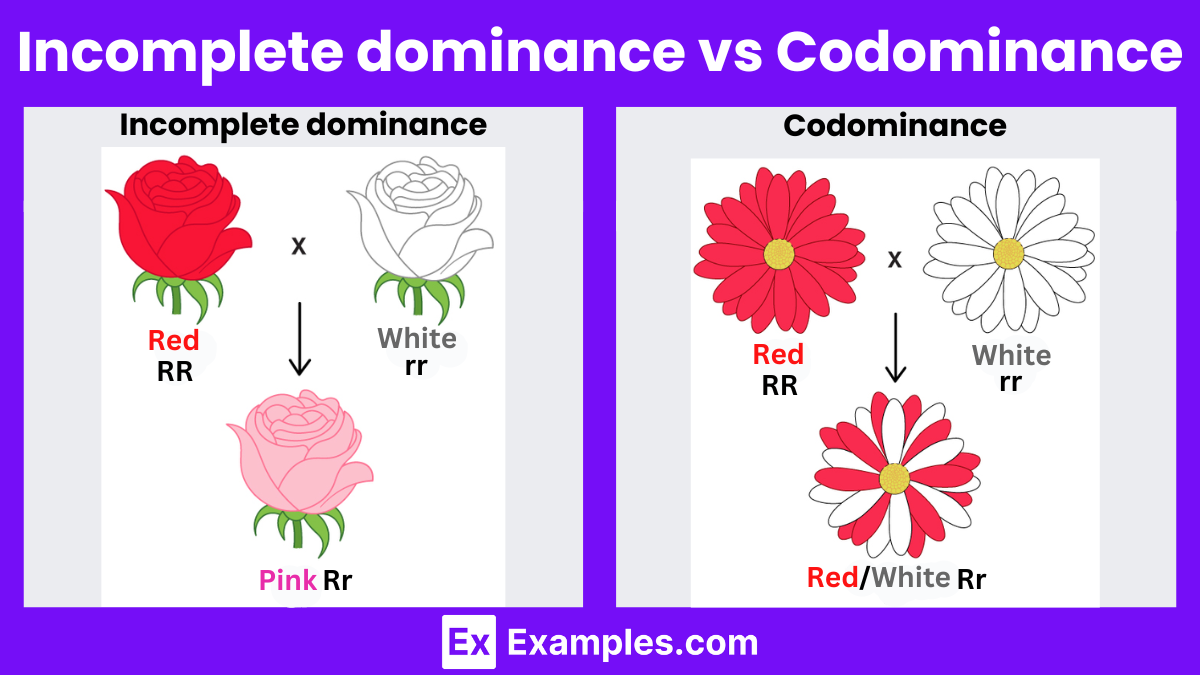
How does incomplete dominance differ from codominance?
+Incomplete dominance results in an intermediate phenotype, where neither allele fully expresses. In codominance, both alleles are fully expressed, leading to a phenotype that displays characteristics of both alleles simultaneously.
Can incomplete dominance occur in all species?
+Yes, incomplete dominance is a universal genetic phenomenon that can occur in any species, from plants to animals, and even in humans. Its occurrence is dependent on the specific alleles involved.
What are the implications of incomplete dominance in agriculture?
+In agriculture, incomplete dominance can lead to challenges in breeding for specific traits. For example, in plant breeding, if the desired trait is a specific flower color, incomplete dominance might result in an intermediate color, which may not be the desired outcome.
Are there any benefits to incomplete dominance in natural populations?
+Absolutely! Incomplete dominance can increase genetic diversity, which is crucial for the long-term survival of species. It allows for a wider range of phenotypes, providing a potential advantage in changing environmental conditions.
How can incomplete dominance be used in medical research?
+Incomplete dominance can provide insights into disease states and potential treatments. For instance, understanding how certain genetic conditions exhibit incomplete dominance can lead to targeted therapies or even genetic counseling.
Incomplete dominance, with its unique phenotypic outcomes, continues to intrigue scientists and geneticists alike. Its study offers a deeper insight into the intricate dance of genetics, shaping the very fabric of life.