5 Easy Ways to Understand Incomplete Dominance
Understanding Incomplete Dominance
The concept of incomplete dominance in genetics is a fascinating yet complex topic, often leaving students and enthusiasts alike wondering how to grasp its intricacies. This phenomenon, where neither allele fully dominates the other, presents a unique challenge to our understanding of inheritance. Let’s explore five simple strategies to demystify incomplete dominance and unlock its secrets.
Visualize the Blend: One of the most effective ways to comprehend incomplete dominance is by visualizing it. Imagine a colorful spectrum where one allele represents a vibrant red, and the other, a deep blue. When these alleles come together, they don’t overpower each other; instead, they blend, creating a unique shade of purple. This visual representation helps us understand that incomplete dominance results in a phenotype that is a mix of both parental traits.
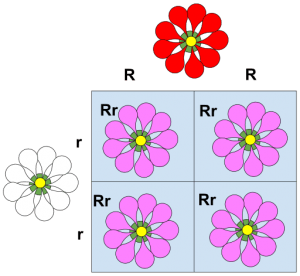
Study Real-World Examples: Nature provides us with countless examples of incomplete dominance. Take the snapdragon flower, for instance. In snapdragons, the alleles for flower color exhibit incomplete dominance. When a red snapdragon (with the allele RR) is crossed with a white snapdragon (with the allele WW), the offspring, having the allele RW, display a pink color. This blending of colors is a perfect illustration of incomplete dominance.
Understand Allele Interactions: In genetics, alleles are like actors in a play. In incomplete dominance, these actors don’t steal the show alone; they share the spotlight. Unlike complete dominance, where one allele dominates and the other remains hidden, in incomplete dominance, both alleles contribute to the final phenotype. It’s like a harmonious duet, where each allele’s melody is heard, creating a unique symphony.
Explore Punnet Squares: Punnet squares are powerful tools to predict genetic outcomes. When dealing with incomplete dominance, these squares become even more intriguing. By arranging the alleles and calculating the probabilities, we can visualize the chances of different phenotypes appearing. For instance, if we cross a snapdragon with genotype RW (pink) with another RW snapdragon, we can predict the probabilities of pink, red, and white flowers in the offspring.
Dive into Gene Expression: Incomplete dominance also offers a window into the fascinating world of gene expression. Here, we explore how genes are translated into observable traits. In this case, the expression of both alleles results in a phenotype that is a combination of both traits. It’s a reminder that our genetic makeup is a complex tapestry, with each thread contributing to the final picture.
Key Takeaway: Understanding incomplete dominance is not just about memorizing definitions; it’s about grasping the beauty of genetic interplay. By visualizing blends, studying real-world examples, understanding allele interactions, exploring Punnet squares, and delving into gene expression, we unlock the secrets of this fascinating phenomenon. So, the next time you encounter incomplete dominance, remember these strategies and embrace the wonders of genetic diversity.
FAQ:
How does incomplete dominance differ from complete dominance?
+Incomplete dominance differs from complete dominance in that both alleles contribute to the phenotype, resulting in a blend of traits. In complete dominance, one allele dominates and masks the effect of the other allele.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can incomplete dominance occur in humans?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes, incomplete dominance can occur in humans. An example is the AB blood type, where individuals inherit an A allele and a B allele, resulting in a phenotype that exhibits both traits, hence the AB blood type.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are some common examples of incomplete dominance in nature?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Some common examples include the snapdragon flower color, where RR results in red, WW in white, and RW in pink; and the four o'clock plant, where red and white alleles blend to produce pink flowers.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can incomplete dominance be predicted using Punnet squares?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>By arranging the alleles in a Punnet square and calculating the probabilities, we can predict the ratio of different phenotypes in the offspring. This helps us understand the likelihood of various traits being expressed.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>