The Ultimate Guide to Selecting Columns in Power BI
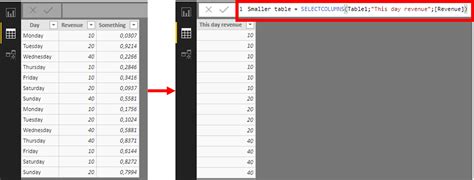
In the world of data visualization and analysis, Microsoft Power BI has become an invaluable tool for businesses and professionals seeking to derive meaningful insights from their data. One of the critical steps in the Power BI workflow is selecting the right columns to include in your visual representations. This process can be intricate and requires a thoughtful approach to ensure that the chosen columns provide the necessary context and depth for effective data storytelling.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide an expert-level understanding of the art of selecting columns in Power BI. By delving into various strategies, techniques, and considerations, we will equip you with the knowledge and skills to make informed decisions when crafting your Power BI reports and dashboards. Whether you're a seasoned Power BI user or a novice looking to master this essential aspect of data visualization, this guide will serve as your ultimate resource.
Understanding the Significance of Column Selection

The process of selecting columns in Power BI is a fundamental step that sets the foundation for your entire data analysis and visualization journey. It involves identifying and choosing the specific columns from your dataset that will be used to create visuals, build calculations, and ultimately, tell a compelling story with your data.
The significance of this step cannot be overstated. The columns you select will determine the level of detail, the granularity of your insights, and the overall clarity of your visualizations. A well-thought-out column selection process ensures that your Power BI reports are not only visually appealing but also rich in information and context.
By carefully choosing columns, you can highlight the key trends, patterns, and relationships within your data. This process enables you to create focused and meaningful visualizations that resonate with your audience and help them make informed decisions. On the other hand, an inadequate or haphazard column selection can lead to cluttered, confusing visuals that fail to convey the intended message.
Key Considerations for Effective Column Selection
- Data Relevance: Ensure that the columns you select are directly relevant to the story you want to tell. This involves understanding the business context, the intended audience, and the specific insights you aim to uncover.
- Data Quality: Assess the quality of the data within each column. Look for accuracy, consistency, and completeness. Poor-quality data can lead to misleading insights and undermine the credibility of your visualizations.
- Column Relationships: Consider the relationships between different columns. Identify columns that can be used together to reveal interesting patterns or correlations. This is crucial for building effective visualizations and calculations.
- Data Granularity: Decide on the level of detail you need in your visualizations. Selecting columns with the appropriate level of granularity ensures that your visuals provide the right balance between detail and readability.
- Data Transformations: Keep in mind that Power BI offers a wide range of data transformation capabilities. You can perform calculations, create new columns, and aggregate data to enhance your analysis. Plan ahead to incorporate these transformations effectively.
Strategies for Effective Column Selection

Selecting the right columns in Power BI requires a strategic approach. Here are some proven strategies to guide your decision-making process:
1. Start with a Clear Objective
Before diving into the details of your dataset, define a clear objective for your Power BI report or dashboard. Understand the key questions you want to answer, the insights you aim to uncover, and the story you want to tell. This will serve as a guiding principle for your column selection.
For instance, if your objective is to analyze customer churn, you might prioritize columns related to customer demographics, purchase history, and engagement metrics. This clear objective will help you focus on the most relevant data and avoid unnecessary complexity.
2. Analyze Data Types and Relationships
Power BI supports various data types, including numeric, textual, date/time, and boolean. Understanding the data types in your columns is essential for effective selection. Different data types lend themselves to specific visualizations and calculations.
For example, numeric data is ideal for creating charts like bar graphs or line charts, while textual data might be more suited for tables or matrices. Date/time data, on the other hand, can be used for time-based visualizations like timelines or trend analyses.
Additionally, consider the relationships between columns. Identify columns that are directly related or dependent on each other. This can help you create more sophisticated visualizations and calculations that reveal deeper insights.
3. Consider the Level of Detail
The level of detail you choose for your columns can significantly impact the clarity and effectiveness of your visualizations. Power BI allows you to aggregate data at various levels, such as sums, averages, counts, or unique values.
For instance, if you're analyzing sales data, you might start with a high-level view, aggregating sales figures by month or quarter. This provides an overview of sales trends over time. However, if you need to drill down into the specifics, you can select columns that provide details at the individual transaction level, such as product SKU, customer ID, or order date.
Finding the right balance between high-level trends and granular details is crucial. It ensures that your visualizations are both informative and understandable for your audience.
4. Leverage Power BI’s Data Modeling Features
Power BI offers powerful data modeling capabilities that can assist in your column selection process. By creating relationships between tables and defining hierarchies, you can organize your data in a way that supports your analysis.
For example, you might create a hierarchy for a "Product Category" column, allowing you to drill down from high-level categories like "Electronics" to more specific subcategories like "Smartphones" or "Laptops." This hierarchical structure simplifies the process of selecting the right columns for different levels of analysis.
5. Perform Exploratory Data Analysis
Before finalizing your column selection, it’s beneficial to conduct exploratory data analysis (EDA). EDA involves examining your dataset to uncover patterns, outliers, and potential relationships between variables.
Tools like Power BI's Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) can be invaluable for this purpose. You can create calculated columns, measures, and custom visualizations to gain a deeper understanding of your data. This step often leads to valuable insights that can guide your column selection and overall data modeling approach.
Best Practices for Column Selection
Adhering to best practices can elevate your column selection process and ensure that your Power BI reports and dashboards are of the highest quality.
1. Keep it Simple
Simplicity is a cornerstone of effective data visualization. When selecting columns, aim for a concise and focused approach. Avoid cluttering your visuals with excessive columns that may confuse your audience or obscure the key insights.
Focus on the columns that are most essential to your analysis and story. If a column doesn't directly contribute to your objectives, consider excluding it. A minimalist approach ensures that your visualizations are easy to interpret and resonate with your audience.
2. Use Descriptive Column Names
Clear and descriptive column names are essential for both you and your audience. They make it easier to understand the purpose and content of each column, especially when working with complex datasets.
For example, instead of using a generic name like "Column1," consider a more descriptive name like "Customer Purchase History" or "Product Sales Trend." This practice improves the readability of your visuals and makes it simpler to navigate your Power BI report.
3. Maintain Data Consistency
Consistency is crucial when working with data. Ensure that the data within each column is consistent in format, structure, and values. Inconsistent data can lead to errors in calculations and visualizations, undermining the reliability of your analysis.
For instance, if you have a column representing customer ages, ensure that all values are in the same format (e.g., years or months) and that there are no missing or erroneous values. Maintaining data consistency ensures that your visualizations and calculations are accurate and trustworthy.
4. Utilize Data Validation and Cleansing
Before selecting columns, perform data validation and cleansing to ensure that your dataset is free from errors, duplicates, and irrelevant data. Power BI provides tools to help with this process, such as the Data Validation feature and the Data Cleansing extension.
Data validation allows you to set rules and constraints for your columns, ensuring that the data meets specific criteria. Data cleansing, on the other hand, helps you identify and remove errors, duplicates, or irrelevant entries from your dataset. These steps ensure that your column selection is based on high-quality, reliable data.
Advanced Column Selection Techniques
For more advanced users, Power BI offers a range of sophisticated techniques to enhance your column selection process and take your data analysis to the next level.
1. Using DAX for Advanced Calculations
Power BI’s Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) language is a powerful tool for creating advanced calculations and measures. DAX allows you to perform complex calculations on your data, providing deeper insights and more sophisticated visualizations.
For example, you can use DAX to calculate rolling averages, moving averages, or custom ratios. These calculations can then be used to create new columns or measures, which can be included in your visualizations. DAX is particularly useful when you need to manipulate data in unique ways that go beyond basic aggregations.
2. Creating Custom Visuals
Power BI’s Custom Visuals feature allows you to create your own custom visualizations or use third-party visuals to showcase your data in innovative ways. This advanced technique can be especially useful when you want to present data in a unique format or when your data requires a specialized visualization approach.
For instance, you might create a custom visual to display a network graph for visualizing customer relationships or a custom heatmap to highlight geographic sales patterns. Custom visuals provide an opportunity to showcase your data in a way that aligns perfectly with your specific analysis needs.
3. Applying Machine Learning for Column Selection
Machine learning techniques can be applied to automate and optimize the column selection process. Power BI integrates with Microsoft’s Azure Machine Learning service, allowing you to leverage advanced algorithms for data analysis.
You can use machine learning to identify patterns and correlations within your data, helping you determine which columns are most relevant for your analysis. This approach can save time and effort, especially when dealing with large and complex datasets.
4. Utilizing Power Query for Data Transformation
Power Query, an integral part of Power BI, is a powerful tool for data transformation and cleaning. It allows you to manipulate and transform your data before it enters the Power BI environment.
With Power Query, you can perform a wide range of transformations, including merging data from multiple sources, standardizing data formats, and creating new columns based on complex calculations. This ensures that your column selection process is based on clean, standardized data, enhancing the quality of your analysis.
Performance Considerations and Optimization
As you select columns and build your Power BI reports, it’s essential to consider the performance implications of your choices. Large datasets and complex visualizations can impact the speed and responsiveness of your reports.
1. Optimize Data Size and Structure
Large datasets can slow down your Power BI reports. Consider optimizing the size and structure of your data to ensure efficient performance. This may involve reducing the number of rows or columns, aggregating data, or using Power BI’s data compression features.
Additionally, ensure that your data is structured efficiently. Power BI works best with properly formatted tables and relationships. Avoid redundant or unnecessary columns, and use data modeling techniques to optimize your dataset's structure.
2. Leverage Power BI’s Performance Features
Power BI offers various performance-enhancing features that can improve the speed and responsiveness of your reports. These include data compression, data caching, and query optimization.
Data compression reduces the size of your dataset, making it more efficient to load and manipulate. Data caching stores frequently used data in memory, improving the speed of report refreshes. Query optimization helps Power BI execute queries more efficiently, especially for complex calculations or large datasets.
3. Use Live Connections with Care
Power BI supports live connections to data sources, allowing you to work with real-time data. However, live connections can impact report performance, especially when dealing with large datasets or frequent data updates.
Consider using direct query mode or importing data into Power BI when working with large datasets. These approaches ensure that Power BI can work with a static copy of your data, improving performance and reducing the load on your data sources.
Future Implications and Trends
As Power BI continues to evolve, several trends and developments are shaping the future of column selection and data visualization.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
AI is increasingly being integrated into Power BI, enhancing its capabilities for data analysis and visualization. AI-powered features can automate tasks, such as column selection, and provide intelligent recommendations based on your data.
For example, Power BI's AI-powered "Ask a Question" feature allows users to ask natural language queries about their data. The tool then suggests relevant columns and visualizations to answer the question, streamlining the data exploration process.
2. Enhanced Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP capabilities are becoming more sophisticated in Power BI. This allows users to interact with their data using natural language, making data analysis more accessible and intuitive.
With NLP, users can ask questions about their data in plain language, and Power BI will suggest relevant columns and visualizations based on the query. This feature simplifies the process of column selection and data exploration, especially for non-technical users.
3. Integration with Other Microsoft Services
Power BI is part of the Microsoft Power Platform, which includes Power Apps and Power Automate. The integration between these services is expected to become tighter, allowing for more seamless data flow and analysis.
For instance, you might use Power Apps to collect real-time data from field workers, which can then be directly analyzed in Power BI. This integration streamlines the data collection and analysis process, providing more timely and accurate insights.
4. Emphasis on Data Storytelling
The future of data visualization in Power BI is moving towards more effective data storytelling. This involves creating visualizations that not only present data but also tell a compelling story, making it easier for audiences to understand and act upon the insights.
Power BI is expected to introduce more features that support data storytelling, such as improved narration and animation capabilities, allowing users to create visually engaging and interactive reports that truly bring their data to life.
💡 Expert Tip: Stay updated with the latest Power BI releases and features to leverage the latest tools and capabilities for column selection and data visualization. The Power BI community and Microsoft's documentation are excellent resources for learning about new features and best practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between selecting columns in Power BI and other data visualization tools?
+Power BI offers a unique combination of powerful data modeling, transformation, and visualization capabilities. Unlike some other tools, Power BI allows for extensive data manipulation and the creation of complex relationships between columns, providing a deeper level of analysis and visualization.
Can I change my column selection after creating a Power BI report?
+Absolutely! Power BI is designed to be flexible, allowing you to easily modify your column selection at any time. You can add or remove columns, adjust their data types, and even create new columns based on calculations or transformations. This flexibility ensures that you can adapt your report as your analysis needs evolve.
How can I ensure that my column selection is optimized for performance?
+To optimize column selection for performance, consider the following: reduce the number of columns and rows in your dataset, aggregate data when appropriate, use data compression and caching features, and leverage Power BI’s query optimization tools. Additionally, avoid live connections for large datasets unless necessary.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when selecting columns in Power BI?
+Some common mistakes include selecting columns without a clear objective, failing to validate and clean data, using inconsistent column names, and ignoring the impact of column selection on report performance. It’s crucial to have a well-defined strategy and to ensure data quality throughout the process.



