Excel Tutorial: Create Cumulative Charts

Creating cumulative charts in Excel is an excellent way to visualize and analyze data that represents a running total or cumulative sum over time. This type of chart is particularly useful for tracking progress, monitoring growth, or identifying trends in various scenarios, such as sales performance, project milestones, or financial investments. In this tutorial, we will delve into the process of constructing cumulative charts in Excel, exploring various techniques and providing real-world examples to enhance your understanding.
Understanding Cumulative Charts
Cumulative charts, also known as cumulative line charts or cumulative area charts, are a powerful visualization tool that displays the cumulative sum of a dataset over a specific period. They are especially valuable when you need to assess the cumulative impact of individual data points or when you want to highlight the overall trend rather than individual data fluctuations.
Imagine you are a sales manager tracking your team's monthly sales performance. By creating a cumulative chart, you can visualize the total sales generated by your team month by month, providing a clear picture of the team's overall progress and growth.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Cumulative Charts
Follow these detailed steps to create cumulative charts in Excel:
Step 1: Prepare Your Data
Before creating your chart, ensure your data is properly formatted. You should have two columns: one for the date or time period and another for the corresponding data values. For instance, if you are tracking sales, your data might look like this:
| Date | Sales |
|---|---|
| Jan-23 | 1200 |
| Feb-23 | 1500 |
| Mar-23 | 1800 |
| Apr-23 | 2000 |
| May-23 | 2200 |
Step 2: Calculate the Cumulative Sum
To create a cumulative chart, you need to calculate the cumulative sum of your data values. Excel provides a straightforward formula for this task. Select a cell adjacent to your data, enter the formula =SUM(Sales), and copy it down the column. This will generate a new column with the cumulative sum of your sales data.
| Date | Sales | Cumulative Sales |
|---|---|---|
| Jan-23 | 1200 | 1200 |
| Feb-23 | 1500 | 2700 |
| Mar-23 | 1800 | 4500 |
| Apr-23 | 2000 | 6500 |
| May-23 | 2200 | 8700 |
Step 3: Create the Cumulative Chart
Now that you have your cumulative data, it’s time to create the chart. Follow these steps:
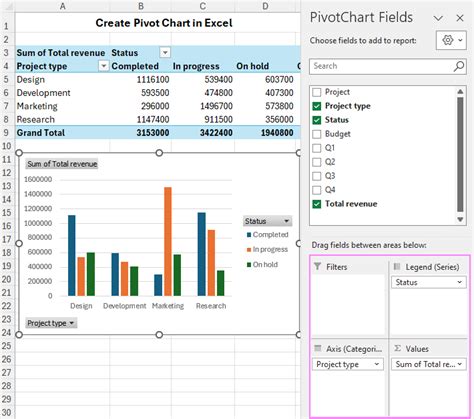
- Select the data, including both the date and cumulative sum columns.
- Go to the Insert tab on the Excel ribbon and choose a line chart or area chart from the Charts group.
- Excel will generate a basic chart. To enhance it, right-click on the chart and select Select Data or Edit Data.
- In the Select Data Source window, you can edit the chart’s data series. Ensure the date column is set as the category (X-axis) and the cumulative sum column as the series (Y-axis) data.
- You can further customize the chart by adding titles, changing colors, and adjusting the chart style to suit your preferences.
Step 4: Interpreting the Cumulative Chart
Once your cumulative chart is created, you can gain valuable insights from it. Here are some key observations you can make:
- The line or area in the chart represents the cumulative sum of your data over time. It shows the overall trend and progress.
- By comparing the chart with your original data, you can identify periods of significant growth or decline.
- You can also spot patterns or trends that might not be apparent in a standard line chart.
Real-World Examples
Cumulative charts have numerous applications across various industries. Let’s explore some practical examples:
Sales Performance Tracking
In the sales industry, cumulative charts are invaluable for tracking overall sales performance. By visualizing the cumulative sales over time, sales managers can assess the team’s progress, identify successful periods, and make informed decisions to improve sales strategies.
Project Management
Project managers can use cumulative charts to monitor project milestones and track the cumulative progress of tasks. This helps in identifying potential delays or areas where the project is ahead of schedule.
Financial Analysis
Financial analysts and investors can create cumulative charts to visualize the cumulative return on investment over time. This provides a clear picture of the investment’s performance and helps in making strategic financial decisions.
Advanced Techniques
While the basic steps outlined above will create a functional cumulative chart, there are advanced techniques to enhance your visualization and analysis:
Using Excel’s Trendline Feature
Excel’s trendline feature can be a powerful addition to your cumulative chart. It allows you to add a trendline to your chart, which can help identify the overall trend or growth rate. To add a trendline:
- Right-click on the data series in your chart and select Add Trendline.
- Choose the appropriate trendline type (linear, exponential, logarithmic, etc.) based on your data.
- Excel will add the trendline to your chart, providing a visual representation of the overall trend.
Customizing Chart Elements
Excel offers a wide range of customization options to make your cumulative chart visually appealing and informative. You can adjust chart titles, axis labels, gridlines, and data labels to enhance clarity and readability. Additionally, you can change the chart type, add error bars, or incorporate secondary axes for complex datasets.
Comparative Analysis
Cumulative charts can be used for comparative analysis by including multiple data series on the same chart. This allows you to compare the cumulative performance of different teams, products, or investment portfolios.
Conclusion

Creating cumulative charts in Excel is a powerful way to visualize and analyze cumulative data, offering insights into overall trends and progress. By following the step-by-step guide and exploring advanced techniques, you can enhance your data visualization skills and make more informed decisions based on your data. Remember, cumulative charts are versatile and applicable to various industries, making them a valuable tool for data analysis and communication.
How can I create a cumulative chart for multiple data series in Excel?
+To create a cumulative chart for multiple data series, follow these steps: First, calculate the cumulative sum for each data series using the SUM function. Then, select all the data, including the date and cumulative sum columns for each series. Go to the Insert tab and choose a line or area chart. Excel will generate a chart with separate lines or areas for each data series. You can customize the chart as needed.
Can I add a trendline to my cumulative chart in Excel?
+Absolutely! Adding a trendline to your cumulative chart can help identify the overall trend or growth rate. Right-click on the data series, select Add Trendline, choose the appropriate trendline type, and Excel will add the trendline to your chart.
What are some common applications of cumulative charts in business settings?
+Cumulative charts are widely used in business to track sales performance, monitor project milestones, analyze financial investments, and compare the cumulative performance of different teams or products. They provide valuable insights into overall trends and progress, aiding in strategic decision-making.