3 Tips to Determine Element Charge

Determining the charge of an element is a fundamental skill in chemistry, offering valuable insights into an element’s behavior and reactivity. Here, we delve into three expert strategies to confidently identify an element’s charge.
Tip 1: Analyze the Atomic Number

The atomic number of an element, often denoted as ‘Z,’ serves as a crucial indicator of its charge. This number, representing the number of protons in the element’s nucleus, provides a direct insight into its charge. Protons carry a positive charge, and in a neutral atom, the number of protons is balanced by an equal number of electrons, which carry a negative charge. Thus, for a neutral atom, the charge is zero.
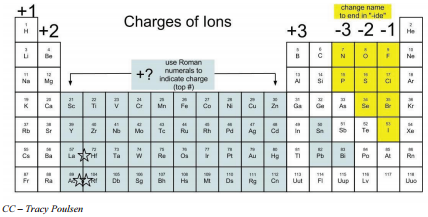
For instance, consider the element sodium, with an atomic number of 11. This indicates that a sodium atom has 11 protons in its nucleus. In a neutral state, it will also have 11 electrons, resulting in a net charge of zero. However, in ionic compounds, elements may gain or lose electrons, altering their charge. Sodium, being highly reactive, often loses an electron to form a sodium ion (Na⁺), giving it a charge of +1.
Tip 2: Understand the Electron Configuration
The arrangement of electrons in an atom, known as its electron configuration, is another vital clue to its charge. This configuration follows specific rules, such as the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle, which dictate how electrons fill atomic orbitals.
For example, consider the element fluorine, with an atomic number of 9. Its electron configuration is 1s²2s²2p⁵. The outermost shell, known as the valence shell, is the 2p orbital, which can hold a maximum of 6 electrons. Fluorine, with only 5 electrons in this shell, has a tendency to gain one electron to complete its valence shell, resulting in a charge of -1.
Tip 3: Study the Ionic Bonding Tendencies
Elements often form ions by gaining or losing electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, akin to that of a noble gas. This process is driven by the element’s position on the periodic table and its associated ionic bonding tendencies.
Take the element magnesium, for instance. With an atomic number of 12, it has a tendency to lose 2 electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration similar to that of neon. This results in the formation of a magnesium ion (Mg²⁺), giving it a charge of +2.
Determining element charge is a fundamental skill in chemistry, offering profound insights into an element's behavior and reactivity. It's an essential step towards understanding the complex world of chemical reactions and interactions.
How does an element's charge affect its reactivity?
+An element's charge significantly influences its reactivity. Elements with a positive charge are more likely to react with elements that have a negative charge, or those that can provide electrons. This is because elements seek to achieve a stable electron configuration, often similar to that of a noble gas, by gaining or losing electrons. This drive towards stability is what fuels many chemical reactions.
Are there elements that don't form ions and maintain a neutral charge?
+Yes, elements in the noble gas group, such as helium, neon, argon, and xenon, typically don't form ions and maintain a neutral charge. This is because their outermost electron shell is already full, giving them a stable configuration. However, under certain conditions, even noble gases can form ions, albeit less commonly.
Can an element have multiple charges?
+Yes, certain elements can exhibit multiple charges, depending on the specific conditions and the compounds they form. For instance, iron can form both Fe²⁺ and Fe³⁺ ions, while sulfur can form S²⁻ and S⁻ ions. The charge an element adopts depends on its tendency to gain or lose electrons and the specific requirements of the compound it's forming.
Remember, the world of chemistry is vast and intricate, and these tips are just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to understanding the complex nature of elements and their charges.



