3 Easy Ways to Identify Lithium Batteries

Lithium batteries have become an integral part of our daily lives, powering everything from our smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems. With their high energy density and lightweight design, these batteries offer numerous advantages. However, proper identification and handling are crucial, especially considering the potential risks associated with lithium-ion chemistry. In this article, we will explore three simple yet effective methods to identify lithium batteries, ensuring your safety and providing valuable insights for various applications.
Visual Inspection: Decoding the Labels and Indicators
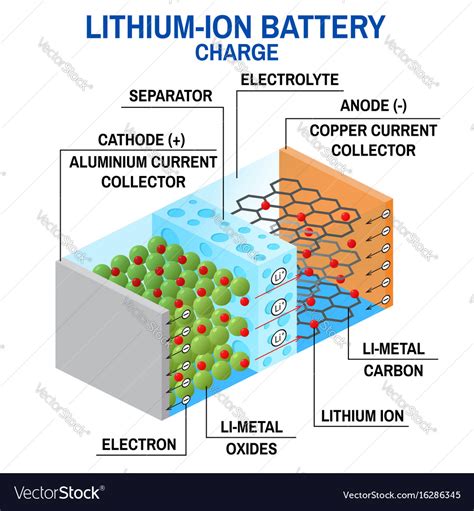
The first step in identifying a lithium battery is a thorough visual inspection. Manufacturers often include essential information on the battery’s label or packaging, providing valuable clues about its type and specifications. Here’s what to look for during your inspection:
Battery Chemistry
Lithium batteries come in various chemistries, each with unique characteristics. Look for labels indicating Lithium-ion (Li-ion), Lithium Polymer (LiPo), or Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4). These labels will give you a clear indication of the battery’s chemistry and potential applications.
Voltage and Capacity
The voltage and capacity of a lithium battery are critical parameters. Check for labels displaying the battery’s voltage, typically in volts (V), and its capacity, often expressed in milliampere-hours (mAh) or ampere-hours (Ah). These values will help you understand the battery’s energy storage capabilities and suitability for different devices.
Manufacturer and Model
Identifying the manufacturer and model of the battery can provide valuable insights. Reputable manufacturers often include their brand name and a unique model number on the battery’s label. This information can be crucial for cross-referencing technical specifications and ensuring compatibility with your device.
Safety and Certification Marks
Safety is paramount when dealing with lithium batteries. Look for safety certifications and marks on the battery, such as the UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CE (Conformité Européenne) logos. These marks indicate that the battery has undergone rigorous testing and meets international safety standards.
Physical Characteristics: Unveiling the Unique Traits

In addition to visual inspection, paying attention to the physical characteristics of a lithium battery can provide further clues for identification. Here are some key traits to consider:
Size and Shape
Lithium batteries come in a wide range of sizes and shapes, tailored to different applications. Common form factors include cylindrical (e.g., AA, AAA), prismatic (rectangular), and pouch (flexible) cells. The size and shape of the battery can give you a good indication of its intended use.
Terminals and Connectors
The type of terminals and connectors on a lithium battery can vary. Some batteries have standard metal terminals, while others may feature unique connector designs specific to certain devices or applications. Understanding the terminal configuration can help identify the battery’s compatibility.
Protective Features
Modern lithium batteries often incorporate protective features to enhance safety. Look for built-in protection circuits or modules that regulate voltage, current, and temperature. These features are essential for preventing overcharging, overheating, and other potentially hazardous conditions.
| Battery Type | Typical Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Li-ion | Widely used in portable electronics; cylindrical, prismatic, or pouch cells; often with protection circuits. |
| LiPo | Flexible pouch cells, ideal for devices with space constraints; may have specific connector types. |
| LiFePO4 | Known for long cycle life and safety; typically used in larger applications like electric vehicles and energy storage systems. |

Performance Analysis: Unlocking the Battery’s Secrets
While visual inspection and physical characteristics provide valuable information, a more in-depth analysis of the battery’s performance can reveal its true nature. Here’s how you can conduct a performance analysis:
Voltage Measurement
Use a multimeter to measure the voltage of the lithium battery. Compare the measured voltage with the rated voltage indicated on the battery’s label. A significant deviation may indicate a damaged or faulty battery.
Load Testing
Subject the battery to a load test by connecting it to a device or a resistor. Observe the battery’s performance under load, monitoring voltage drop and current draw. This test can help identify any abnormal behavior and assess the battery’s health.
Charge and Discharge Characteristics
Study the battery’s charge and discharge curves using specialized equipment or software. These curves provide insights into the battery’s capacity, internal resistance, and overall performance. Abnormalities in these curves may indicate issues with the battery’s chemistry or aging.
Temperature Monitoring
Lithium batteries are sensitive to temperature. Use a thermocouple or temperature sensor to monitor the battery’s temperature during operation. Excessive heat generation or rapid temperature changes can be indicative of potential issues.
FAQ
Can I use any lithium battery for my device?
+No, it’s crucial to use batteries specifically designed for your device. Different devices have unique voltage and capacity requirements. Using an incompatible battery can lead to performance issues or even safety hazards.
How long do lithium batteries typically last?
+The lifespan of a lithium battery depends on various factors, including its chemistry, usage patterns, and maintenance. On average, lithium-ion batteries can last 2-5 years, while lithium polymer batteries may have a slightly shorter lifespan.
Are there any safety precautions I should follow when handling lithium batteries?
+Absolutely! Always handle lithium batteries with care. Avoid exposing them to extreme temperatures, puncturing, or short-circuiting. Store batteries in a cool, dry place, and ensure proper disposal or recycling when they reach the end of their life.



