5 Simple Steps to Calculate Average Speed

Understanding Average Speed
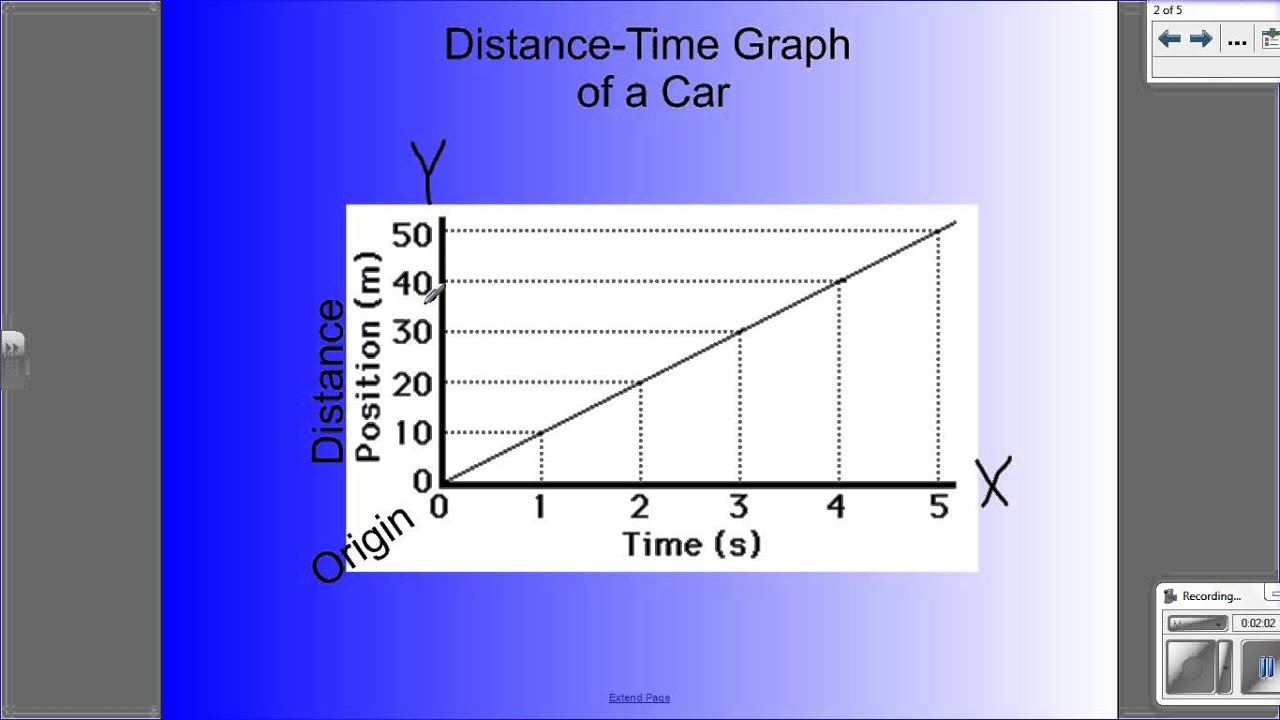
Average speed is a fundamental concept in physics and a practical tool for everyday life. Whether you’re planning a road trip, analyzing sports performance, or simply curious about the world around you, understanding how to calculate average speed is essential. This process is not just about mathematics; it’s a gateway to exploring the dynamics of motion and the principles that govern our physical world.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the five simple steps to accurately calculate average speed. We’ll explore the theoretical framework behind this concept and provide practical examples to ensure a clear understanding. By the end of this article, you’ll not only be equipped with the mathematical tools but also gain insights into the broader implications of average speed in various fields.
Step 1: Define the Terms

Before we dive into the calculations, it’s crucial to establish a clear understanding of the terms involved. Let’s define average speed and the variables we’ll be working with:
Average Speed: This is the ratio of the total distance traveled to the total time taken. It represents the overall pace of an object’s motion, regardless of any changes in velocity along the way.
Distance: The total distance covered during the motion. It is a scalar quantity, meaning it has magnitude but no direction.
Time: The duration of the motion. It is a scalar quantity as well, measured in units such as seconds, minutes, or hours.
By clearly defining these terms, we establish the foundation for our calculations and ensure a common understanding of the concepts we’ll be working with.
Step 2: Gather Data
Calculating average speed requires precise data collection. Here’s what you need to gather:
Distance Traveled: Measure or obtain the total distance covered during the motion. This could be the length of a track, the distance between two cities, or any other distance you’re interested in.
Time Taken: Record the duration of the motion. Ensure that the time is measured accurately and in the same units as the distance. For example, if the distance is in miles, the time should be in hours or minutes.
Additional Data: Depending on the context, you might need other relevant data. For instance, in a sports scenario, you might also need information about the athlete’s performance at different intervals.
By collecting this data, you’re laying the groundwork for an accurate calculation. Ensure that your measurements are as precise as possible to minimize errors in your results.
Step 3: Apply the Formula
The formula for calculating average speed is straightforward:
\[ \begin{equation*} \text{Average Speed} = \frac{\text{Total Distance}}{\text{Total Time}} \end{equation*} \]
Let’s break down this formula and understand its components:
Total Distance: This is the sum of all the distances covered during the motion. If you have multiple segments with different distances, add them together to get the total distance.
Total Time: Similarly, the total time is the sum of all the time intervals taken to cover those distances. Ensure that the units of time are consistent throughout.
By plugging in the values of total distance and total time into the formula, you can calculate the average speed. This simple equation provides a snapshot of the overall pace of the motion.
Step 4: Interpret the Results
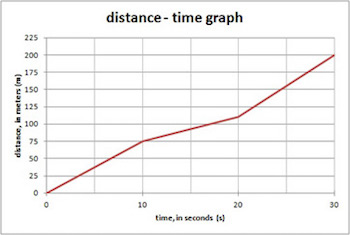
Once you’ve calculated the average speed, it’s essential to interpret the results in the context of your specific scenario. Consider the following:
Units of Measurement: Ensure that your average speed is in the appropriate units. For example, if you’re calculating the average speed of a car, it’s typically expressed in miles per hour (mph) or kilometers per hour (km/h).
Comparison: Compare your calculated average speed with other relevant data. For instance, if you’re analyzing a runner’s performance, you might compare it with their previous records or with the performance of other athletes.
Practical Implications: Think about how the average speed relates to the real-world scenario. For example, a high average speed on a road trip might mean efficient travel, while a low average speed could indicate traffic congestion or a less direct route.
Interpreting the results allows you to draw meaningful conclusions and gain insights into the dynamics of the motion you’re studying.
Step 5: Analyze and Apply
The calculation of average speed is just the beginning. Here’s how you can further analyze and apply your findings:
Identify Variations: If you have data for multiple trials or scenarios, analyze the variations in average speed. This can provide insights into the consistency of the motion or the impact of different factors.
Make Predictions: Use your calculated average speed to make predictions about future motions. For example, if you know the average speed and the distance, you can estimate the total time taken for a similar journey.
Optimize Performance: In practical applications, average speed calculations can guide improvements. For instance, in sports, understanding average speed can help athletes and coaches set training goals and strategies.
By analyzing and applying your average speed calculations, you unlock a deeper understanding of the motion and its implications.
FAQ
<div class="faq-container">
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can average speed be negative?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>No, average speed cannot be negative because it is a scalar quantity representing the magnitude of motion. While velocity can be negative, indicating motion in the opposite direction, average speed always represents the overall pace and is positive.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-container">
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How does average speed differ from instantaneous speed?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Average speed represents the overall pace of motion over a period, while instantaneous speed is the speed at a specific moment. Instantaneous speed is a snapshot of velocity at a particular instant, whereas average speed considers the entire journey.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-container">
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What if the motion is not constant, and the speed varies during the journey?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>In such cases, the average speed calculation still applies. It provides an overall representation of the journey's pace. If you have data for different speeds at various intervals, you can calculate the average speed by summing up the distances and times for each segment.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-container">
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Are there any real-world applications of average speed calculations outside of physics?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Absolutely! Average speed calculations are widely used in transportation, sports, logistics, and even in daily life. For example, calculating the average speed of a delivery vehicle can help optimize routes, and understanding average speeds in sports can aid in performance analysis and strategy development.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-container">
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can I improve my average speed in a running event?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Improving average speed in running involves a combination of factors, including training intensity, strategy, and endurance. Focus on consistent training, vary your workouts to build different muscle groups, and consider interval training to boost your speed. Additionally, optimizing your running form and minimizing external factors like wind resistance can also help.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
In conclusion, calculating average speed is a powerful tool that provides insights into the dynamics of motion. By following these five simple steps, you can accurately determine average speed and apply this knowledge in various contexts. Remember, average speed calculations are not just about mathematics; they are a gateway to understanding the physical world and optimizing performance in diverse fields.



